Solifenacin succinate
- CAS NO.:242478-38-2
- Empirical Formula: C27H32N2O6
- Molecular Weight: 480.56
- MDL number: MFCD00954234
- EINECS: 620-505-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-11 08:41:34
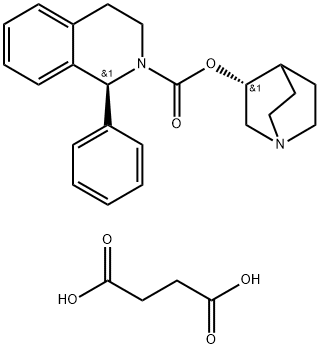
What is Solifenacin succinate?
Description
Solifenacin is an M3 muscarinic receptor antagonist that was developed and launched for the treatment of overactive bladder (pollakiuria) in Europe. M3 receptors have been implicated in neurally evoked smooth muscle contractions of the bladder, and M2 receptors have also been suspected of playing a role because of their dominance in the detrusor muscle. Solifenacin displays affinity for both M3 and M2 receptors with Ki values of 9.9nM and 120 nM, respectively. Since muscarinic salivary glands are of the M3 persuasion, a common side effect of antimuscarinic therapy is dry mouth. At the cellular level, solifenacin possesses a selective preference for bladder over salivary gland that is 15-fold greater than that of atropine suggesting a lower probability of inducing dry mouth at pharmacologically relevant doses. The synthesis of solifenacin involves the preparation of racemic 1-phenyl- 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline via cyclization of N-(2-phenylethyl)benzamide, and subsequent reaction with ethyl chloroformate and transesterification with (R)- 3-quinuclidinol. Chiral chromatography affords the isolation of the desired diastereomer. Alternatively, 1-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline may be subjected to optical resolution with (+)-tartaric acid prior to treatment with ethyl chloroformate and subsequent transesterification. The pooled results of four phase III trials concluded that 63% of women receiving 5mg of solifenacin once daily and 68% of women receiving 10mg once daily reported a 50% or more reduction in urgency episodes, compared to 44% of women taking placebo. This compares with a 53% reduction in patients receiving tolterodine twice daily. In another placebo-controlled trial, with the change in the number of micturitions in a 24-h period as the primary endpoint, once-daily solifenacin recorded an 18% decrease for a 5-mg dose and a 21% decrease for a 10-mg dose compared to 10% with placebo. Pharmacokinetic studies have demonstrated that solifenacin has an oral bioavailability of 90%, a long elimination half-life (50 h), low clearance (9.39 L/h), a mean Vss of 599 L, a Cmax of approximately 14 ng/mL, and a time to maximal plasma concentration of 4 h making it suitable for q.d. dosing. Furthermore, these PK parameters are not affected by food ingestion. Solifenacin is excreted predominantly in the feces with only 3–6% found in urine. It is contraindicated in patients with hepatic impairment, gastric retention, urinary retention, or uncontrolled narrow angle glaucoma. Further precautions, such as dose adjustment, should be considered for patients with concurrent use of ketoconazole or other potent CYP3A4 inhibitors or for patients with a history of QT prolongation or currently on medications known to prolong the QT interval. Finally, while other muscarinic antagonists have been explored in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), it is too early to predict the therapeutic utility of solifenacin for IBS although animal studies are promising.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Yamanouchi (Japan)
The Uses of Solifenacin succinate
Solifenacin succinate is a urinary antispasmodic of the antimuscarinic class.
The Uses of Solifenacin succinate
Muscarinic M3 receptor antagoinst. Used in treatment of urinary incontinence.
The Uses of Solifenacin succinate
sedative
What are the applications of Application
Solifenacin succinate salt is a mAChR M3 (muscarinic M3 receptor) antagonist
Definition
ChEBI: Solifenacin succinate is a member of isoquinolines.
brand name
Vesicare (Astellas).
General Description
Solifenacin succinate (Vesicare),(+)-(1S, 3'R)-quinuclidin-3'-yl 1-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-2-carboxylate, is a competative antagonistfor M1, M2, and M3 receptor subtypes. One of the issues surroundingthe use of such antagonists is the selectivity for thebladder over other tissue such as the salivary glands. It isreported that the selectivity of solifenacin for bladder muscarinicreceptors over salivary receptors is superior to theeffects observed with oxybutynin.
