Sinemet
- CAS NO.:57308-51-7
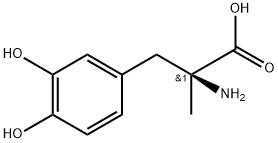
- Empirical Formula: C19H25N3O8
- Molecular Weight: 423.42
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-04-26 16:55:04
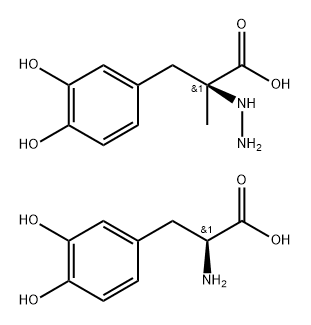
What is Sinemet?
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anaesthetics: risk of arrhythmias with volatile liquid
anaesthetics such as halothane.
Antidepressants: hypertensive crisis with MAOIs
and linezolid (including moclobemide) - avoid for at
least 2 weeks after stopping MAOI.
Bupropion: increased risk of side effects of levodopa
Ferrous sulphate: reduces AUC of levodopa by
30-50%, clinically significant in some but not all
patients.
Metabolism
Levodopa is rapidly decarboxylated by the enzyme
aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase, mostly in the gut,
liver, and kidney, to dopamine, which is metabolised
in turn, principally to dihydroxyphenylacetic acid
(DOPAC) and homovanillic acid (HVA). Other routes
of metabolism include O-methylation, transamination,
and oxidation, producing a variety of minor metabolites
including noradrenaline and 3-O-methyldopa; the latter
may accumulate in the CNS due to its relatively long
half-life.
About 80% of an oral dose of levodopa is excreted in the
urine within 24 hours, mainly as dihydroxyphenylacetic
and homovanillic acids. Only small amounts of levodopa
are excreted unchanged in the faeces.
Carbidopa inhibits the peripheral decarboxylation of
levodopa to dopamine. It is rapidly excreted in the urine
both unchanged and in the form of metabolites.
Safety information for Sinemet
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1