Rupatadine
- CAS NO.:158876-82-5
- Empirical Formula: C26H26ClN3
- Molecular Weight: 415.96
- MDL number: MFCD09039284
- EINECS: 825-304-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-08-14 13:33:12
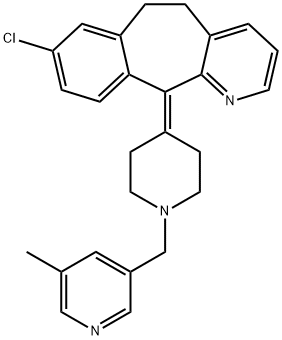
What is Rupatadine?
Absorption
Rupatidine is rapidly absorbed with a Tmax of 1 h . Administration with a high fat meal increases exposure by 23% and increases Tmax to 2 h.
Chemical properties
Rupatadine is off white to pinkish crystalline powder. It is soluble in methanol and ethanol slightly soluble in Chloroform and insoluble inwater.
The Uses of Rupatadine
Rupatadine Fumarate is a dual antagonist of histamine H1 and platelet-activating factor receptors. Rupatadine fumarate has been approved for the treatment of allergic rhinitis and chronic urticaria in adults and children over 12 years.
The Uses of Rupatadine
Rupatadine is an intermediate in the synthesis of Rupatadine (5-Methyl-3-pyridinyl)methyl)pyridinium Chloride (M326740). (5-Methy-3-pyridinyl)methyl-Rupatadine is an impurity of Rupatadine (R701650), a dual antagonist of histamine H1 and platelet-activating factor receptors
Background
Rupatadine is a dual histamine H1 receptor and platelet activating factor receptor antagonist that is used for symptomatic relief in seasonal and perennial rhinitis as well as chronic spontaneous urticaria. It was approved for marketing in Canada under the tradename Rupall and comes in tablet formulation for adult use and liquid formulation for pediatric use.
Indications
For the symptomatic relief of nasal and non-nasal symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis and perennial allergic rhinitis in patients 2 years of age and older . Also used for the symptomatic relief of chronic spontaneous urticaria in patients 2 years of age and older.
Definition
ChEBI: Rupatadine is a benzocycloheptapyridine.
Biological Activity
Rupatadine is an antagonist of histamine H1 and platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptors. It binds to rabbit platelet membranes and guinea pig cerebellum membranes with apparent Ki values of 0.55 and 0.1 μM, respectively, in radioligand binding assays. It inhibits contraction of isolated guinea pig ileum induced by histamine (pA2 = 9.29) and platelet aggregation induced by PAF in washed rabbit platelets (pA2 = 6.68). Rupatadine prevents histamine- or PAF-induced hypotension in rats (ID50s = 1.4 and 0.44 mg/kg, respectively) and reverses histamine- or PAF-induced bronchoconstriction in guinea pigs (ID50s = 113 and 9.6 mg/kg, respectively). It does not reduce locomotor activity or potentiate sleep induced by barbiturates in mice, indicating a lack of sedative effects.
Pharmacokinetics
Rupatadine is an anti allergenic and acts to reduce allergic symptoms like urticaria, rhinorrhea, sneezing and itching .
Pharmacokinetics
Rupatadine was rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with a time taken to reach the maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) of 1 hour (median value). The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) obtained after single and repeated doses of 10 mg rupatadine were from 1.54 to 4.03 ng/mL and from 1.99 to 4.74 ng/mL respectively. Steady state was reached by the fifth day of therapy without extensive accumulation and the plasma concentration-time curve during a time dose interval (AUCτ) ranged from 8.37 to 16.2 ng.h/mL. Pharmacokinetics of rupatadine was linear for a dose between 10 and 20 mg after single and repeated doses. The plasma concentration followed a bi-exponential drop-off with a mean elimination half-life after a single dose of 6.1 hours.
Side Effects
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
Sleepiness, headache, dizziness, dry mouth, sensation of weakness and fatigue.
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
Increased appetite, irritability, difficulty concentrating, nosebleed, nasal dryness, sore throat, cough, dry throat, rhinitis, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, indigestion, vomiting, constipation, rash, back pain, joint pain, muscle pain, thirst, general discomfort, fever, abnormal liver function test and increased weight.
Metabolism
Rupatadine is metabolized by oxidation mediated primarily by CYP3A4 . CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP2D6 are also involved to a lesser extent. The metabolites desloratidine and hydroxylated forms of desloratidine retain some activity as H1 receptor antagonists.
Mode of action
Rupatadine is a second generation, non-sedating, long-acting histamine antagonist with selective peripheral H1receptor antagonist activity. It further blocks the receptors of the platelet-activating factor (PAF) according to in vitro and in vivo studies.
Rupatadine possesses anti-allergic properties such as the inhibition of the degranulation of mast cells induced by immunological and non-immunological stimuli, and inhibition of the release of cytokines, particularly of the tumor necrosis factors (TNF) in human mast cells and monocytes.
Properties of Rupatadine
| Melting point: | 58-61°C |
| Boiling point: | 586.4±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.233±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | Dichloromethane; Ethyl Acetate |
| form | Oil |
| pka | 6.95±0.20(Predicted) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 158876-82-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Rupatadine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H413:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
Computed Descriptors for Rupatadine
Rupatadine manufacturer
TAGOOR LABORATORIES PVT LTD
Ralington Pharma
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 158876-82-5 Rupatadine Fumarate IP >98%View Details
158876-82-5 Rupatadine Fumarate IP >98%View Details
158876-82-5 -
 RUPATADINE 99%View Details
RUPATADINE 99%View Details -
 Rupatadine 98%View Details
Rupatadine 98%View Details
158876-82-5 -
 Rupatadine 158876-82-5 98%View Details
Rupatadine 158876-82-5 98%View Details
158876-82-5 -
 Rupatadine CAS 158876-82-5View Details
Rupatadine CAS 158876-82-5View Details
158876-82-5 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8