Sevoflurane
Synonym(s):1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-2-(fluoromethoxy)propane;Sevoflurane
- CAS NO.:28523-86-6
- Empirical Formula: C4H3F7O
- Molecular Weight: 200.05
- MDL number: MFCD00153189
- EINECS: 643-089-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
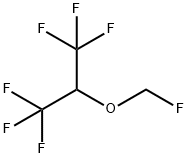
What is Sevoflurane?
Absorption
Sevoflurane is rapidly absorbed into circulation through the lungs; however, solubility in the blood is low (blood/gas partition coefficient at 37°C ranges from 0.63 to 0.69). Therefore, a minimal amount of sevoflurane needs to be dissolved in blood in order to induce anesthesia.
Toxicity
In the event of sevoflurane overdosage (or what may appear to be overdosage) discontinue administration, maintain a patent airway, initiate assisted or controlled ventilation with oxygen, and maintain adequate cardiovascular function. Patients experiencing an overdose may be at an increased risk of severe adverse effects such as renal injury, respiratory depression, severe bradycardia and cardiac arrest. Fatalities due to sevoflurane abuse have been reported as well. Symptomatic and supportive measures are recommended. Animal studies have shown that the use of anesthetic agents during periods of rapid brain growth or synaptogenesis results in alterations in synaptic morphology and neurogenesis. In primates, anesthetic regimens of up to 3 hours did not increase neuronal cell loss, but regimens of 5 hours or longer did have a significant effect. The oral LD50 of sevoflurane is 10.8 g/kg in rats and 18.2 g/kg in mice.
Description
Sevoflurane is a rapidly acting, potent inhalation anesthetic with rapid uptake and and elimination. While somewhat less potent than halothane, sevoflurane does not induce arrhythmias and reportedly has no effect on renal function.
Description
Sevoflurane is a halogenated ether with anesthetic properties. It enhances the activity of GABAA and glycine receptors and inhibits the activity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) and glutamate receptors. Sevoflurane enhances the responses of α2β1 subunit-containing GABAA and α1 subunit-containing glycine receptors at submaximal agonist concentrations in HEK293 cells (EC50s = 0.45 and 0.36 mM, respectively). Sevoflurane (360 μM) also increases the amplitude of GABAA receptor responses to GABA stimulation for receptors with an α1β2γ2 subunit composition. It inhibits binding of the high affinity nicotinic agonist epibatidine to nAChRs in mouse brain membranes (IC50 = 0.77 mM). Formulations containing sevoflurane have been used in the induction and maintenance of general anesthesia.
Chemical properties
Clear, colourless, volatile liquid.
Originator
Baxter (USA)
The Uses of Sevoflurane
antibacterial
The Uses of Sevoflurane
1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-2-(fluoromethoxy)propane is an volatile anesthetic which inhibited activation of inflammatory neutrophil and granulocyte in human blood during simulated extracorporeal circulati on.
The Uses of Sevoflurane
Fluoromethyl 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoroisopropyl ether is a volatile anesthetic, which inhibits the activation of inflammatory neutrophil and granulocyte in human blood during simulated extracorporeal circulation. It also serves as an antibacterial and used as an inhalational anaesthetic for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia. Further, it finds application in anesthesia of children and infants to make them asleep for surgery. In addition to this, it is used in veterinary medicine.
Background
Sevoflurane is an ether inhalation anesthetic agent used to induce and maintain general anesthesia. It is a volatile, non-flammable compound with a low solubility profile and blood/gas partition coefficient. Sevoflurane was patented in 1972, was approved for clinical use in Japan in 1990, and approved by the FDA in 1996. Sevoflurane is three times more potent than desflurane, but has lower potency compared to halothane and isoflurane. Unlike other volatile anesthetics, sevoflurane has a pleasant odor and does not irritate the airway. The hemodynamic and respiratory depressive effects of sevoflurane are well tolerated, and most patients receiving this anesthetic agent present little toxicity. Therefore, it can be used for inhalational induction in adults and children for a wide variety of anesthetic procedures.
Indications
Sevoflurane is used for the induction and maintenance of general anesthesia in adult and pediatric patients for inpatient and outpatient surgery.
Definition
ChEBI: An ether compound having fluoromethyl and 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoroisopropyl as the two alkyl groups.
Manufacturing Process
164 g (2.31 mole) of chlorine is slowly bubbled into a flask containing 370 g
(2.03 mole) of methyl 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoroisopropyl ether illuminated with a
250 watt incandescent lamp, starting at room temperature. The product is
washed with a potassium carbonate solution until neutral, dried over MgSO4
and vacuum distilled to yield 304 g (1.5 mole) of chloromethyl 1,1,1,3,3,3-
hexafluoroisopropyl ether (chloromethyl 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propyl
ether), boiling point 78°C.
A solution of chloromethyl 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propyl ether (754 g, 3.49
moles) in dry tetrahydrothiophene 1,1-dioxide (203 g, 3,49 moles) were stirred
and heated to 130°C in a creased flask fitted with a fractional distillation
assembly. A distillate (200 ml), b748 56.0° to 62°C, was collected during 5 h.
Then the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, dry potassium
fluoride (100 g, 1.74 moles) was added, and the cycle of operations was
repeated 3 times at temperatures between 138° to 185°C to give distillates
(100 ml, 100 ml and 50 ml), b746 58° to 61°C, 55.5° to 57°C, and 54.2° to
55.9°C, respectively. From this portionwise addition of potassium fluoride (503
g, 8.7 moles) there was obtained distillates totalling 672 g, b746 54.2° to
62.0°C, which by GLC analysis was about 92% fluoromethyl and 6.8%
chloromethyl 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propyl ether.
