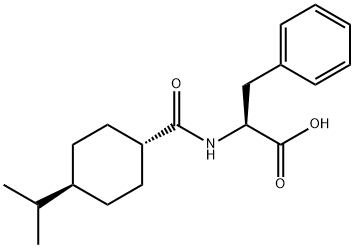
Nateglinide
Synonym(s):Fastic;N-[(trans-4-Isopropylcyclohexyl)carbonyl]-D-phenylalanine;Starlix;Starsis
- CAS NO.:105816-04-4
- Empirical Formula: C19H27NO3
- Molecular Weight: 317.42
- MDL number: MFCD00875706
- EINECS: 641-756-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 15:53:33
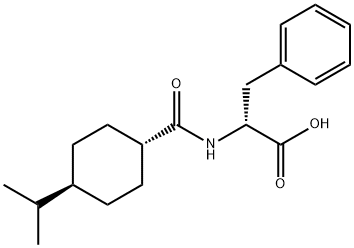
What is Nateglinide?
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed following oral administration prior to a meal, absolute bioavailability is estimated to be approximately 73%. Peak plasma concentrations generally occur within 1 hour of oral administration. Onset of action is <20 minutes and the duration of action is approximately 4 hours.
Toxicity
An overdose may result in an exaggerated glucose-lowering effect with the development of hypoglycemic symptoms.
Description
Nateglinide is a N-acylated D-phenylalanine marketed in Japan as novel orally active insulinotropic agent for the treatment of type-2 diabetes mellitus. It belongs to the class of nonsulfonylureas and shows some structural similarity to repaglinide, the only other representative in this family. In single pancreatic beta-cells isolated from rats, Nateglinide was found to specifically block the ATP-sensitive K+ channel resulting in an increase in intracellular calcium concentration. This primary action would underlie the mechanism by which Nateglinide markedly stimulates or potentiates, depending on glucose concentrations, insulin secretion from pancreatic beta-cells. Clinical studies demonstrated a good safety profile with a low potential for hypoglycemia. The pharmacokinetic profile was consistent with the changes of the blood glucose and plasma insulin level. Interestingly, Nateglinide exerts a rapid onset and short duration of action due to a rapid absorption and clearance. Unlike other similar agents, Nateglinide suppresses postprandial glucose elevations.
Chemical properties
Cyrstalline Solid
Originator
Ajinomoto (Japan)
The Uses of Nateglinide
An Amino-acid derivative that stimulates insulin secretion. Used as an antidiabetic
The Uses of Nateglinide
antidiabetic KATP channel blocker
The Uses of Nateglinide
An amino-acid derivative that stimulates insulin secretion. Used as an antidiabetic.
Indications
For the treatment of non-insulin dependent-diabetes mellitus in conjunction with diet and exercise.
Background
Nateglinide is an oral antihyperglycemic agent used for the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). It belongs to the meglitinide class of short-acting insulin secretagogues, which act by binding to β cells of the pancreas to stimulate insulin release. Nateglinide is an amino acid derivative that induces an early insulin response to meals decreasing postprandial blood glucose levels. It should only be taken with meals and meal-time doses should be skipped with any skipped meal. Approximately one month of therapy is required before a decrease in fasting blood glucose is seen. Meglitnides may have a neutral effect on weight or cause a slight increase in weight. The average weight gain caused by meglitinides appears to be lower than that caused by sulfonylureas and insulin and appears to occur only in those na?ve to oral antidiabetic agents. Due to their mechanism of action, meglitinides may cause hypoglycemia although the risk is thought to be lower than that of sulfonylureas since their action is dependent on the presence of glucose. In addition to reducing postprandial and fasting blood glucose, meglitnides have been shown to decrease glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, which are reflective of the last 8-10 weeks of glucose control. Meglitinides appear to be more effective at lowering postprandial blood glucose than metformin, sulfonylureas and thiazolidinediones. Nateglinide is extensively metabolized in the liver and excreted in urine (83%) and feces (10%). The major metabolites possess less activity than the parent compound. One minor metabolite, the isoprene, has the same potency as its parent compound.
What are the applications of Application
Nateglinide is an amino-acid derivative that stimulates insulin secretion
Definition
ChEBI: An N-acyl-D-phenylalanine resulting from the formal condensation of the amino group of D-phenylalanine with the carboxy group of trans-4-isopropylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid. An orally-ad inistered, rapidly-absorbed, short-acting insulinotropic agent, it is used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
brand name
Starlix (Novartis);Fastic;Starsis.
General Description
Although nateglinide, N-(4-isopropylcyclohexanecarbonyl)-D-phenylalanine (Starlix), belongs tothe metaglinides, it is a phenylalanine derivative and representsa novel drug in the management of type 2 diabetes.
