Silver acetate
Synonym(s):Acetic acid silver salt;Silver acetate
- CAS NO.:563-63-3
- Empirical Formula: C2H3AgO2
- Molecular Weight: 166.91
- MDL number: MFCD00012446
- EINECS: 209-254-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
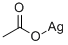
What is Silver acetate ?
Description
Silver acetate is an organic compound with the empirical formula CH3COOAg (or AgC2H3O2). It is a photosensitive, white crystalline solid. It is a useful reagent in the laboratory as a water soluble source of silver lacking an oxidizing anion. It has been used in some antismoking drugs.
Chemical properties
Off-White/Brown Crystalline Powder
The Uses of Silver acetate
In the health field, silver acetate-containing products have been used in gum, spray, and lozenges to deter smokers from smoking. The silver in these products, when mixed with smoke, creates an unpleasant metallic taste in the smoker's mouth, thus deterring them from smoking. Lozenges containing 2.5 mg of silver acetate showed "modest efficacy" on 500 adult smokers tested over a three-month period. However, over a period of 12 months, prevention failed. In 1974, silver acetate was first introduced in Europe as an over-thecounter smoking-deterrent lozenge (Repaton) and then three years later as a chewing gum (Tabmint).
The Uses of Silver acetate
Oxidizing agent for use in liquid ammonia: Kline, Kershner, Inorg. Chem. 5, 932 (1966).
The Uses of Silver acetate
It is a reagent in the laboratory as a source of silver ions lacking an oxidizing anion. It is a reagent for direct ortho-arylation, and for conversion of organohalogen compounds into alcohols. Woodward cis-hydroxylation reaction employs silver acetate and iodine for selective conversin of alkenes into cis-diols. Silver acetate is the more preferred reagent for facile carbonylation of primary and secondary amines. It is also employed in the preparation of highly reflective, conductive silvered polymer films.
What are the applications of Application
Silver acetate is a cycloaddition catalyst and conductive film reagent
Reactions
3 – 1 - Carbonylation
Silver acetate, when combined with carbon monoxide (CO), can induce the carbonylation of primary and secondary amines. Other silver salts can be used but the acetate gives the best yield.
2 R2NH + 2 AgOAc + CO → [R2N]2CO + 2 HOAc + 2 Ag
3 – 2 - Hydrogenation
Silver acetate in a solution of pyridine absorbs hydrogen and is reduced to metallic silver.
3 – 3 - Direct ortho - arylation
Silver acetate is a useful reagent for direct ortho-arylation (to install two adjacent substituents on an aromatic ring) for of benzylamines and N-methylbenzylamines. The reaction is palladiumcatalized and requires a slight excess of silver acetate.This reaction is shorter than previous ortho-arylation methods.
brand name
Smokerette;Tabmint.
World Health Organization (WHO)
Silver acetate has been used as a disinfectant and as an antismoking aid. It was refused registration in Cyprus on the grounds that prolonged use of silver salts can cause permanent argyria and that no well-controlled trials have been performed to establish the safety and efficacy of the preparation. It remains registered as an aid to stopping smoking in Canada and the United States.
General Description
White crystalline plates. Light sensitive. Density 3.26 g / cm3.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Silver acetate is freely soluble in dilute nitric acid [Merck]. Can serve as an oxidizing agent.
Hazard
Toxic material.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust irritates nose and throat. Contact with eyes or skin causes irritation. If continued for a long period, ingestion or inhalation of silver compounds can cause permanent discoloration of skin (argyria).
Safety
The LD50 of silver acetate in mice is 36.7 mg/kg. Low doses of silver acetate in mice produced hyper-excitability, ataxia, central nervous system depression, labored breathing, and even death. The U.S. FDA recommends that silver acetate intake be limited to 756 mg over a short period of time; excessive intake may cause argyria.
Synthesis
The silver acetate salt can be synthesized by the reaction of acetic acid and silver carbonate at 45 – 60 °C. After allowing cooling to room temperature, the solid product precipitates.
2 CH3CO2H + Ag2CO3 → 2 AgO2CCH3 + H2O + CO2
It can also be precipitated from concentrated aqueous solutions of silver nitrate by treatment with a solution of sodium acetate.
The structure of silver acetate consists of 8-membered Ag2O4C2 rings formed by a pair of acetate ligands bridging a pair of silver centres.
Purification Methods
Shake it with acetic acid for three days, and the process is repeated with fresh acid. The solid is then dried in a vacuum oven at 40o for 48hours. It has also been recrystallised from water containing a trace of acetic acid, and dried in air. Store it in the dark. [Beilstein 2 IV 112.]
Properties of Silver acetate
| Melting point: | decomposes [STR93] |
| Density | 3.25 |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 10.2g/l |
| form | Powder/Solid |
| Specific Gravity | 3.259 |
| color | White to gray |
| Water Solubility | 10.2 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 4: no reaction with water under neutral conditions |
| Merck | 14,8505 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 2.71 |
| BRN | 3595636 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.01 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 10 mg/m3; TWA 0.01 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable, but light sensitive. Incompatible with strong reducing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 563-63-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Silver acetate(563-63-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Silver acetate (563-63-3) |
Safety information for Silver acetate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Silver acetate
| InChIKey | CQLFBEKRDQMJLZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Silver acetate manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 563-63-3 SILVER ACETATE 99%View Details
563-63-3 SILVER ACETATE 99%View Details
563-63-3 -
 Silver acetate 99%View Details
Silver acetate 99%View Details -
 Silver acetate, Anhydrous CAS 563-63-3View Details
Silver acetate, Anhydrous CAS 563-63-3View Details
563-63-3 -
 Silver Acetate pure CAS 563-63-3View Details
Silver Acetate pure CAS 563-63-3View Details
563-63-3 -
 Silver acetate CAS 563-63-3View Details
Silver acetate CAS 563-63-3View Details
563-63-3 -
 Silver acetate, 98% CAS 563-63-3View Details
Silver acetate, 98% CAS 563-63-3View Details
563-63-3 -
 Silver Acetate CASView Details
Silver Acetate CASView Details -
 SILVER ACETATE Extra Pure CAS 563-63-3View Details
SILVER ACETATE Extra Pure CAS 563-63-3View Details
563-63-3