Fractional distillation of 659 g gave a forerun (46 g), b745 53.5° to 57.0°C,
and then 99.6% pure fluoromethyl 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propyl ether (505
g), b745 57.0° to 57.7°C.
brand name
Ultane (Abbott);Sevofrane.
Therapeutic Function
Anesthetic
Biological Functions
Sevoflurane (Ultane) is the most recently introduced inhalation
anesthetic. It has low tissue and blood solubility,
which allows for rapid induction and emergence and
makes it useful for outpatient and ambulatory procedures.
It has the advantage of not being pungent, a characteristic
that permits a smooth inhalation induction,
and is particularly useful in pediatric anesthesia.
Hypotension is produced by sevoflurane as systemic
vasodilation occurs and cardiac output decreases. Since
it does not directly produce tachycardia, it is a useful alternative
to consider in patients with myocardial ischemia.
However, a concern for reflex-induced tachycardia
remains.
Sevoflurane undergoes hepatic biotransformation
(about 3% of the inhaled dose), and it is somewhat degraded
by conventional CO2 absorbents. The degradation
product from the absorbent has been reported to
be nephrotoxic, although the report is controversial and
not substantiated by more recent studies. Sevoflurane’s
actions on skeletal muscle and on vascular regulation
within the CNS are similar to those described for the
other halogenated hydrocarbon anesthetics.
General Description
Sevoflurane is a volatile, nonpungent, nonflammable, andnonexplosive liquid with a boiling point of 58.6°C. Theblood:gas partition coefficient is 0.65, the oil:gas partitioncoefficient is 50, and the MAC is 2.1%. Sevoflurane reactswith desiccated carbon dioxide adsorbents, to produce compounds(A and B) with known toxicity . The typeof CO2 absorbent used, the temperature of the absorbent,and the duration of exposure can influence the degree towhich sevoflurane breaks down. The major breakdownproduct, compound A, pentafluoroisopropenyl fluoromethylether, (PIFE, C4H2F6O) has been studied extensively.Compound A is nephrotoxic in rats and nonhuman primatesand remains a theoretical risk to humans. As discussedpreviously under the stability of inhaled anesthetics,sevoflurane breakdown by CO2 absorbents generates heatand has resulted in sporadic operating room fires.
Pharmacokinetics
Sevoflurane induces muscle relaxation and reduces sensitivity by altering tissue excitability with a fast onset of action. It does so by decreasing the extent of gap junction-mediated cell-cell coupling and altering the activity of the channels that underlie the action potential. Compared to halothane and isoflurane, sevoflurane has a shorter emergence time, as well as a shorter time to first analgesia. To reach an equilibrium between alveolar and arterial partial pressure, only a minimal amount of sevoflurane needs to be dissolved in blood.
The use of sevoflurane can increase the risk of renal injury, respiratory depression, and QT prolongation. Also, it can lead to malignant hyperthermia, perioperative hyperkalemia, and pediatric neurotoxicity. Episodes of severe bradycardia and cardiac arrest have been reported in pediatric patients with Down Syndrome given sevoflurane. Sevoflurane anesthesia may impair the performance of activities requiring mental alertness, such as driving or operating machinery.
Clinical Use
Sevoflurane has been shown to cause epileptic changeson EEGs and case reports of seizures during surgery, especiallyin children, have been reported.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Sevoflurane may be useful in a variety of species when rapid induction and/or rapid recoveries are desired with an inhalational anesthetic.
Metabolism
Sevoflurane is metabolized to hexafluoroisopropanol by cytochrome P450 2E1 in a reaction that promotes the release of inorganic fluoride and carbon dioxide. Hexafluoroisopropanol is rapidly conjugated with glucuronic acid and eliminated in urine. In vivo metabolism studies suggest that approximately 5% of the sevoflurane dose may be metabolized. In most cases, inorganic fluoride reaches its highest concentration within 2 hours of the end of sevoflurane anesthesia, and returns to baseline levels within 48 hours. Sevoflurane metabolism may be induced by chronic exposure to isoniazid and ethanol, and it has been shown that barbiturates do not affect it.
Properties of Sevoflurane
| Melting point: | <25 °C |
| Boiling point: | 58°C |
| Density | 1.505 |
| Flash point: | 58°C |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Slightly soluble in water, miscible with ethanol (96 per cent). |
| form | neat |
| color | Colourless |
| Specific Gravity | 1.505 |
| Water Solubility | Slightly miscible with water. |
| Merck | 14,8475 |
| BRN | 2041023 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 28523-86-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Propane,1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-(fluoromethoxy)- (28523-86-6) |
Safety information for Sevoflurane
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Sevoflurane
| InChIKey | DFEYYRMXOJXZRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

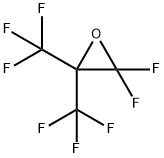

You may like
-
 Fluoromethyl 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoroisopropyl ether CAS 28523-86-6View Details
Fluoromethyl 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoroisopropyl ether CAS 28523-86-6View Details
28523-86-6 -
 Sevoflurane 98% CAS 28523-86-6View Details
Sevoflurane 98% CAS 28523-86-6View Details
28523-86-6 -
 Fluoromethyl 1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoroisopropyl Ether CAS 28523-86-6View Details
Fluoromethyl 1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoroisopropyl Ether CAS 28523-86-6View Details
28523-86-6 -
 Sevoflurane CAS 28523-86-6View Details
Sevoflurane CAS 28523-86-6View Details
28523-86-6 -
 Sevoflurane CAS 28523-86-6View Details
Sevoflurane CAS 28523-86-6View Details
28523-86-6 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1