Clinical Use
Selective M3
antimuscarinic
Symptomatic treatment of urge incontinence and/or
increased urinary frequency and urgency
in vitro
in radioligand receptor binding assay, the kivalues of solifenacin for human muscarinic m1, m2, m3, m4and m5receptors were 26, 170, 12, 110 and 31 nm, respectively. in isolated rat urinary bladder, solifenacin competitively antagonized carbachol-induced contractions, with a pa2value of 7.44±0.09[3].in bladder smooth muscle cells and salivary gland cells isolated from rats, solifenacin and the other antimuscarinic drugs inhibited carbachol-induced increases in intracellular ca2+levels in a concentration-dependent manner. thepki was 8.12for bladder smooth muscle cells, 3.6-fold more potent than that for salivary gland cells (pki=7.57) [1].
in vivo
in anesthetized rats, solifenacin dose-dependently inhibited carbachol-induced intravesical pressure elevation and salivary secretion, and exhibited selectivity (3.7- to 6.5-fold) for urinary bladder over salivary gland [1]. in anesthetized rats, solifenacin and oxybutynin increased the maximum bladder capacity in a dose-dependent manner and also decreased the maximum intravesical pressure [3].in healthy young men, multidose study evaluated doses. in the single-dose of solifenacin succinate (5-, 10-, 20-, and 30-mg), mean time to maximal concentration and elimination half-life ranged from 3.3 to 4.8 and from 40.2 to 57.6 hours, respectively.in the multidose study, the ranges were 2.9 to 5.8 and 45.0 to 64.8, respectively. the single-dose administration was well tolerated. the common adverse events were dry mouth, blurred vision, and headache [4].
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Avoid if GFR<30 mL/min if also taking
itraconazole, ketoconazole or ritonavir.
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of antimuscarinic
side effects with disopyramide.
Metabolism
Extensively metabolised in the liver, mainly by the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4 and is excreted mainly as metabolites in urine and faeces.
References
[1]. ohtake a, ukai m, hatanaka t, et al. in vitro and in vivo tissue selectivity profile of solifenacin succinate (ym905) for urinary bladder over salivary gland in rats[j]. european journal of pharmacology, 2004, 492(2): 243-250.
[2]. yang j, williams j a, yule d i, et al. mutation of carboxyl-terminal threonine residues in human m3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor modulates the extent of sequestration and desensitization[j]. molecular pharmacology, 1995, 48(3): 477-485.
[3]. ohtake a, saitoh c, yuyama h, et al. pharmacological characterization of a new antimuscarinic agent, solifenacin succinate, in comparison with other antimuscarinic agents[j]. biological and pharmaceutical bulletin, 2007, 30(1): 54-58.
[4]. smulders r a, krauwinkel w j, swart p j, et al. pharmacokinetics and safety of solifenacin succinate in healthy young men[j]. the journal of clinical pharmacology, 2004, 44(9): 1023-1033.
[5]. cardozo l, lisec m, millard r, et al. randomized, double-blind placebo controlled trial of the once daily antimuscarinic agent solifenacin succinate in patients with overactive bladder[j]. the journal of urology, 2004, 172(5): 1919-1924.
Properties of Solifenacin succinate
| Melting point: | ~145° |
| storage temp. | under inert gas (nitrogen or Argon) at 2-8°C |
| solubility | Methanol (Slightly, Heated, Sonicated), Water (Slightly, Sonicated) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Merck | 14,8712 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 242478-38-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Solifenacin succinate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. |
Computed Descriptors for Solifenacin succinate
Solifenacin succinate manufacturer
Archerchem Healthcare Pvt., Ltd. (part of Archerchem Group)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

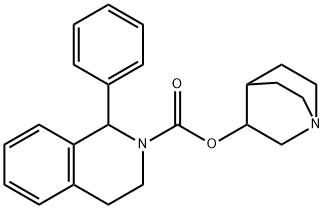
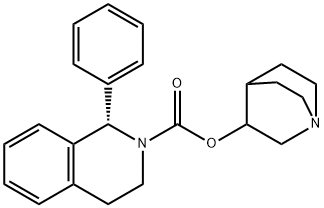


You may like
-
 Solifenacin succinate 98%View Details
Solifenacin succinate 98%View Details
242478-38-2 -
 SOLIFENACIN SUCCINATE 5% DC GRANULES 242478-38-2 98%View Details
SOLIFENACIN SUCCINATE 5% DC GRANULES 242478-38-2 98%View Details
242478-38-2 -
 Solifenacin succinate 99%View Details
Solifenacin succinate 99%View Details -
 242478-38-2 Solifenacin succinate 98%View Details
242478-38-2 Solifenacin succinate 98%View Details
242478-38-2 -
 Solifenacin Succinate 99%View Details
Solifenacin Succinate 99%View Details -
 Solifenacin Succinate CAS 242478-38-2View Details
Solifenacin Succinate CAS 242478-38-2View Details
242478-38-2 -
 Solifenacin Succinate CAS 242478-38-2View Details
Solifenacin Succinate CAS 242478-38-2View Details
242478-38-2 -
 Solifenacin Succinate APIView Details
Solifenacin Succinate APIView Details
242478-38-2
