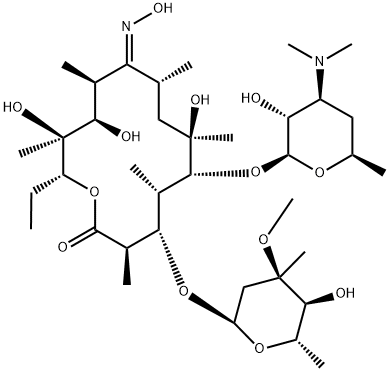
Roxithromycin
Synonym(s):Erythromycin 9-(-O-[2-methoxyethoxy]methyloxime)
- CAS NO.:80214-83-1
- Empirical Formula: C41H76N2O15
- Molecular Weight: 837.05
- MDL number: MFCD00214389
- EINECS: 617-007-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
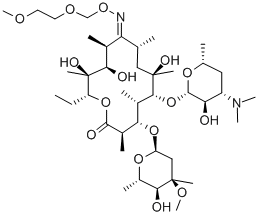
What is Roxithromycin?
Absorption
Very rapidly absorbed and diffused into most tissues and phagocytes.
Toxicity
Roxithromycin primarily causes gastrointestinal adverse events, such as diarrhoea, nausea, abdominal pain and vomiting. Less common adverse events include headaches, rashes, abnormal liver function values and alteration in senses of smell and taste.
Description
Roxithromycin, an oxime ether derivative of erythromycin, is a new macrolide antibiotic of high potency and long duration. Its in v i m activity spectrum is similar to that of erythromycin, but is superior to the latter against Legionella, Mycoplasma and Chlamydia.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Roussel (France)
The Uses of Roxithromycin
Roxithromycin was one of the new generation erythromycins introduced in the 1980s. Improved acid stability was achieved by converting the 9-keto group to the more stable oxime and alkylation of the oxime to provide the methoxyethoxymethyl ether oxime. In vivo, roxithromycin exhibits higher tissue levels and a longer half-life while being slightly less potent than erythromycin in vitro.
The Uses of Roxithromycin
Semisynthetic erythromycin derivative. Antibacterial
The Uses of Roxithromycin
anesthetic (local)
Indications
Used to treat respiratory tract, urinary and soft tissue infections.
Background
Roxithromycin is a semi-synthethic macrolide antibiotic that is structurally and pharmacologically similar to erythromycin, azithromycin, or clarithromycin. It was shown to be more effective against certain Gram-negative bacteria, particularly Legionella pneumophila. Roxithromycin exerts its antibacterial action by binding to the bacterial ribosome and interfering with bacterial protein synthesis. It is marketed in Australia as a treatment for respiratory tract, urinary and soft tissue infections.
What are the applications of Application
Roxithromycin is an antibiotic and antibacterial compound
Definition
ChEBI: Roxithromycin is semisynthetic derivative of erythromycin A. It has a role as an antibacterial drug. It is an erythromycin derivative, a macrolide and a semisynthetic derivative. It is functionally related to an erythromycin A.
brand name
Rulide (Hoechst-Roussel).
Antimicrobial activity
Activity against common pathogens is comparable to that of erythromycin. It is active against L. monocytogenes, C. jejuni, H. ducreyi, G. vaginalis, Bord. pertussis, C. diphtheriae, B. burgdorferi, H. pylori, the M. avium complex, Chlamydia spp., and U. urealyticum.
Pharmaceutical Applications
A semisynthetic derivative of erythromycin A formulated for oral use.