General Description
Nateglinide (Starlix) is D-Phenylalanine, N-[[trans-4-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl]carbonyl]-; or (-)-N-[(trans-4-isopropylcyclohexyl)carbonyl]-D-phenylalanine. Itis noteworthy that, although nateglinide is much less potenton a dosage basis than is repaglinide and most of the sulfonylureas,this drug seems to exhibit unique molecularpharmacodynamics. Nateglinide closes ATP-sensitive K channels some threefold more rapidly than repaglinide, andexhibits an off-rate twice as fast as that of glyburide orglimepiride and five times faster than repaglinide. Thesecharacteristics are reflected by the systemic pharmacodynamicsof this drug, translating clinically to improvedsafety, among other apparent benefits.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Nateglinide is a Kir6.2/SUR1 channel inhibitor and antidiabetic. It is selective for the SUR1 subtype, which is found on pancreatic islet cells. Nateglinide evokes KATP channel-dependent insulin secretion (50-200 μM) in the absence and presence of insulin.
Mechanism of action
Approved in the United States in late 2000, nateglinide is a rapidly absorbed insulin secretagogue that has a mechanism of action similar to that of repaglinide, with effects appearing within 20 minutes following oral dosing. Bioavailability is 73%, and it is 98% protein bound, primarily to albumin. Nateglinide is tissue selective, with low affinity for cardiac and skeletal muscle.
Pharmacokinetics
Insulin secretion by pancreatic β cells is partly controlled by cellular membrane potential. Membrane potential is regulated through an inverse relationship between the activity of cell membrane ATP-sensitive potassium channels (ABCC8) and extracellular glucose concentrations. Extracellular glucose enters the cell via GLUT2 (SLC2A2) transporters. Once inside the cell, glucose is metabolized to produce ATP. High concentrations of ATP inhibit ATP-sensitive potassium channels causing membrane depolarization. When extracellular glucose concentrations are low, ATP-sensitive potassium channels open causing membrane repolarization. High glucose concentrations cause ATP-sensitive potassium channels to close resulting in membrane depolarization and opening of L-type calcium channels. The influx of calcium ions stimulates calcium-dependent exocytosis of insulin granules. Nateglinide increases insulin release by inhibiting ATP-sensitive potassium channels in a glucose-dependent manner.
Clinical Use
Treatment of type 2 diabetes in combination with metformin
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: concentration reduced by rifampicin.
Antifungals: hypoglycaemic effect possibly enhanced
by fluconazole.
Lipid-lowering agents: hypoglycaemic effect possibly
enhanced by gemfibrozil.
Metabolism
Hepatic, via cytochrome P450 isoenzymes CYP2C9 (70%) and CYP3A4 (30%). Metabolism is via hydroxylation followed by glucuronidation. The major metabolites have less antidiabetic activity than nateglinide, but the isoprene minor metabolite has antidiabetic activity comparable to that of nateglinide.
Metabolism
It is metabolized in the liver, with 16% excreted in the urine unchanged. The major metabolites are hydroxyl derivatives (CYP2C9, 70%; CYP3A4, 30%) that are further conjugated to the glucuronide derivatives.
storage
Store at RT
Properties of Nateglinide
| Melting point: | 137-141°C |
| Boiling point: | 527.6±39.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D20 -9.4° (c = 1 in methanol) |
| Density | 1.104±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | DMSO: >5mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 3.61±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | white to off-white |
| Merck | 14,6428 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 105816-04-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Nateglinide
Computed Descriptors for Nateglinide
Nateglinide manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![[2(S)-cis]-Octahydro-gamma-oxo-alpha-(phenylmethyl)-2H-isoindole-2-butanoic acid](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/145375-43-5.gif)


You may like
-
 105816-04-4 96%View Details
105816-04-4 96%View Details
105816-04-4 -
 Nateglinide 98%View Details
Nateglinide 98%View Details
105816-04-4 -
 Nateglinide 97% CAS 105816-04-4View Details
Nateglinide 97% CAS 105816-04-4View Details
105816-04-4 -
 Nateglinide CAS 105816-04-4View Details
Nateglinide CAS 105816-04-4View Details
105816-04-4 -
 Nateglinide 105816-04-4 99%View Details
Nateglinide 105816-04-4 99%View Details
105816-04-4 -
 105816-04-4 Nateglinide 99%View Details
105816-04-4 Nateglinide 99%View Details
105816-04-4 -
 Nateglinide CAS 105816-04-4View Details
Nateglinide CAS 105816-04-4View Details
105816-04-4 -
 Nateglinide CAS 105816-04-4View Details
Nateglinide CAS 105816-04-4View Details
105816-04-4