Saquinavir
Synonym(s):2-[2-Methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenylamino]nicotinic acid
- CAS NO.:127779-20-8
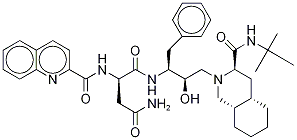
- Empirical Formula: C38H50N6O5
- Molecular Weight: 670.84
- MDL number: MFCD00866925
- EINECS: 1806241-263-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 08:49:36
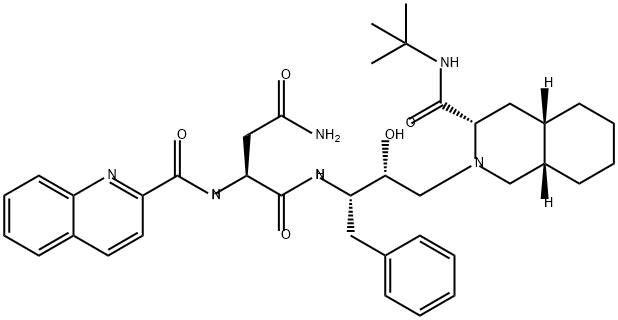
What is Saquinavir?
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of orally administered saquinavir is only ~4%, thought to be a consequence of incomplete absorption and extensive first-pass metabolism. It is co-administered with ritonavir, another protease inhibitor and a potent inhibitor of the enzymes responsible for saquinavir's first-pass metabolism, in order to dramatically boost its serum concentrations and, by extension, its therapeutic efficacy. Following administration of saquinavir 1000mg twice daily with ritonavir 100mg twice daily the AUC24h at steady-state was 39026 ng.h/mL.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 of saquinavir in both rats and mice is >5 g/kg. Data regarding overdose with saquinavir are limited. No acute toxicities or sequelae were noted in a patient ingesting 8 grams of saquinavir as a single dose, and a second subject ingesting 2.4 grams as a single dose experienced throat pain that lasted for 6 hours and subsequently resolved. Treatment of overdose should consist of symptomatic and supportive measures. Dialysis is unlikely to be of benefit given saquinavir's extensive protein-binding.
Description
Saquinavir mesylate, the first HIV protease inhibitor to reach the market, was launched in the U.S.A.. It is indicated for use in combination with approved nucleoside analogs for the treatment of advanced HIV infection. Saquinavir, a transition state analog of Phe-Pro, is a very potent and competitive inhibitor of HIV-1 and HIV-2 proteases with high specificity. Saquinavir inhibits the last stage in the replication process of HIV and prevents virion maturation in both acute and chronically infected cells. Combination of saquinavir with the nucleoside analogs such as zidovudine (AZT) or/and zalcitabine which inhibit the enzyme reverse transcriptase and target at an earlier stage in the HIV replication process, shows a greater than additive effect in increase in CD4 cell counts and reduction in viral load, with the combination delaying the onset of resistance to either drug alone. Saquinavir is well tolerated alone and in combination with A n .
Originator
Roche (Switzerland)
The Uses of Saquinavir
Antiviral (HIV protease inhibitor).
Background
Saquinavir is an HIV-1 protease inhibitor used in combination with ritonavir and other antiretrovirals for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) infection. In 1995 it became the first protease inhibitor approved by the FDA, followed shortly by ritonavir in 1996, and remains in clinical use today due to a relatively benign adverse effect profile as compared to other antiretroviral therapies. While its efficacy was initially limited by exceptionally poor oral bioavailability (approximately 4%), its current indications require the co-administration of ritonavir - a potent enzyme inhibitor - that increases the bioavailability and subsequent serum concentrations of saquinavir, thus dramatically improving antiviral activity.
Indications
Saquinavir is indicated, in combination with ritonavir and other antiretroviral agents, for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in patients 16 years of age and older.
Definition
ChEBI: An aspartic acid derivative obtained by formal condensation of the primary amino group of (2S,3R)-4-[(3S,4aS,8aS)-3-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)octahydroisoquinolin- (1H)-yl]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-ylamine with the carboxy group of N2(-quinolin-2-ylcarbonyl)-L-asparagine. An inhibitor of HIV-1 protease.
