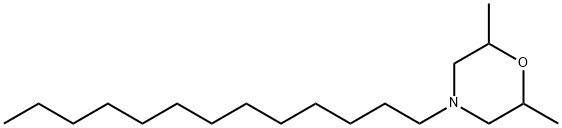
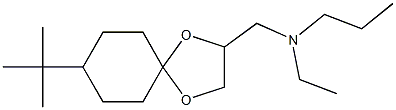
SPIROXAMINE
Synonym(s):N-Ethyl-N-propyl-8-tert-butyl-1,4-dioxaspiro[4.5]dec-2-ylmethylamine
- CAS NO.:118134-30-8
- Empirical Formula: C18H35NO2
- Molecular Weight: 297.48
- MDL number: MFCD03095708
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
What is SPIROXAMINE?
Description
Spiroxamine is a tertiary amine fungicide and an inhibitor of Δ14 reductase/Δ8→Δ7 isomerase. It inhibits the growth of N. parvum, B. dothidea, D. seriata, and L. theobromae isolates from grape vines (EC50s = 0.97-10.28 mg/L). Spiroxamine (0.03-30 μM) reduces network formation in rat cortical cultures. It is also cytotoxic to MDA-kb2 cells (EC20 = 9.29 μM).
The Uses of SPIROXAMINE
Spiroxamine is a spiroketalamine fungicide for use on cereal crops. Spiroxamine inhibits ergosterol synthesis. Spiroxamine is used as agricultural fungicide.
Definition
ChEBI: The spiroketal resulting from the formal condensation of 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone with 3-[ethyl(propyl)amino]propane-1,2-diol. An inhibitor of ergosterol synthesis, it is a broad spectrum agricultural fungicide used particularly against powde y mildew in the production of cereals, bananas and grapes.
Metabolic pathway
Spiroxamine is metabolized rapidly in plants, soils, water, and animals via similar degradation pathways. The metabolic pathways include hydrolysis and oxidation at several places in the molecule. Side chains are also degraded to various water-soluble conjugates in animals and in plants, and at the end of complete degradation to natural constituents, carbon dioxide is formed in soils as the principal metabolite. The favorable sorption characteristics rule out any possibility of appreciable translocation in soil. In wheat, the total residue is determined in forage, grain, and harvest-ready straw. In the field studies, the residues in the grain are mostly below 0.05 mg kg-1, and only in a few cases up to 0.3 mg kg-1. In the milk of cows ingesting spiroxamine residues with the feed, no residues are found in the least favorable case. In eggs of laying hens, the residue concentrations are below the limit of quantification. There are no residue concentrations detected in the hen fat, meat, and liver.
Properties of SPIROXAMINE
| Melting point: | <25 °C |
| Boiling point: | bp 120° at 0.067 hPa |
| Density | 0.96±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| refractive index | nD20 1.4662 |
| Flash point: | 147 °C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Chloroform: Slightly Soluble |
| form | Liquid |
| form | neat |
| pka | 6.9(at 25℃) |
| color | Colorless to light yellow |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Spiroxamine (118134-30-8) |
Safety information for SPIROXAMINE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for SPIROXAMINE
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Spiroxamine CAS 118134-30-8View Details
Spiroxamine CAS 118134-30-8View Details
118134-30-8 -
 Spiroxamine CAS 118134-30-8View Details
Spiroxamine CAS 118134-30-8View Details
118134-30-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8