ROSE BENGAL
Synonym(s):Rose Bengal;Acid Red 94;Rose Bengal sodium salt;Aniline Rose;Bengal Rose B sodium salt
- CAS NO.:632-68-8
- Empirical Formula: C20H5Cl4I4KO5
- Molecular Weight: 1013.77
- MDL number: MFCD00068422
- EINECS: 211-182-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
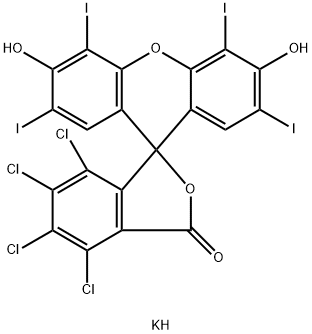
What is ROSE BENGAL?
Absorption
No information available.
Toxicity
Rose Bengal induces cytotoxic effects in different cell lines .
Background
Rose bengal is a pink stain derived as an analogue of fluorescein. Its disodium salt in ophthalmic solutions has been used as a diagnostic agent in suspected damage to conjunctival and corneal cells. It is also used in laboratory settings, including the preparation of Foraminifera for microscopic analysis and suppression of bacterial growth in several microbiological media. A direct cytotoxic effect of Rose bengal on microorganisms and cancer cells has been observed, questioning its potential antitumor actions via intralesional injections. The clinical applications of rose bengal as injectable formulation under the name PV-10 in melanoma, breast cancer and skin conditions such as eczema and psoriasis are being investigated in clinical trials.
Indications
Indicated as a diagnostic agent in routine ocular examinations or when superficial conjunctiva or corneal tissue change is suspected, and as an aid in the diagnosis of keratoconjunctivitis sicca, keratitis, abrasions or corrosions as well as the detection of foreign bodies.
Preparation
Resorcinol and 4,5,6,7-Tetrachloroisobenzofuran-1,3-dione condensation, The resulting 2-(1,2,7,8-Tetrachloro-3,6-dihydroxy-9H-xanthen-9-yl)benzoic acid?tetraiodide, potassium or sodium salt is then transformed into.
Pharmacokinetics
Rose bengal is a staining agent that visualized ocular surfaces of both diseased and dead cells in vivo . It has also shown to stain healthy cultured cells, including rabbit corneal epithelial cells, in a rapid, dose-dependent manner . Various studies demonstrate the cytotoxic effects of rose bengal in different cell cultures, including smooth-muscle cells from human intestine, endothelial cells from bovinepulmonary artery, rabbit Tenon fibro-blasts, and rabbit and human corneal epithelial cells . Cellular morphological changes such as detachment, separation, loss of motility and disruption, in addition to swelling, intracytoplasmic vacuole formation and lysis have been manifested with the treatment of rose bengal , indicating that rose Bengal is not a vital dye.
Metabolism
No information available.
Properties and Applications
bright blue light pink. Soluble in water for blu-ray red, no fluorescence. The strong sulfuric acid for brown, after diluted pink precipitation.
| Standard | Light Fastness | Soaping | Persperation Fastness | Oxygen bleaching | Fastness to seawater | |||
| Fading | Stain | Fading | Stain | Fading | Stain | |||
| ISO | 1 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 5 | |||
| AATCC | 1 | 4 | 4 | 3-4 | ||||
Properties of ROSE BENGAL
| form | Powder |
| color | Dark red to rust |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Spiro[isobenzofuran-1(3H),9'-[9H]xanthen]-3-one, 4,5,6,7-tetrachloro-3',6'-dihydroxy-2',4',5',7'-tetraiodo-, dipotassium salt (632-68-8) |
Safety information for ROSE BENGAL
Computed Descriptors for ROSE BENGAL
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![Benzo[6,7]furo[3',4':5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]quinoline, 5-ethyl-6,7-dihydro-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/1042-81-5.gif)
You may like
-
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
1310-58-3 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