Indications
Saquinavir is a potent inhibitor of HIV-1 and HIV-2 protease. Fortovase, a soft gel preparation of saquinavir, has largely replaced saquinavir mesylate capsules (Invirase) because it has improved bioavailability. Saquinavir is usually well tolerated and most frequently produces mild gastrointestinal side effects.
brand name
Fortovase (Roche).
Acquired resistance
Resistance is associated with an amino acid substitution at position 48 in the HIV protease (G48V). An L90M mutation also confers resistance, as it does for most protease inhibitors. Saquinavir-resistant isolates from patients on long-term therapy often show cross-resistance to other protease inhibitors.
General Description
Saquinavir (Invirase) is well tolerated following oral administration.Absorption of saquinavir is poor but is increasedwith a fatty meal. The drug does not distribute intothe CSF, and it is approximately 98% bound to plasma proteins.Saquinavir is extensively metabolized by the firstpasseffect. Bioavailability is 4% from a hard capsule and12% to 15% from a soft capsule. Saquinavir lowers p24antigen levels in HIV-infected patients, elevates CD4+counts, and exerts a synergistic antiviral effect when combinedwith RT inhibitors such as AZT and ddC.Although HIV-1 resistance to saquinavir and other HIVPIs occurs in vivo, it is believed to be less stringent andless frequent than resistance to the RT inhibitors.Nevertheless,cross-resistance between different HIV PIsappears to be common and additive,suggesting thatusing combinations of inhibitors from this class would notconstitute rational prescribing. The drug should be used incombination with at least two other antiretroviral drugs tominimize resistance. Dosage forms are Invirase (hard capsule)and Fortovase (soft capsule).
Pharmaceutical Applications
A peptidomimetic protease inhibitor formulated as the mesylate for oral use.
Pharmacokinetics
Saquinavir exerts its antiviral activity by inhibiting an enzyme critical for the HIV-1 viral lifecycle. Like other protease inhibitors, saquinavir has a propensity for participating in drug interactions - use caution when administering saquinavir to patients maintained on other pharmaceutical agents as pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic interactions are common. Saquinavir is known to increase the QTc-interval in otherwise healthy individuals, and should therefore be used with caution in patients maintained on other QTc-prolonging medications or for whom prolongation of the QTc-interval may be of particular consequence (e.g. patients with pre-existing heart disease). Careful and regular monitoring of patient bloodwork is recommended, as saquinavir has been associated with the development of metabolic complications (e.g. diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia) and worsening of pre-existing liver disease.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: c. 4%
Cmax 1200 mg thrice daily: c. 1–2.2 mg/L
Cmin 1200 mg thrice daily: c. 0.1–0.22 mg/L
Plasma half-life: c. 7–12 h
Volume of distribution: c. 700 L
Plasma protein binding: c. 98%
Absorption and distribution
It is poorly absorbed and penetrates poorly into the CNS. The semen:plasma ratio is 0.04. It is not known if it is distributed into human breast milk.
Metabolism and excretion
It is metabolized via CYP3A4, principally to mono- and dihydroxylated derivatives. Around 88% of the dose is excreted in feces and 1% in urine. Caution should be exercised in severe renal impairment and moderate hepatic impairment; use in decompensated hepatic impairment is contraindicated.
Clinical Use
Treatment of HIV infection (in combination with other antiretroviral drugs)
Side Effects
The most frequently reported adverse effects include abdominal discomfort, diarrhea and nausea. Ritonavir-boosted saquinavir is associated with a dyslipidemic profile characteristic of those treated with a boosted protease inhibitor requiring 200 mg of the ritonavir ‘booster’.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Analgesics: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with alfentanil, fentanyl and methadone - avoid.
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with amiodarone, disopyramide,
dronedarone, flecainide, lidocaine or propafenone -
avoid.
