SAXITOXIN
- CAS NO.:35523-89-8
- Empirical Formula: C10H17N7O4
- Molecular Weight: 299.29
- MDL number: MFCD05662361
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
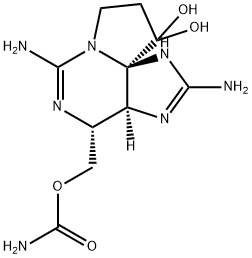
What is SAXITOXIN?
Description
First recognized in 1957 by Shantz et al. in the butter clam
Saxidomus giganteus, saxitoxin is a naturally occurring toxin that
is synthesized by various marine dinoflagellates and cyanobacteria.
It is used in neurochemical and molecular biology
research, but regulatory concerns have focused on its weaponization
and potent toxicological effects on animals and
humans. Saxitoxin causes paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) in
humans and other animals; whales having ingested organisms
contaminated with the toxin have died just hours after exposure.
In humans, PSP can occur as a result of consuming
shellfish or other seafood in which saxitoxin has accumulated.
While effects have been documented worldwide, the sources of
contaminated seafood have been identified as primarily the
west and east coasts of the United States.
To date, more than 30 different saxitoxin analogs have been
identified. These include pure saxitoxin (STX), neosaxitoxin
(neoSTX), the gonyautoxins (GTX), and decarbamoylsaxitoxin
(dc-STX); of these, STX, 6NeoSTX, GTX1, and dc-STX seem to
be the most toxic. The term saxitoxin typically refers to this
collection of compounds produced naturally by cyanobacteria.
Saxitoxin is far more potent than the classic puffer fish toxin
tetrodotoxin, and is one of only two naturally occurring
Schedule 1 chemical warfare agents (the other is ricin). In 1970,
President Nixon ordered stocks of the toxin destroyed in
compliance with U.N. agreements on biological weapons;
however, the Central Intelligence Agency revealed in 1975
that there was a remaining supply, which was distributed to research facilities by the National Institutes of Health in order
to study neurological diseases.
Description
Saxitoxin is a pyrrolopurine alkaloid and potent neurotoxin found in a variety of shellfish, including mussels, clams, and scallops. It is produced by marine dinoflagellates (e.g., Gonyaulax catenella and Alexandrium tamarense), freshwater cyanobacteria (e.g., Dolichospermum cicinale), and other microorganisms that the shellfish ingest. The term saxitoxin is also used for a series of structurally related microbe-derived neurotoxins.
Saxitoxin takes its name from the Alaskan butter clam (Saxidomus gigantea) from which it was first identified in 1937 by Hermann Sommer1 and co-workers at the University of California, San Francisco. In 1966, Edward J. Schantz1 and colleagues at the US Army Biological Laboratories (Fort Detrick, MD) purified saxitoxin and determined its properties. By 1975, Schantz was at the University of Wisconsin (Madison); he and collaborators there and at Iowa State University (Ames) elucidated the structure of saxitoxin.
In 2008, Mark A. Simmons at Northeast Ohio Medical University (Rootstown) wrote:
Saxitoxin (STX), a highly selective and potent blocker of voltage-dependent sodium channels in motor nerves, causes skeletal muscle paralysis. It is found in filter-feeding mollusks [that] consume planktonic algae. . . . Ingestion of these mollusks by humans results in paralytic shellfish poisoning, which may result in death in a matter of hours if sufficient toxin is absorbed. There is no antidote for STX poisoning.
Also in 2008, Brian A. Neilan and co-workers at the University of New South Wales (Sydney) proposed a 10-step biosynthetic pathway to saxitoxin in the freshwater cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. For much more information about saxitoxin, see the ScienceDirect information page.
1. Sommer and Schantz were pioneers in characterizing shellfish toxins.
Chemical properties
Crystalline solid; soluble in water and me thanol; forms dihydrochloride with HCl.
The Uses of SAXITOXIN
Saxitoxin is an alkaloid of nonplant origin.It is the neurotoxic constituent of dinoflagel lates (Gonyaulax catenella and G. excavata)the so-called “red tide” found along the U.S.coast. Shellfish, clams, and scallops consumethis and become extremely poisonous forhuman consumption.
The Uses of SAXITOXIN
Mussel poison; clam poison; paralytic shellfish poison; gonyaulax toxin. These poisonous shellfish have been connected to instances of toxic”red-tides” where the high concentration of algae discoloring the water were of the Gonyaulax genus. Used as a too
The Uses of SAXITOXIN
As a Schedule 1 controlled substance under the Chemical Weapons Convention of 1993, the use of saxitoxin is extremely limited outside of weaponized forms. Its use as a chemical reagent in research is its other important use, as it has been instrumental in experiments to elucidate the mechanisms involved in sodium channels used in cellular communication.
Definition
ChEBI: An alkaloid isolated from the marine dinoflagellates and cyanobacteria that causes paralytic shellfish poisoning.
Health Hazard
Saxitoxin is an extremely toxic substance.It binds to sodium channels and the blocksnerve membrane. In humans, ingestion ofthis compound can produce tingling andburning in the lip, tongue, face, and thewhole body within an hour. This is fol lowed by numbness, muscular incoordina tion, confusion, headache, and respiratoryfailure. Death may occur within 12 hours.
LD50 value intraperitoneal (mice): 0.005mg/kg
LD50 value oral (mice): 0.26 mg/kg
Intravenous administration of 1 mL of1:2000 solution of prostigmine methylsulfatehas been reported to be effective againstsaxitoxin poisoning (Hodgson et al. 1988).
Environmental Fate
Dinoflagellates (flagellate protists, plankton) are primarily
responsible for the biosynthesis of saxitoxin, and bioaccumulation
tends to occur in several shellfish such as
mussels, clams, scallops, and cockles. Broth made from shellfish
can harbor saxitoxin as well due to its stability at normal
cooking temperatures. Consumption of the shellfish leads to
toxicity in humans, while consumption of other organisms in
which saxitoxin has accumulated (up the food chain, for
example) has historically affected other animals such as whales.
Data describing the environmental fate of saxitoxin is
extremely limited. There have been some studies investigating
the absorption/desorption capacities of various soils for the
compound, but more exhaustive studies are yet to be
reported.
Toxicity evaluation
Saxitoxin interrupts nerve transmissions by binding to voltagegated
sodium channels. Positively charged guanidinium
groups of saxitoxin interact with negatively charged carboxyl
groups at a site on the sodium channel (in a one-to-one ratio)
of neurons and muscle cells, resulting in blocked action
potentials and interrupted transmissions. The inactivation of
vasomotor nerves along with vascular smooth-muscle relaxation
follows and hypotension can additionally occur. When
muscles in the respiratory or cardiovascular system are affected,
death can result.
Intraperitoneal inoculation with STX extract in the freshwater
fish Hoplias malabaricus resulted in a variety of systemic
effects culminating in oxidative stress observed in the brain,
leading to lipid, protein, and DNA damage. Although the
exposure in this study was subchronic, apoptotic cellular
processes were implicated.
References
Schantz et al., J. Arner. Chern. Soc., 97, 1238 (1975)
Properties of SAXITOXIN
| Melting point: | not reported |
| Boiling point: | 440.62°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3010 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6400 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| solubility | very soluble |
| appearance | white hygroscopic powder |
| pka | 13.32±0.50(Predicted) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Saxitoxin (35523-89-8) |
Safety information for SAXITOXIN
Computed Descriptors for SAXITOXIN
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![SAXITOXIN DIACETATE [11-3H]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure8/GIF/CB0775933.gif)


You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8