Streptomycin sulfate
Synonym(s):Streptomycin sulfate salt;Streptomycin Sulfate, Streptomyces sp. - CAS 3810-74-0 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:3810-74-0
- Empirical Formula: C21H41N7O16S
- Molecular Weight: 679.65
- MDL number: MFCD00037023
- EINECS: 223-286-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 16:15:04
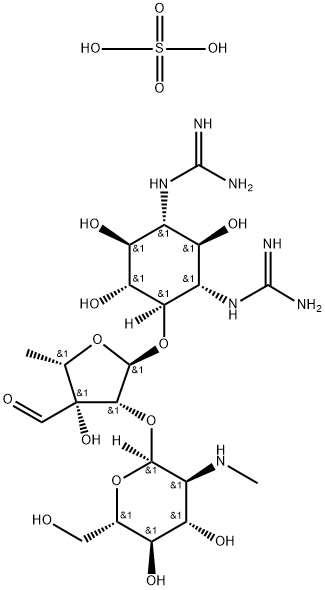
What is Streptomycin sulfate ?
Description
Streptomycin was found in the culture broth of Streptomyces griseus by S. A. Waksman of Rutgers University in 1944; it was the second antibiotic introduced clinically (after penicillin). This drug is a water soluble, basic substance having an aminoglycoside structure and showing strong activity against a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria including Mycobacterium. Streptomycin is the first choice among antituberculotic antibiotics and has been used for the therapy of Spirochaeta and Treponema infections.
Chemical properties
White to off-white powder
The Uses of Streptomycin sulfate
Streptomycin sulfate is a sulfate salt of streptomycin that is a protein synthesis inhibitor. Streptomycin is an antibiotic drug, the first of a class of drugs called aminoglycosides to be discovered, and was the first antibiotic remedy for tuberculosis.
The Uses of Streptomycin sulfate
Antibiotic substance produced by aerobic fermentation. Antibacterial (tuberculostatic).
The Uses of Streptomycin sulfate
Triacetine
What are the applications of Application
Streptomycin sulfate is An antibiotic for cell culture
Definition
ChEBI: Streptomycin sulfate is an aminoglycoside sulfate salt. It is functionally related to a streptomycin.
brand name
Strycin (Bristol-Myers Squibb).
General Description
An antibacterial. White to light gray or pale buff powder with faint amine-like odor.
Air & Water Reactions
Hygroscopic. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Streptomycin sulfate is a medicinal amino saccharide.
Health Hazard
SYMPTOMS: Symptoms of exposure to Streptomycin sulfate include skin rashes, eosinophilia, blood dyscrasias, stomatitis, anaphylactic shock, pruritus, scaling, and fever.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Streptomycin sulfate are not available, however Streptomycin sulfate is probably combustible.
Clinical Use
Streptomycin sulfate is a white, odorless powder that is hygroscopicbut stable toward light and air. It is freely solublein water, forming solutions that are slightly acidic or nearlyneutral. It is very slightly soluble in alcohol and is insolublein most other organic solvents. Acid hydrolysis yields streptidineand streptobiosamine, the compound that is a combinationof L-streptose and N-methyl-L-glucosamine.
Streptomycin acts as a triacidic base through the effectof its two strongly basic guanidino groups and the moreweakly basic methylamino group. Aqueous solutions maybe stored at room temperature for 1 week without any lossof potency, but they are most stable if the pH is between 4.5and 7.0. The solutions decompose if sterilized by heating,so sterile solutions are prepared by adding sterile distilledwater to the sterile powder. The early salts of streptomycincontained impurities that were difficult to remove andcaused a histamine-like reaction. By forming a complexwith calcium chloride, it was possible to free the streptomycinfrom these impurities and to obtain a product thatwas generally well tolerated.
The organism that produces streptomycin, S. griseus, alsoproduces several other antibiotic compounds: hydroxystreptomycin,mannisidostreptomycin, and cycloheximide (q.v.).Of these, only cycloheximide has achieved importance as amedicinally useful substance. The term streptomycin A hasbeen used to refer to what is commonly called streptomycin,and mannisidostreptomycin has been called streptomycin B.Hydroxystreptomycin differs from streptomycin in having ahydroxyl group in place of one of the hydrogen atoms of thestreptose methyl group. Mannisidostreptomycin has a mannoseresidue attached in glycosidic linkage through the hydroxylgroup at C-4 of the N-methyl-L-glucosamine moiety.The work of Dyer et al. to establish the stereochemicalstructure of streptomycin has been completed, and confirmedwith the total synthesis of streptomycin and dihydrostreptomycinby Japanese scientists.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intravenous routes. Moderately toxic by subcutaneous route. An experimental teratogen. Human systemic effects by intraperitoneal route: flaccid paralysis without anesthesia, motor activity changes and pulmonary changes. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx. See also STREPTOMYCIN and SULFATES.
