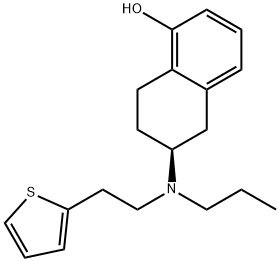
ROTIGOTINE
- CAS NO.:99755-59-6
- Empirical Formula: C19H25NOS
- Molecular Weight: 315.47
- MDL number: MFCD00870193
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
What is ROTIGOTINE?
Absorption
Bioavailability varies depending on the application site. Differences in bioavailability were very small between the abdomen and hip (<1%). In contrast, the shoulder and thigh had a very large different in measured bioavailability (46%), with the shoulder showing the higher value. Tmax, 8 mg dose = 15 - 18 hours (it take approximately 3 hours until rotigotine reaches detectable levels in the plasma). The peak concentration cannot be observered. Steady state is reached in 2-3 days.
Toxicity
The most likely symptoms of overdose would be those related to the pharmacodynamic profile of a dopamine agonist, including nausea, vomiting, hypotension, involuntary movements, hallucinations, confusion, convulsions, and other signs of excessive dopaminergic stimulation.
Description
While levodopa is still considered the cornerstone of treatment of Parkinson’s disease, many patients begin to experience treatment-related problems, such as a wearing-off phenomenon and the development of dyskinesias as the disease progresses. Continuous dopaminergic stimulation by means of a dopamine agonist has been recognized as being associated with a lower incidence of dyskinesias. Using a selective dopamine agonist as monotherapy in early disease may delay the onset of levodopa therapy, or at a minimum, lower its dose in adjunctive situations to minimize the adverse neurotoxic effects of levodopa. Rotigotine is a nonergolinic dopamine D3/D2/D1 receptor agonist, and it is the first dopamine agonist to be launched as a transdermal patch.
Description
Rotigotine is a non-selective dopamine receptor agonist with pEC50 values of 9.6, 10.4, 8.2, 7.7, and 7.7 for D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5, respectively. It demonstrates a high-affinity for D1, D2, and D3 with lesser affinity for D4 and D5 receptor subtypes. This binding profile is similar to that of apomorphine and pergolide but differentiated from that of pramipexole and ropinirole, which have a more narrow profile of receptor specificity. Each of these agonists demonstrates anti-Parkinsonian effects in animal and clinical models through their ability to directly activate dopamine receptors.
Originator
Aderis (US)
The Uses of ROTIGOTINE
It is a non-ergot dopamine agonist drug and is indicated for the treatment of Parkinson disease.
Indications
For use/treatment in neurologic disorders and parkinson's disease as well as moderate-to-severe primary Restless Legs Syndrome.
Background
Rotigotine (Neupro) is a non-ergoline dopamine agonist indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD) and restless legs syndrome (RLS) in Europe and the United States. It is formulated as a once-daily transdermal patch which provides a slow and constant supply of the drug over the course of 24 hours.
Like other dopamine agonists, rotigotine has been shown to possess antidepressant effects and may be useful in the treatment of depression as well.
Rotigotine was developed by Aderis Pharmaceuticals. In 1998 Aderis licensed worldwide development and commercialization rights to Schwarz Pharma of Germany. It was approved by the European Medicines Agency in 2006 and by the FDA in 2007. However, all Neupro patches in the United States and some of Europe were recalled in 2008 due to delivery mechanism issues. Rotigotine has been authorized as a treatment for RLS since August 2008.
Definition
ChEBI: Rotigotine is a member of tetralins.
brand name
Neupro
General Description
Rotigotine, (6S)-6-{propyl[2-(2-thienyl)ethyl]amino}-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1-naphthalenol (Neupro),is a nonergoline that is available as a silicone-based, selfadhesivematrix, transdermal system for continuous delivery over a 24-hour period. Approximately 45% of the drug is releasedwithin 24 hours. The terminal half-life of rotigotine is5 to 7 hours after removal of the patch. Rotigotine is 90%bound to plasma proteins. The compound undergoes extensivemetabolism and has low bioavailability by the oralroute. The major metabolites of rotigotine are the glucuronideand sulfate conjugates of rotigotine and sulfateconjugates of N-despropylrotigotine and N-desthienylethylrotigotine. Rotigotine is excreted in the urine (71%) andfeces (11%).Studies using human liver microsomes didnot find any interactions with CYP1A2, CYP2C9,CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4 substrates.Rotigotinetransdermal system contains sodium metabisulfite, and individualssensitive to sulfite could be at risk for allergic reactions.Additionally, somnolence is a common adverse reactionwith individuals on rotigotine, and patients should beclosely monitored during therapy.In transfected Chinesehamster ovary (CHO) cells, rotigotine binds with high affinityat D3 and D2L receptors (variants in the D2 receptor subtypeare caused by insertion of the 29 amino acids into thethird loop to give D2s and D2L).Using rat CHO cells,rotigotine shows over 30-fold selectivity at D3 versus D2 receptors.48 Rotigotine was approved in May 2007 for thetreatment of early-stage PD.
