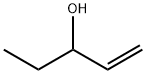
STIRIPENTOL
Synonym(s):4,4-dimethyl-1-[3,4(methylenedioxy)-phenyl]-1-penten-3-ol;Diacomit
- CAS NO.:49763-96-4
- Empirical Formula: C14H18O3
- Molecular Weight: 234.29
- MDL number: MFCD00869310
- EINECS: 256-480-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-11 08:41:34
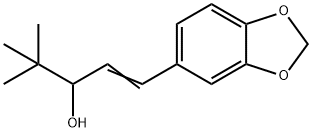
What is STIRIPENTOL?
Absorption
After oral administration, stiripentol is quickly and readily absorbed with a median Tmax of two to three hours. The systemic exposure increases dose-proportionally. Stiripentol has a low bioavailability due to water insolubility and extensive metabolism.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 in rats is >3 g/kg.
There is limited clinical data on stiripentol overdose in humans. In mice, high doses of stiripentol (600 to 1800 mg/kg i.p.) caused decreased motor activity and respiration. Overdose should be managed with supportive and symptomatic treatment.
Description
Stiripentol is a third-generation antiepileptic compound. It is a positive allosteric modulator of GABAA receptors, potentiating GABA-mediated activation to a greater extent in receptors expressing α3 subunits and to a lower extent in those containing β1 or ε subunits. It also inhibits GABA reuptake in vitro and increases the release of GABA in neonatal rat hippocampal slices. Stiripentol (500 μM) inhibits lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), blocking both lactate-to-pyruvate and pyruvate-to-lactate conversions by human LDH1 and LDH5. Formulations containing stiripentol have been used in the adjunctive treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome.
Chemical properties
White Solid
The Uses of STIRIPENTOL
Stiripentol is an epilepsy drug, it has been used as co-therapy for treatment of epilepsy.
The Uses of STIRIPENTOL
An antiepileptic drug
The Uses of STIRIPENTOL
Stiripentol has been used in pharmacokinetic analysis and as a reference standard in fluorescence spectra analysis.
Background
Stiripentol is an antiepileptic agent that is an aromatic allylic alcohol drug, which makes it structurally unique from other antiepileptic drugs. The clinical development and marketing of stiripentol were first delayed due to the drug's potent inhibitory effects on hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes. However, its clinical efficacy as adjunctive therapy for epilepsies stems from its inhibitory action on CYP enzymes, as stiripentol reduces the degradation of CYP-sensitive antiepileptic drugs, hence boosting their therapeutic efficacy. Stiripentol may also exhibit direct anticonvulsant properties, although the exact mechanism of action is fully understood.
Approved in the US, Canada, and Europe, stiripentol is used to treat seizures associated with Dravet syndrome. It is marketed under the brand name Diacomit.
Indications
In the US, stiripentol is indicated for the treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome in patients taking clobazam who are 6 months of age and older and weighing 7 kg or more. There are no clinical data to support the use of stiripentol as monotherapy in Dravet syndrome.
In Europe and Canada, stiripentol is indicated for use as adjunctive therapy with clobazam and valproate to refractory generalized tonic-clonic seizures in patients with Dravet syndrome in infancy whose seizures are not adequately controlled with clobazam and valproate alone.
What are the applications of Application
Stiripentol is an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2C19 and CYP3A4
Definition
ChEBI: 1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-4,4-dimethyl-1-penten-3-ol is a phenylpropanoid.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Anti-convulsant drug
Pharmacokinetics
Stiripentol is an antiepileptic agent that works to reduce seizure frequency. It demonstrates anticonvulsant properties when administered alone and may potentiate GABAergic inhibition via several proposed mechanisms. It provides a therapeutic advantage in improving the efficacy of other antiepileptic drugs by inhibiting cytochrome P450 enzymes that normally metabolize those drugs. The anticonvulsant activity of stiripentol is age-dependent, with increased efficacy in younger patients.
Metabolism
Stiripentol is extensively metabolized. About 13 different metabolites have been found in urine. The main metabolic processes are demethylenation (oxidative cleavage of the methylenedioxy ring system) and glucuronidation, although precise identification of the enzymes involved has not yet been achieved. Other metabolic pathways include O-methylation of catechol metabolites, hydroxylation of the t-butyl group, and conversion of the allylic alcohol side-chain to the isomeric 3-pentanone structure.
In vitro studies suggested that the phase I metabolism of stiripentol is catalyzed by CYP1A2, CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 and possibly other enzymes.
Properties of STIRIPENTOL
| Melting point: | 73-74°C |
| Boiling point: | 365.4±11.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.139±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥20mg/mL |
| pka | 14.45±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 49763-96-4 |
Safety information for STIRIPENTOL
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for STIRIPENTOL
| InChIKey | IBLNKMRFIPWSOY-FNORWQNLSA-N |
STIRIPENTOL manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Stiripentol 98%View Details
Stiripentol 98%View Details -
 Stiripentol 98%View Details
Stiripentol 98%View Details -
 Stiripentol 98%View Details
Stiripentol 98%View Details
49763-96-4 -
 Stiripentol CAS 49763-96-4View Details
Stiripentol CAS 49763-96-4View Details
49763-96-4 -
 Stiripentol 95% CAS 49763-96-4View Details
Stiripentol 95% CAS 49763-96-4View Details
49763-96-4 -
 Stiripentol CAS 49763-96-4View Details
Stiripentol CAS 49763-96-4View Details
49763-96-4 -
 Luci-Stir 250mg, (Stiripentol)View Details
Luci-Stir 250mg, (Stiripentol)View Details
49763-96-4 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
