rosoxacin
- CAS NO.:40034-42-2
- Empirical Formula: C17H14N2O3
- Molecular Weight: 294.3
- MDL number: MFCD00057294
- EINECS: 254-758-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
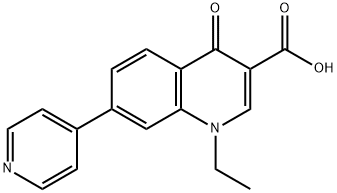
What is rosoxacin?
The Uses of rosoxacin
Antibacterial.
Indications
For the treatment of bacterial infection of respiratory tract, urinary tract, GI, CNS and immuno compromised patients.
Background
Rosoxacin is a quinolone derivative antibiotic for the treatment of bacterial infection of respiratory tract, urinary tract, GI, CNS and immuno compromised patients. Rosoxacin is known to be effective against penicillin resistant strains and is a single dose orally administered drug, which avoids all complications of parenteral administration seen with penicillin, especially anaphylactic shock.
Definition
ChEBI: A quinolinemonocarboxylic acid that is 1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid that is substituted by an ethyl group at position 1 and by a pyridin-4-yl group at position 7. An antibacterial drug, active against Neisseria gonorrhoeae, it has be n used for treating urinary tract infections and certain sexually transmitted diseases.
brand name
Roxadyl (Sterling Winthrop).
Pharmacokinetics
Rosoxacin is a nonfluorinated quinolone antibiotic. Its mode of action depends on blocking of bacterial DNA replication by binding itself to an enzyme called DNA gyrase, which allows the untwisting required to replicate one DNA double helix into two. Rosoxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Pharmacokinetics
A single oral dose of 300 mg produces a mean peak plasma concentration of 4–5 mg/L at about 2–4 h, with an apparent elimination half-life of about 6 h. Elimination in the urine is partly as the N-oxide metabolite and the glucuronide of this metabolite.
Side effects are those common to quinolones, notably gastrointestinal tract and CNS disturbances. About 50% of patients treated with single oral doses of 100–400 mg developed dizziness, drowsiness, altered visual perception and other CNS effects.
It is effective as single-dose treatment of patients with urethral and anorectal gonorrhea, but coexistent C. trachomatis infection is not eliminated from most patients and postgonococcal urethritis develops in up to 30%.
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of rosoxacin
| Melting point: | 290° |
| Boiling point: | 500.8±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.317±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | DMF (Very Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 6.48±0.41(Predicted) |
| color | Light Beige to Beige |
Safety information for rosoxacin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for rosoxacin
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Rosoxacin 95% CAS 40034-42-2View Details
Rosoxacin 95% CAS 40034-42-2View Details
40034-42-2 -
 55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 207557-35-5 99%View Details
207557-35-5 99%View Details
207557-35-5 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1