Antibacterials: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with clarithromycin, dapsone,
erythromycin or moxifloxacin - avoid; increased
risk of ventricular arrhythmias with delamanid;
concentration of rifabutin increased; rifampicin and
rifabutin can reduce saquinavir levels by 80% and
40% respectively (metabolism accelerated); increased
hepatoxicity with rifampicin - avoid; concentration
of both drugs increased with fusidic acid.
Anticoagulants: avoid with apixaban and
rivaroxaban.
Antidepressants: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with trazodone or tricyclics - avoid;
concentration reduced by St John’s wort - avoid.
Antiepileptics: carbamazepine, phenobarbital,
and phenytoin and possibly primidone can reduce
saquinavir levels.
Antifungals: concentration increased by ketoconazole
- avoid.
Antihistamines: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with mizolastine - avoid.
Antimalarials: avoid with piperaquine with
artenimol; use artemether/lumefantrine with
caution; increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with quinine - avoid.
Antipsychotics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with clozapine, haloperidol or
phenothiazines - avoid; possibly increased risk
of ventricular arrhythmias with pimozide and
quetiapine - avoid; possibly inhibits aripiprazole
metabolism - reduce aripiprazole dose; possibly
increases lurasidone concentration - avoid.
Antivirals: tipranavir and efavirenz can reduce
saquinavir levels; increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with atazanavir or lopinavir - avoid;
concentration increased by indinavir and ritonavir;
reduced darunavir concentration; concentration
of maraviroc increased, consider reducing dose of
maraviroc.
Anxiolytics and hypnotics: midazolam concentration
possibly increased (prolonged sedation) - avoid with
oral midazolam.
Beta-blockers: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with sotalol - avoid.
Ciclosporin: concentration of both drugs increased.
Cytotoxics: possibly increases concentration of
axitinib, ibrutinib and panobinostat, reduce dose
of axitinib, ibrutinib and panobinostat; possibly
increases bosutinib, cabazitaxel, ceritinib and
docetaxel concentration - avoid or consider reducing
dose; possibly increases concentration of crizotinib
and everolimus - avoid; avoid with lapatinib,
olaparib and pazopanib; reduce dose of ruxolitinib.
Dapoxetine: increased risk of toxicity - avoid.
Domperidone: possibly increases risk of ventricular
arrhythmias - avoid.
Ergot alkaloids: risk of ergotism - avoid.
Guanfacine: concentration possibly increased - halve
guanfacine dose.
Lipid-lowering drugs: increased risk of myopathy
with rosuvastatin and simvastatin - avoid; possibly
increased myopathy with atorvastatin; avoid with
lomitapide.
Naloxegol: possibly increases naloxegol concentration
- avoid.
Orlistat: absorption possibly reduced by orlistat.
Pentamidine: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias - avoid.
Ranolazine: possibly increases ranolazine
concentration - avoid.
Metabolism
Saquinavir is extensively metabolized in the liver following oral administration, and in vitro studies have shown that >90% of its biotransformation is mediated by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme. Saquinavir is rapidly metabolized to a number of inactive mono- and di-hydroxylated compounds.
Metabolism
Saquinavir is absorbed to a limited extent (about 30%)
after oral doses of the mesilate and undergoes extensive
first-pass hepatic metabolism via cytochrome P450
isoenzyme, CYP3A4 to form a range of mono- and
di-hydroxylated inactive compounds.
It is excreted mainly in the faeces.
Properties of Saquinavir
| Boiling point: | 1015.0±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D20 -55.9° (c = 0.5 in methanol) |
| Density | 1.211±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (149.07 mM; Need ultrasonic) |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 11.05±0.46(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | 35.8mg/L(25 ºC) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 127779-20-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Saquinavir
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P363:Wash contaminated clothing before reuse. P301+P330+P331:IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Saquinavir
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
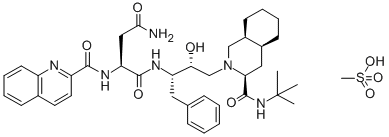
![SAQUINAVIR [3H(G)]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure8/GIF/CB9135617.gif)



You may like
-
 127779-20-8 Saquinavir 98%View Details
127779-20-8 Saquinavir 98%View Details
127779-20-8 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
