SODIUM ARSENATE
- CAS NO.:7778-43-0
- Empirical Formula: AsHNa2O4
- Molecular Weight: 185.91
- MDL number: MFCD00003495
- EINECS: 231-902-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
What is SODIUM ARSENATE?
Chemical properties
Clear, colorless crystals; mild alkaline taste. Soluble in water; slightly soluble in alcohol and glycerol; insoluble in ether.
Chemical properties
Arsenic acid disodium salt is not combustible. It emits irritating or toxic fumes or gases in a fi re.
Chemical properties
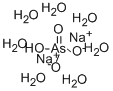
Sodium arsenate is currently registered for use as ant bait. These baits are used in approximately 1% of US homes. Sodium arsenate is a pentavalent form of inorganic arsenic. It is a heptahydrate that normally exists as colorless crystals with no discernible odor. Sodium arsenate contains 24% arsenic.
Chemical properties
White crystalline, odorless solids.
The Uses of SODIUM ARSENATE
Mordant and assist in dyeing and printing, other arsenates, germicide.
Definition
ChEBI: An inorganic sodium salt composed from sodium cations and arsenate dianions in a 2:1 ratio.
Preparation
Sodium arsenate is obtained by roasting a mixture of arsenic oxide with sodium carbon ate and sodium nitrate in the presence of air.In addition, this compound can be easily obtained by calcining sodium arsenate(III) in the pres ence of air.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation.
Health Hazard
Exposures to arsenic acid disodium salt cause adverse health effects. The symptoms of poisoning include, but are not limited to, cough, headache, sore throat, weakness, respiratory distress, labored breathing, irritation to the eyes, and skin, dermatitis, mucous membranes, the respiratory tract, and pigmentation disorders. Repeated or prolonged contact with arsenic acid disodium salt causes cardiovascular disorders affects the nervous system, neuropathy, and kidneys, resulting in severe gastroenteritis, loss of fl uids and electrolytes, kidney impairment, collapse, shock, and death.
Health Hazard
Inorganic arsenical compounds have been classifi ed as Class A oncogenes, demonstrating
positive oncogenic effects based on suffi cient human epidemiological evidence.
Inorganic arsenicals are known to be acutely toxic. The symptoms that follow oral exposure
include severe gastrointestinal damage resulting in vomiting and diarrhea, and
general vascular collapse leading to shock, coma, and death. Muscular cramps, facial
edema, and cardiovascular reactions are also known to occur following oral exposure
to arsenic.
On ingestion, organic arsenic compounds cause severe health effects, including burning
lips, throat constriction, abdominal pain, dysphagia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, convulsions,
coma, and death. Irritation of the respiratory tract, skin, and eyes may result from
inhalation exposures. Chronic exposure to organic arsenic compounds may result in dermatitis,
anemia, leukocytopenia, or the effects associated with several forms of cancer.
Contact allergens
Arsenic salts are sensitizers, but most often irritants. They are used in copper or gold extraction, glass, feeds, weedkillers, insecticides, and ceramics. A recent case was reported in a crystal factory worker with positive patch tests to sodium arsenate.
Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen. Poison by intraperitoneal route. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of arsenic. See ARSENIC COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Sodium arsenate is used in dyeing and printing; making other arsenates; as a germicide; in dyeing with turkey-red oil.
storage
It is important to keep stored organic arsenic compounds in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area in tightly sealed containers and with proper labels and identifi cation. The storage containers of organic arsenic compounds should be protected from physical damage and stored separately from oxidizers such as perchlorates, peroxides, permanganates, chlorates, or nitrates, and strong acids such as hydrochloric, sulfuric, or nitric acid. Further, specifi c organic arsenic compounds must have separate storage requirements, which should be evaluated prior to storage.
Precautions
During handling and use of arsenic compounds, workers should use appropriate personal protective clothing and equipment. Users/workers must be careful during use, and maintain effective measures to prevent skin contact with organic arsenic compounds. The selection of the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, sleeves, and encapsulating suits should be based on the extent of the worker’s potential exposure to organic arsenic compounds. The users and the management should periodically evaluate and determine the effectiveness of the chemical-resistant clothing in preventing dermal contact and ensuring users’ safety.
Properties of SODIUM ARSENATE
| Melting point: | 86℃ [HAW93] |
| Boiling point: | decomp at 150°C |
| Density | 1.7539 [HAW93] |
| solubility | soluble in H2O; slightly soluble in ethanol; insoluble in ethyl ether |
| color | Colorless white powder or solid, effloresces |
| Water Solubility | g/100g solution H2O: 5.59 (0.1°C), 29.33 (25°C), 66.5 (98.5°C); solid phase, Na2HAsO4 ·12H2O (0.1°C), Na2HAsO4 ·7H2O (25°C), Na2HAsO4(98.5°C) [KRU93]; slightly soluble alcohol [MER06] |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Arsenic acid (H3AsO4), disodium salt (7778-43-0) |
Safety information for SODIUM ARSENATE
Computed Descriptors for SODIUM ARSENATE
SODIUM ARSENATE manufacturer
DeFINE CHEMICALS
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde Electrolytic Iron Powder 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 4-Ethylbenzylamine N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 2-(BOC-Amino)4-picoline 1-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,3-benzotriazoleRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
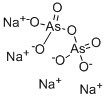
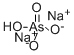
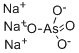
You may like
-
 7778-43-0 Sodium arsenate 98%View Details
7778-43-0 Sodium arsenate 98%View Details
7778-43-0 -
 7778-43-0 99%View Details
7778-43-0 99%View Details
7778-43-0 -
 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 127464-43-1 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 13162-05-5 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 1446013-08-6 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 -
 Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
1169630-40-3