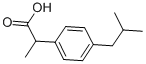
(S)-(+)-Ibuprofen
Synonym(s):(S)-(+)-2-(4-Isobutylphenyl)propionic acid;(S)-(+)-4-Isobutyl-α-methylphenylacetic acid;S-(+)-IBU
- CAS NO.:51146-56-6
- Empirical Formula: C13H18O2
- Molecular Weight: 206.28
- MDL number: MFCD00069289
- EINECS: 610-620-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55

What is (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen ?
Absorption
The time it take to reach peak plasma concentration is 2.25-5 hours post-administration of oral tablets containing 300mg of dexibuprofen. For more information, refer to ibuprofen.
Toxicity
Oral LD50 value in rats is 636 mg/kg. For more information, refer to ibuprofen.
Description
Dexibuprofen, the S-(+)-isomer of the widely used NSAID agent ibuprofen, was launched in Austria for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. While the racemic compound is commonly used clinically, the antiinflammatory activity is mediated via the S-isomer by inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. It has also been demonstrated that the R-isomer is converted to the Santipode in vivo via a CoA thioester intermediate. Since CoA plays a pivotal role in intermediary metabolism and maintenance of the [acyl-CoA], generation of R-ibuprofen-CoA competitively inhibits many CoA-dependent reactions, which consequently produces perturbations of hepatocyte Intermediary metabolism and mitocondrial function. Pure S-ibuprofen usage, therefore, is preferred allowing a reduction in dosage level and an improved side effect profile.
Description
Ibuprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with diverse biochemical actions, most notably inhibiting COX-1 and COX-2 (IC50s = 2.6 and 1.53, μM, respectively). It is commonly synthesized as a racemic mixture of (S)- and (R)-isomers. (S)-Ibuprofen is an enantiomer that more potently inhibits COX activity, thromboxane formation, and platelet aggregation than the (R)-form. (S)-Ibuprofen also inhibits activation of NF-κB more effectively than (R)-ibuprofen (IC50s = 62 and 122 μM, respectively). However, the enantiomers are equipotent in blocking superoxide formation, β-glucuronidase release, and LTB4 generation by stimulated neutrophils (IC50 values range from 0.14 to 0.58 μM). A majority of (R)-ibuprofen can be inverted to (S)-ibuprofen in humans after oral administration.
Chemical properties
Colourless, Crystalline Solid
Originator
Gebro Broschek (Austria)
The Uses of (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen
A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID); activity resides primarily in the (S)-isomer
The Uses of (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen
sedative
The Uses of (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with diverse biochemical actions, most notably inhibiting COX-1 and COX-2 (IC50s = 2.6 and 1.53, μM, respectively). It is commonly synthesized as a racemic mixture of (S)- and (R)-isomers. (S)-Ibuprofen is an enantiomer that more potently inhibits COX activity, thromboxane formation, and platelet aggregation than the (R)-form. (S)-Ibuprofen also inhibits activation of NF-κB more effectively than (R)-ibuprofen (IC50s = 62 and 122 μM, respectively). However, the enantiomers are equipotent in blocking superoxide formation, β-glucuronidase release, and LTB4 generation by stimulated neutrophils (IC50 values range from 0.14 to 0.58 μM). A majority of (R)-ibuprofen can be inverted to (S)-ibuprofen in humans after oral administration.
Indications
For more information, refer to ibuprofen.
Background
Dexibuprofen, S(+)-ibuprofen, is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is a pharmacologically effective enantiomer of racemic ibuprofen that differs in physicochemical properties. It is proposed to be more pharmacologically active and tolerable with a better safety profile than ibuprofen due to higher concentration of active S enantiomer. Dexibuprofen has a slower dissolution rate in the simulated gastric and enteric juices compared with the racemic ibuprofen and displays improved oral bioavilability . For Metabolism, Enzymes, Carriers, Transporters Sections, refer to Ibuprofen.