Pharmacokinetics
Roxithromycin has the following antibacterial spectrum in vitro: Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pneumoniae (Pneumococcus), Neisseria meningitides (Meningococcus), Listeria monocytogenes, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Legionella pneumophila, Helicobacter (Campylobacter), Gardnerella vaginalis, Bordetella pertussis, Moraxella catarrhalis (Branhamella Catarrhalis), and Haemophilus ducreyi. Roxithromycin is highly concentrated in polymorphonuclear leukocytes and macrophages, achieving intracellular concentrations greater than those outside the cell. Roxithromycin enhances the adhesive and chemotactic functions of these cells which in the presence of infection produce phagocytosis and bacterial lysis. Roxithromycin also possesses intracellular bactericidal activity.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption:50–55%
Cmax 150 mg oral : 7.9 mg/L after 1.9 h
300 mg oral :10.8 mg/L after 1.5 h
Plasma half-life :10.5–11.9 h
Plasma protein binding :c. 90%
absorption and metabolism
Absorption is not affected by food. Oral administration with antacids or H2-receptor antagonists does not significantly affect bioavailability. In a direct comparison, the area under the time–concentration curve (AUC) produced by a 150 mg dose was 16 times greater than that produced by 250 mg erythromycin A. Behavior in children is broadly similar to that in adults, repeated doses of 2.5 mg/kg producing age-independent mean peak plasma concentrations around 10 mg/L at 1–2 h, but the apparent elimination half-life was longer (approximately 20 h).
It is saturably bound to α-acid glycoprotein in plasma. The plasma clearance appears to be dose dependent or plasma concentration dependent.
DistributionIt is widely distributed, but does not reach the CSF. Concentrations close to the simultaneous serum level have been found in tonsillar, lung, prostatic and other tissues. It achieves high levels in skin.
Distribution
It is widely distributed, but does not reach the CSF. Concentrations close to the simultaneous serum level have been found in tonsillar, lung, prostatic and other tissues. It achieves high levels in skin.
Metabolism and excretion
Less than 5% of the administered dose is eliminated as degradation products. Rather more than half the dose appears in the feces and only 7–10% (including metabolites) in the urine: up to 15% is eliminated via the lungs. Renal clearance increased in volunteers as the dose was raised from 150 to 450 mg,
and is decreased in elderly subjects. In patients in whom the creatinine clearance was <10 mL/min, the apparent elimination half-life rose to around 15.5 h and total body clearance was significantly reduced. The apparent elimination half-life was somewhat increased in patients with hepatic cirrhosis.
Side Effects
It is generally well tolerated, adverse effects being described in 3–4% of patients, mostly gastrointestinal disturbance (abdominal pain, nausea and diarrhea). Headache, weakness, dizziness, rash and reversible changes in liver function tests and increased eosinophils and platelets have also been described.
Metabolism
Hepatic. Roxithromycin is only partially metabolised, more than half the parent compound being excreted unchanged. Three metabolites have been identified in urine and faeces: the major metabolite is descladinose roxithromycin, with N-mono and N-di-demethyl roxithromycin as minor metabolites. The respective percentage of roxithromycin and these three metabolites is similar in urine and faeces.
Properties of Roxithromycin
| Melting point: | 111-118?C |
| Boiling point: | 864.7±75.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D25 -77.5 ±2° (c = 0.45 in chloroform) |
| Density | 1.25±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point: | >110°(230°F) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | chloroform: soluble10mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | pKa 9.27±0.01(H2O
t = 25.0
I = 0.15 (KCl)) (Uncertain) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water to 18µg/ml |
| Merck | 14,8276 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 80214-83-1 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Erythromycin, 9-[O-[(2-methoxyethoxy)methyl]oxime], (9E)- (80214-83-1) |
Safety information for Roxithromycin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Roxithromycin
| InChIKey | RXZBMPWDPOLZGW-HEWSMUCTSA-N |
Roxithromycin manufacturer
Ralington Pharma
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 ROXITHROMYCIN BP/EP 99%View Details
ROXITHROMYCIN BP/EP 99%View Details -
 Roxithromycin 99%View Details
Roxithromycin 99%View Details -
 Roxithromycin 95.00% CAS 80214-83-1View Details
Roxithromycin 95.00% CAS 80214-83-1View Details
80214-83-1 -
 80214-83-1 98%View Details
80214-83-1 98%View Details
80214-83-1 -
 80214-83-1 Roxithromycin 99%View Details
80214-83-1 Roxithromycin 99%View Details
80214-83-1 -
 80214-83-1 98%View Details
80214-83-1 98%View Details
80214-83-1 -
 Roxithromycin 97.00% CAS 80214-83-1View Details
Roxithromycin 97.00% CAS 80214-83-1View Details
80214-83-1 -
 Roxithromycin CAS 80214-83-1View Details
Roxithromycin CAS 80214-83-1View Details
80214-83-1