Purification Methods
The sulfate is recrystallised from H2O/EtOH, washed with a little EtOH, Et2O and dried in a vacuum. [UV and IR: Grove & Randall Antibiotics Monographs 2 163 1855, Heuser et al. J Am Chem Soc 75 4013 1953, Kuehl et al. J Am Chem Soc 68 1460 1946, Regna et al. J Biol Chem 165 631 1946.] During protein synthesis it inhibits initiation and causes misreading of mRNA [Zierhut et al. Eur J Biochem 98 577 1979, Chandra & Gray Methods Enzymol 184 70 1990]. [Beilstein 18/11 V 82.]
Properties of Streptomycin sulfate
| Melting point: | >185°C (dec.) |
| alpha | -79~-88°(20℃/D)(c=1,H2O)(calculated on the dried basis) |
| Density | 1.2302 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | -85 ° (C=1, H2O) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 g/mL, clear |
| form | powder |
| color | white to off-white |
| PH | pH (100g/l, 25℃) : 4.5~7.0 |
| Water Solubility | >=0.01 g/100 mL at 18 ºC |
| Merck | 14,8826 |
| BRN | 3894995 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 3810-74-0 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Streptomycin sulfate (3810-74-0) |
Safety information for Streptomycin sulfate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Streptomycin sulfate
| InChIKey | QTENRWWVYAAPBI-YZTFXSNBSA-N |
Streptomycin sulfate manufacturer
Innovative
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
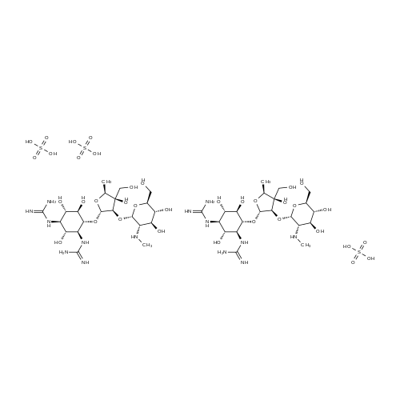
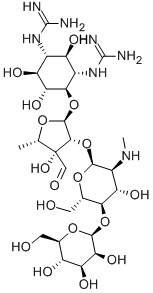
![4-O-[2-O-[2-(Methylamino)-2-deoxy-α-L-glucopyranosyl]-3,5-dideoxy-3-hydroxymethyl-α-L-arabinofuranosyl]-N,N'-bis(aminoiminomethyl)-D-streptamine](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180808/GIF/26086-49-7.gif)
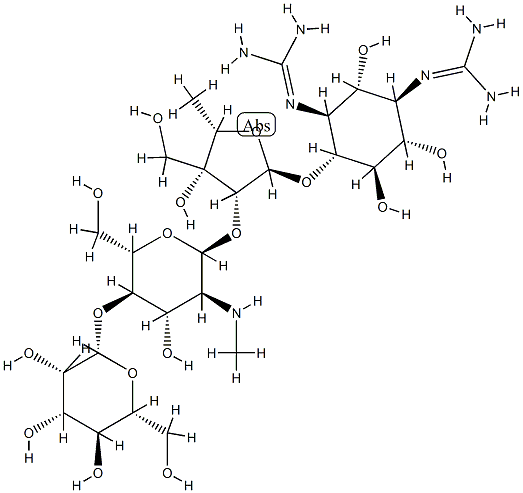

![6-[(α-Apiofuranosyl-(1→6) -β-D-glucopyranosyl)-oxyrubrofu-sarin]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/)
![STREPTOMYCIN SULFATE (1:3) SALT),streptomycin sulfate [1:3]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/)
You may like
-
 Streptomycin Sulphate 99%View Details
Streptomycin Sulphate 99%View Details -
 Streptomycin Sulphate (STM) CAS 3810-74-0View Details
Streptomycin Sulphate (STM) CAS 3810-74-0View Details
3810-74-0 -
 Streptomycin Sulphate for tissue culture CAS 3810-74-0View Details
Streptomycin Sulphate for tissue culture CAS 3810-74-0View Details
3810-74-0 -
 Streptomycin Sulfate API, 5KgView Details
Streptomycin Sulfate API, 5KgView Details
3810-74-0 -
 Streptomycin Sulfate API Powder, 5KgView Details
Streptomycin Sulfate API Powder, 5KgView Details
3810-74-0 -
 Streptomycin SulphateView Details
Streptomycin SulphateView Details
3810-74-0 -
 Streptomycin Sulphate (STM) (CAS Number: 3810-74-0), 1 kg / 5 kg / 10 kg / 25 kgView Details
Streptomycin Sulphate (STM) (CAS Number: 3810-74-0), 1 kg / 5 kg / 10 kg / 25 kgView Details
3810-74-0 -
 500gm Streptomycin Sulfate Powder, 99%View Details
500gm Streptomycin Sulfate Powder, 99%View Details
3810-74-0
