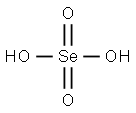
Selenic acid
- CAS NO.:7783-08-6
- Empirical Formula: H2O4Se
- Molecular Weight: 144.97
- MDL number: MFCD00012191
- EINECS: 231-979-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
What is Selenic acid?
Absorption
Following single oral administration of sodium selenate concentrations ranging from 1 mg Se/kg to 4 mg Se/kg in lambs, the peak plasma concentrations ranged from 0.79 mg Se/L to 2.54 mg Se/L . The time to reach peak plasma concentrations ranged from 7 to 12 hours .
Toxicity
Injectable selenium is more acutely toxic than oral administration, with an intramuscular LD50 of 0.5 mg/kg BW in lambs .
Chemical properties
colourless or white crystals
The Uses of Selenic acid
Selenic acid is used as an oxidizing agent. Its derivative sodium selenate is used in the preparation of glass and animal feeds. It acts as an analytical reagent and also used for the preparation of other selenium salts such as gold(III) selenate. Further, it reacts with fluorosulfuric acid to get selenoyl fluoride.
Background
Selenic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula H2SeO4. It may be found in over-the-counter daily dietary supplements as a source of Selenium, an essential trace mineral for human health.
Indications
Indicated for use as a nutritional supplement.
Definition
ChEBI: Selenic acid is a selenium oxoacid. It is a conjugate acid of a hydrogenselenate.
General Description
A white crystalline solid. Very corrosive to skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Corrosive to metal. Toxic by skin absorption and by ingestion.
Air & Water Reactions
Very hygroscopic. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Selenic acid, LIQUID reacts exothermically with chemical bases (for example: amines and inorganic hydroxides) to form salts. The reactions can generate dangerously large amounts of heat in small spaces. A good oxidizing agent. May oxidize organic matter such as wood, cotton, fiberboard, etc.. Reacts with active metals, including iron and aluminum, and also less active metals, to dissolve the metal and liberate hydrogen and/or toxic gases. Can initiate polymerization in certain classes of organic compounds. Reacts with cyanide salts and compounds to release gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases are also often generated with dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, nitriles, sulfides, and weak or strong reducing agents. Additional gas-generating reactions occur with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), and even carbonates: the carbon dioxide gas from the last is nontoxic but the heat and spattering from the reaction can be troublesome. May often catalyze (increase the rate) of chemical reactions.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Pharmacokinetics
Selenium is an essential trace mineral that plays a critical role in antioxidant actions, anti-inflammatory effects, immune function, and the production of active thyroid hormone .
Safety Profile
Selenium compounds are poisons. A corrosive irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Se. See also SELENIUM COMPOUNDS,
Metabolism
No pharmacokinetic data available.
Properties of Selenic acid
| Melting point: | 58°C |
| Boiling point: | 260°C |
| Density | 1.407 g/mL at 25 °C |
| refractive index | n20/D 1.5174(lit.) |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| solubility | Miscible with sulfuric acid. Immiscible with ammonia. |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 4.19±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | Colorless |
| PH | 2.74(1 mM solution);1.83(10 mM solution);0.97(100 mM solution) |
| Water Solubility | g/100g H2O: 426 (0°C), 567 (20°C), 1328 (30°C) [LAN05]; decomposed by alcohol [HAW93] |
| Merck | 14,8429 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.2 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 1 mg/m3; TWA 0.2 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable, but decomposes on heating. Non-flammable. Incompatible with metals, combustible materials. Hygroscopic. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7783-08-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Selenic acid (7783-08-6) |
Safety information for Selenic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. |
Computed Descriptors for Selenic acid
Selenic acid manufacturer
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran






You may like
-
 Selenic acid CAS 7783-08-6View Details
Selenic acid CAS 7783-08-6View Details
7783-08-6 -
 Selenic acid CAS 7783-08-6View Details
Selenic acid CAS 7783-08-6View Details
7783-08-6 -
 SELENIC ACID 99%View Details
SELENIC ACID 99%View Details
77-83-6 -
 Selenic acid CAS 7783-08-6View Details
Selenic acid CAS 7783-08-6View Details
7783-08-6 -
 SELENIC ACID CAS 7783-08-6View Details
SELENIC ACID CAS 7783-08-6View Details
7783-08-6 -
 Selenic acid solution CAS 7783-08-6View Details
Selenic acid solution CAS 7783-08-6View Details
7783-08-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1