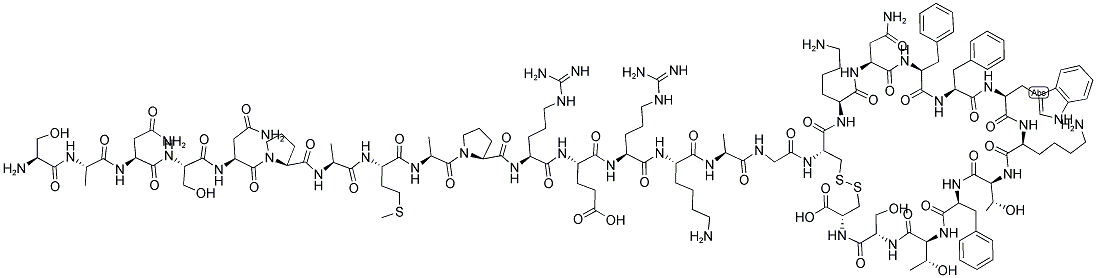
Somatostatin
Synonym(s):Growth hormone release inhibiting factor;Somatostatin-14;Somatotropin release inhibiting factor;SRIF
- CAS NO.:51110-01-1
- Empirical Formula: C76H104N18O19S2
- Molecular Weight: 1637.88
- MDL number: MFCD00076762
- EINECS: 256-969-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-29 18:21:28
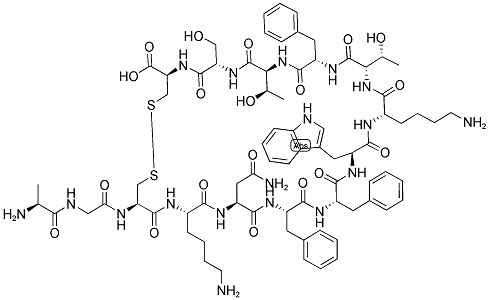
What is Somatostatin?
Description
Originally isolated from hypothalamic tissue, somatostatin is characterized as an inhibitor of growth hormone (GH) release. The structure was determined in 1971. Subsequent investigations led to the recognition that somatostatin also was released from the pancreas and has a role of inhibiting the secretion of both insulin and glucagon. A total of five somatostatin receptor subtypes have been characterized and cloned (sst1 to sst5). Subtype sst4 is associated with the inhibition of insulin release, and an sst4-selective inhibitor has been reported. The somatostatin analogue SOM230 has exhibited selectivity for sst1, sst2, sst3, and sst5 in rats and effectively decreased plasma GH and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) levels by 75% without significant effects on insulin or glucagon. Another analogue, PT R3173, with selectivity for recombinant human somatostatin receptor (hsst2, hsst4, hsst5) was substantially more effective in inhibiting GH secretion compared to glucagon and insulin release in rats.
The Uses of Somatostatin
Somatostatin is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system.
What are the applications of Application
Somatostatin is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system
Indications
Somatostatin (or somatotropin release–inhibiting factor [SRIF]) occurs primarily as a 14–amino acid peptide, although a 28–amino acid form also exists.As with the other hypothalamic peptides, it is formed by proteolytic cleavage of a larger precursor. Somatostatin, originally isolated from the hypothalamus, is also in many other locations, including the cerebral cortex, brainstem, spinal cord, gut, urinary system, and skin. Somatostatin inhibits the secretion of many substances in addition to growth hormone.
General Description
Somatostatin was discovered in the hypothalamus. It is elaboratedby the δ-cells of the pancreas and elsewhere in thebody. Somatostatin is an oligopeptide (14 amino acidresidues) and is referred to as somatotropin release–inhibitingfactor (SRIF).
Its primary action is inhibiting the release of GH from thepituitary gland. Somatostatin also suppresses the release ofboth insulin and glucagon. It causes a decrease in bothcAMP levels and adenylate cyclase activity. It also inhibitscalcium ion influx into the pituitary cells and suppressesglucose-induced pancreatic insulin secretion by activatingand deactivating potassium ion and calcium ion permeability,respectively. The chemistry, SARs, and potential clinicalapplications have been reviewed.
Clinical Use
Somatostatin has a very brief half-life in serum and is not useful clinically.An 8–amino acid analogue with 2 D-amino acids substituted for the naturally occurring L-amino acids is more stable, and monthly injections of a depot form of this analogue (octreotide, Sandostatin LAR) have several uses. Long-acting octreotide is used to treat acromegaly, as described earlier. It is also used to counteract unpleasant effects caused by overproduction of secreted bioactive substances produced by neuroendocrine tumors, including hyperinsulinemia from insulinomas and secretions from carcinoid tumors that cause severe diarrhea. Octreotide may also control severe diarrhea associated with AIDS that has not responded to other treatments.
Side Effects
Somatostatin analogues (SSA) are a common treatment for some forms of neuroendocrine tumours (NETs). Somatostatin analogues are usually well tolerated which means you may not have many side effects.
The main side effects are
Loss of appetite
Feeling sick
Feeling bloated
Stomach pain
Fatigue (tiredness)
Increased diarrhoea (this is rare)
Soreness at the injection site
Uncommon side effects include sinus bradycardia, asthenia, headache,pruritus, decreased libido, increased serum bilirubin, and constipation.
Transient side effects, gastrointestinal discomfort and decreased glucose tolerance, usually last only a few weeks after initiation of therapy.
The most significant side effect associated with prolonged use of octreotide is formation of gallstones resulting from reduced bile flow.
storage
-20°C
Properties of Somatostatin
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| solubility | H2O: 1 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (0.3 mg/ml) |
Safety information for Somatostatin
Computed Descriptors for Somatostatin
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid Electrolytic Iron Powder 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole N-Boc-L-proline methyl ester 2-(BOC-Amino)4-picoline 1-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,3-benzotriazole 1-(2-Chlorobenzyl)-4-nitro-1H-pyrazoleRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 181228-33-1 99%View Details
181228-33-1 99%View Details
181228-33-1 -
 Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
1169630-40-3 -
 1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 -
 127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5