Pharmacokinetics
Rotigotine is an agonist at all 5 dopamine receptor subtypes (D1-D5) but binds to the D3 receptor with the highest affinity. It is also an antagonist at α-2-adrenergic receptors and an agonist at the 5HT1A receptors. Rotigotine also inhibits dopamine uptake and prolactin secretion. There is no indication of a QT/QTc prolonging effect of Neupro in doses up to 24 mg/24 hours. The effects of Neupro at doses up to 24 mg/24 hours (supratherapeutic doses) on the QT/QTc interval was evaluated in a double-blind, randomized, placebo- and positive-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg IV, single dose) parallel-group trial with an overall treatment period of 52 days in male and female patients with advanced-stage Parkinson's disease. Assay sensitivity was confirmed by significant QTc prolongation by moxifloxacin.
Clinical Use
Treatment of Parkinson’s disease
Restless legs syndrome (RLS)
Synthesis
The synthesis described by the originators at Discovery Therapeutics Inc. (now known as Aderis Pharmaceuticals) is shown in the scheme. The synthesis utilizes the chiral methoxy tetralin 62 as starting precursor which was obtained via chiral crystallization procedure described in a patent literature [34]. Demethylation of tetraline 62 with refluxing 40% HBr solution for several hours provided phenol 63 in 96% yield. Reaction of the amine 63 with 2- thiophenylethyl tosylate 64 in refluxing xylene for 24-32 h in the presence of 0.6 equiv sodium carbonate gave the desired rotigotine (IX) without requiring chromatographic purification. The ratio of sodium carbonate to the amine was critical to achieving good yields (59-84% yield) without requiring extensive purification. Rotigotine was isolated as the HCl salt.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antipsychotics: avoid concomitant use (antagonism
of effect).
Metoclopramide: avoid concomitant use (antagonism
of effect).
Metabolism
Hepatic (CYP-mediated). Rotigotine is extensively and rapidly metabolized by conjugation and N-dealkylation. After intravenous dosing the predominant metabolites in human plasma are sulfate conjugates of rotigotine, glucuronide conjugates of rotigotine, sulfate conjugates of the N-despropyl-rotigotine and conjugates of N-desthienylethyl-rotigotine. Multiple CYP isoenzymes, sulfotransferases and two UDP-glucuronosyltransferases catalyze the metabolism of rotigotine.
Metabolism
Rotigotine is metabolised in the gut wall and liver by N-dealkylation as well as direct and secondary conjugation. Main metabolites are sulfates and glucuronide conjugates of the parent compound as well as N-desalkyl-metabolites, which are biologically inactive. Approximately 71% of the rotigotine dose is excreted in urine and a smaller part of about 23% is excreted in faeces.
Properties of ROTIGOTINE
| Melting point: | 78 °C |
| Boiling point: | 470.1±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.15±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | DMF: 30 mg/ml; DMF:PBS(pH7.2) (1:2): 0.33 mg/ml; DMSO: 20 mg/ml; Ethanol: 1 mg/ml |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water |
| form | powder to crystal |
| pka | 10.49±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White to Almost white |
Safety information for ROTIGOTINE
Computed Descriptors for ROTIGOTINE
ROTIGOTINE manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![1-Naphthalenol, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-6-[propyl[2-(2-thienyl)ethyl]amino]-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/92206-54-7.gif)
You may like
-
 Rotigotine 98%View Details
Rotigotine 98%View Details -
 99755-59-6 98%View Details
99755-59-6 98%View Details
99755-59-6 -
 Rotigotine CAS 99755-59-6View Details
Rotigotine CAS 99755-59-6View Details
99755-59-6 -
 Rotigotine CASView Details
Rotigotine CASView Details -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8