Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate
Synonym(s):Disodium phosphate;Sodium phosphate dibasic;Disodium hydrogen phosphate;Disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate;Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate
- CAS NO.:10039-32-4
- Empirical Formula: H25Na2O16P
- Molecular Weight: 358.14
- MDL number: MFCD00149181
- EINECS: 600-088-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-10 18:36:46
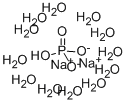
What is Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate?
Chemical properties
white crystals
Chemical properties
The USP 32 states that dibasic sodium phosphate is dried or
contains, 1, 2, 7, or 12 molecules of water of hydration.
Anhydrous dibasic sodium phosphate occurs as a white powder.
The dihydrate occurs as white or almost white, odorless crystals.
The heptahydrate occurs as colorless crystals or as a white granular
or caked salt that effloresces in warm, dry air. The dodecahydrate
occurs as strongly efflorescent, colorless or transparent crystals.
The Uses of Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate
Sodium Phosphate Dibasic Dodecahydrate is used in method for preparing self-supporting membrane.
The Uses of Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate
Laxative.
What are the applications of Application
Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate is a reagent with high buffering capacity
Definition
ChEBI: A hydrate that is the dodecahydrate form of disodium hydrogenphosphate
Production Methods
Either bone phosphate (bone ash), obtained by heating bones to
whiteness, or the mineral phosphorite is used as a source of tribasic
calcium phosphate, which is the starting material in the industrial
production of dibasic sodium phosphate.
Tribasic calcium phosphate is finely ground and digested with
sulfuric acid. This mixture is then leached with hot water and
neutralized with sodium carbonate, and dibasic sodium phosphate
is crystallized from the filtrate.
General Description
Sodium phosphate is a colorless crystalline sodium salt. It is widely used as a buffer in molecular biology, biochemistry, and chromatographic studies. It exists in three forms: monobasic (NaH2PO4), dibasic (Na2HPO4), and tribasic (Na3PO4). Monobasic and dibasic forms in varying ratios are commonly used to compose the neutral sodium phosphate buffer solution.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Dibasic sodium phosphate is used in a wide variety of pharmaceutical
formulations as a buffering agent and as a sequestering agent.
Therapeutically, dibasic sodium phosphate is used as a mild laxative
and in the treatment of hypophosphatemia.
Dibasic sodium phosphate is also used in food products; for
example as an emulsifier in processed cheese.
Safety
Dibasic sodium phosphate is widely used as an excipient in
parenteral, oral, and topical pharmaceutical formulations.
Phosphate occurs extensively in the body and is involved in
many physiological processes since it is the principal anion of
intracellular fluid. Most foods contain adequate amounts of
phosphate, making hypophosphatemia (phosphate deficiency)
virtually unknown except for certain disease states or in patients
receiving total parenteral nutrition. Treatment is usually by the oral
administration of up to 100 mmol of phosphate daily.
Approximately two-thirds of ingested phosphate is absorbed
from the gastrointestinal tract, virtually all of it being excreted in the
urine, and the remainder is excreted in the feces.
Excessive administration of phosphate, particularly intravenously,
rectally, or in patients with renal failure, can cause
hyperphosphatemia that may lead to hypocalcemia or other severe
electrolyte imbalances. Adverse effects occur less frequently
following oral consumption, although phosphates act as mild saline
laxatives when administered orally or rectally. Consequently,
gastrointestinal disturbances including diarrhea, nausea, and
vomiting may occur following the use of dibasic sodium phosphate
as an excipient in oral formulations. However, the level of dibasic
sodium phosphate used as an excipient in a pharmaceutical
formulation is not usually associated with adverse effects.
LD50 (rat, oral): 17 g/kg
Storage
The anhydrous form of dibasic sodium phosphate is hygroscopic.
When heated to 40℃, the dodecahydrate fuses; at 100℃ it loses its
water of crystallization; and at a dull-red heat (about 240℃) it is
converted into the pyrophosphate, Na4P2O7. Aqueous solutions of
dibasic sodium phosphate are stable and may be sterilized by
autoclaving.
The bulk material should be stored in an airtight container, in a
cool, dry place.
Incompatibilities
Dibasic sodium phosphate is incompatible with alkaloids, antipyrine, chloral hydrate, lead acetate, pyrogallol, resorcinol and calcium gluconate, and ciprofloxacin. Interaction between calcium and phosphate, leading to the formation of insoluble calcium-phosphate precipitates, is possible in parenteral admixtures.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted in Europe for use as a food additive. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (injections; infusions; nasal, ophthalmic, oral, otic, topical, and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate
| Melting point: | 35 °C |
| Density | 1,52 g/cm3 |
| storage temp. | Store at +15°C to +25°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Crystals |
| color | White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 9.0-9.3 (25℃, 50mg/mL in H2O) |
| PH Range | 8.4 - 9.6 at 36 g/l at 25 °C |
| Water Solubility | 218 g/L (20 ºC) |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.01 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/2Na.H3O4P.12H2O/c;;1-5(2,3)4;;;;;;;;;;;;/h;;(H3,1,2,3,4);12*1H2/q2*+1;;;;;;;;;;;;;/p-2 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10039-32-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Disodium phosphate dodecahydrate (10039-32-4) |
Safety information for Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate
| InChIKey | DGLRDKLJZLEJCY-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| SMILES | P([O-])([O-])(=O)O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.[Na+].[Na+] |
Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate manufacturer
Zama Chemical
Halogens
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate 98%View Details
Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate 98%View Details -
 Sodium Phosphate Dibasic Dodecahydrate extrapure CAS 10039-32-4View Details
Sodium Phosphate Dibasic Dodecahydrate extrapure CAS 10039-32-4View Details
10039-32-4 -
 Sodium Phosphate Dibasic Dodecahydrate extrapure AR CAS 10039-32-4View Details
Sodium Phosphate Dibasic Dodecahydrate extrapure AR CAS 10039-32-4View Details
10039-32-4 -
 Sodium phosphate, dibasic, dodecahydrate, 99% CAS 10039-32-4View Details
Sodium phosphate, dibasic, dodecahydrate, 99% CAS 10039-32-4View Details
10039-32-4 -
 25 kg Technical Grade Disodium Hydrogen Orthophosphate Dodecahydrate, For Industrial, 99%View Details
25 kg Technical Grade Disodium Hydrogen Orthophosphate Dodecahydrate, For Industrial, 99%View Details
10039-32-4 -
 Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate Dodecahydrate BP, For Pharma, 25Kg BagView Details
Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate Dodecahydrate BP, For Pharma, 25Kg BagView Details
10039-32-4 -
 DISODIUM HYDROGEN PHOSPHATE DODECAHYDRATE CAS Number: 10039-32-4View Details
DISODIUM HYDROGEN PHOSPHATE DODECAHYDRATE CAS Number: 10039-32-4View Details
10039-32-4 -
 Industrial Grade Disodium Hydrogen Orthophosphate DodecahydrateView Details
Industrial Grade Disodium Hydrogen Orthophosphate DodecahydrateView Details
10039-32-4
