SILICA
- CAS NO.:14464-46-1
- Empirical Formula: O2Si
- Molecular Weight: 60.08
- MDL number: MFCD00011232
- EINECS: 238-455-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-08-28 13:53:24
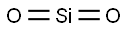
What is SILICA?
Chemical properties
Silicon dioxide/crystalline silica is a component of many mineral dusts and materials which melts to a glass at very high temperature.
The Uses of SILICA
Because of its unique physical and chemical properties, crystalline silica has many uses. Commercially produced silica products include quartzite, tripoli, ganister, chert, and novaculite. Crystalline silica also occurs in nature as agate, amethyst, chalcedony, cristobalite, flint, quartz, tridymite, and, in its most common form, sand (IARC 1997). Naturally occurring silica materials are classified by end use or industry. Sand and gravel are produced almost exclusively for road building and concrete construction, depending on particle size and shape, surface texture, and porosity (IARC 1987).
Definition
A hygroscopic substance such as activated alumina, calcium chloride, silica gel, or zinc chloride. Such substances adsorb water vapor from the air and are used to maintain a dry atmosphere in containers for food packaging, chemical reagents, etc.
Definition
Cristobalite: a mineral form of silicon(IV) oxide, SiO2.
General Description
Rounded silica sand is the naturally occurring sand usually mined from glacial deposits, sometimes called Ottawa sands. Silica sand is essentially made of quartz (SiO2 ) grains.
Pressure range: 28 < σc < 35 MPa (4 < σc < 5 ksi)
Advantages: Low cost, low density, wide availability, and excellent chemical resistance in acidic media except those containing free HF
Drawbacks: Low permeability, low crushing strength, and poor resistance to flow back
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and tumorigenic data. Poison by intratracheal route. An inhalation hazard. Human systemic effects by inhalation: cough, dyspnea, fibrosis. About twice as toxic as silica in causing sihcosis. See also other sdica entries
Potential Exposure
Cristobalite is used in the manufacture of water glass, refractories, abrasives, ceramics and enamels. Quartz is used as a mineral, natural or synthetic fiber. Tridymite is used as a filtering and insulating media and as a refractory material for furnace linings. Workers are potentially exposed to crystalline silica in such industries as granite quarrying and cutting, foundry operations; metal, coal, dentistry, painting, and nonmetallic mining; and manufacture of clay and glass products.
Carcinogenicity
Respirable crystalline silica, primarily quartz dusts occurring in industrial and occupational settings, is known to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in humans. Respirable crystalline silica was first listed in the Sixth Annual Report on Carcinogens in 1991 as reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals; the listing was revised to known to be a human carcinogen in the Ninth Report on Carcinogens in 2000.
Incompatibilities
Violent reactions with powerful oxidizers: fluorine, chlorine trifluoride; manganese trioxide; oxygen difluoride, hydrogen peroxide, etc.; acetylene; ammonia.
Waste Disposal
Sanitary landfill
Properties of SILICA
| Melting point: | 1610 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | >100 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 2.6 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O, acid solutions; soluble in HF |
| form | tablets (~0.5 g each) |
| color | colorless hexagonal, hexane crystals, crystalline |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cristobalite (14464-46-1) |
Safety information for SILICA
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for SILICA
| InChIKey | VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Respirable cristobalite CAS 14464-46-1View Details
Respirable cristobalite CAS 14464-46-1View Details
14464-46-1 -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4