What are the applications of Application
(S)-Ibuprofen is an inhibitor of Cox-1 and Cox-2
Definition
ChEBI: Dexibuprofen is an ibuprofen. It has a role as a non-narcotic analgesic and a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. It is an enantiomer of a levibuprofen.
brand name
Seractil
General Description
(S)-(+)-Ibuprofen is the enantiomer associated with the anti-inflammatory action of ibuprofen, which is widely used as a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug in racemic form.
Biological Activity
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that inhibits cyclooxygenase 1 and cyclooxygenase 2 (IC 50 values are 12 and 80 μ M respectively). Active isomer of ibuprofen.
Pharmacokinetics
For more information, refer to ibuprofen.
Clinical Use
NSAID and analgesic
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II antagonists:
antagonism of hypotensive effect, increased risk of
nephrotoxicity and hyperkalaemia.
Analgesics: avoid concomitant use of 2 or more
NSAIDs, including aspirin (increased side effects);
avoid with ketorolac (increased risk of side effects
and haemorrhage).
Antibacterials: possibly increased risk of convulsions
with quinolones.
Anticoagulants: effects of coumarins and
phenindione enhanced; possibly increased risk of
bleeding with heparins, dabigatran and edoxaban -
avoid long term use with edoxaban.
Antidepressants: increased risk of bleeding with
SSRIs and venlaflaxine.
Antidiabetic agents: effects of sulphonylureas
enhanced.
Antiepileptics: possibly increased phenytoin
concentration.
Antivirals: increased risk of haematological toxicity
with zidovudine; concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir
Ciclosporin: may potentiate nephrotoxicity
Cytotoxics: reduced excretion of methotrexate;
increased risk of bleeding with erlotinib
Diuretics: increased risk of nephrotoxicity;
antagonism of diuretic effect; hyperkalaemia with
potassium-sparing diuretics.
Lithium: excretion decreased.
Pentoxifylline: increased risk of bleeding.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of nephrotoxicity
Metabolism
For more information, refer to ibuprofen.
Metabolism
Dexibuprofen is the S(+)-enantiomer of ibuprofen. After metabolic transformation in the liver (hydroxylation and carboxylation), the pharmacologically inactive metabolites are completely excreted, mainly by the kidneys (90%), but also in the bile.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the (+) and (-) acids from EtOH or aqueous EtOH. The racemate which crystallises from pet ether with m 75-77o is sparingly soluble in H2O and has IR (film) 1705 (C=O), 2300—3700 (OH broad)cm-1. It is used as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory. [Shiori et al. J Org Chem 43 2936 1978, Kaiser et al. J Pharm Sci 65 269 1976, J Pharm Sci 81 221 1992, Freer Acta Cryst (C) 49 1378 1993 for the (S+)-enantiomer.]
Properties of (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen
| Melting point: | 49-53 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 285.14°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 57 º (c=2, EtOH) |
| Density | 1.0364 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 59 ° (C=2, EtOH) |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | 45% (w/v) aq 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin: 1.5 mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 4.41±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | white |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +59°, c = 2 in ethanol |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| BRN | 3590022 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 51146-56-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen
| InChIKey | HEFNNWSXXWATRW-JTQLQIEISA-N |
(S)-(+)-Ibuprofen manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

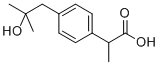
You may like
-
 511406-56-6 Dexibuprofen 98%View Details
511406-56-6 Dexibuprofen 98%View Details
511406-56-6 -
 51146-56-6 S-Ibuprofen 98%View Details
51146-56-6 S-Ibuprofen 98%View Details
51146-56-6 -
 51146-56-6 98%View Details
51146-56-6 98%View Details
51146-56-6 -
 S-Ibuprofen 98%View Details
S-Ibuprofen 98%View Details
51146-56-6 -
 51146-56-6 S-Ibuprofen 98%View Details
51146-56-6 S-Ibuprofen 98%View Details
51146-56-6 -
 Dex-Ibuprofen 99%View Details
Dex-Ibuprofen 99%View Details -
 (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen CAS 51146-56-6View Details
(S)-(+)-Ibuprofen CAS 51146-56-6View Details
51146-56-6 -
 (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen CAS 51146-56-6View Details
(S)-(+)-Ibuprofen CAS 51146-56-6View Details
51146-56-6
