RENNIN
- CAS NO.:9015-94-5
- Molecular Weight: 0
- MDL number: MFCD00132171
- EINECS: 232-796-2
- Update Date: 2023-04-23 13:52:06
What is RENNIN?
Description
Renin is the rate-limiting enzyme for the initiation of the cascade of the renin-angiotensin system. Plasma renin activity is a marker for hypertension. This is a drug target for hypertension and renal disease. In the late 18th century, renin was discovered based on the observation that the injection of saline extracts from fresh rabbit kidneys into other rabbits increased arterial blood pressure.
The Uses of RENNIN
Rennin is a milk coagulant that is an enzyme obtained from the abo- masum portion of the stomach of suckling mammals. it is most active at ph 3.8. one part purified rennin will coagulate more than five million parts of milk. the commercial extract of rennin is termed rennet. it is used to coagulate milk in making cheese, junket, and custard. see rennet.
Definition
An enzyme secreted by cellslining the stomach in mammals thatis responsible for clotting milk. Itacts on a soluble milk protein (caseinogen),which it converts to theinsoluble form casein. This ensuresthat milk remains in the stomachlong enough to be acted on by protein-digesting enzymes.
Biological Functions
Renin is an enzyme that is synthesized and stored in the
renal juxtaglomerular apparatus and that catalyzes the
formation of a decapeptide, angiotensin I, from a
plasma protein substrate. Renin has a narrow substrate
specificity that is limited to a single peptide bond in angiotensinogen,
a precursor of angiotensin I. Renin is
considered to control the rate-limiting step in the ultimate
production of angiotensin II. Control of renin secretion
by the juxtaglomerular apparatus is important
in determining the plasma renin concentration.
Three generally accepted mechanisms are involved
in the regulation of renin secretion. The first
depends on renal afferent arterioles that act as stretch
receptors or baroreceptors. Increased intravascular
pressure and increased volume in the afferent arteriole
inhibits the release of renin. The second mechanism is
the result of changes in the amount of filtered sodium
that reaches the macula densa of the distal tubule.
Plasma renin activity correlates inversely with dietary
sodium intake. The third renin secretory control mechanism
is neurogenic and involves the dense sympathetic
innervation of the juxtaglomerular cells in the afferent
arteriole; renin release is increased following activation
of 1-adrenoceptors by the neurotransmitter norepinephrine.
Angiotensin II, the primary end product of the
renin–angiotensin system, acts on the juxtaglomerular
cells to inhibit the release of renin; this process is therefore
a negative feedback mechanism. The half-life of
renin in the circulation is 10 to 30 minutes, with inactivation
occurring primarily in the liver. Small amounts of
renin are eliminated by the kidneys. Pure human renin has been used to develop specific inhibitors of the enzyme.
Low-molecular-weight orally effective renin inhibitors
are under development.
Clinical Use
Renin inhibitors can be used for the treatment of hypertension. In current medical practice, PRA is the indicator of RAS overactivity and is more commonly treated using either ACE blockers and/or AT1 blockers rather than a direct oral renin inhibitor. ACE inhibitors and/or AT1 blockers are also part of the standard treatment after a heart attack. The diagnosis of kidney cancer includes a juxtaglomerular cell tumor (reninoma), Wilms’ tumor, and renal cell carcinoma, all of which may produce renin and lead to hypertension in patients.
Structure and conformation
Renin is a highly specific endopeptidase whose only known function is to generate angiotensin I (Ang I) from angiotensinogen (AGT), initiating a cascade of reactions that produces elevated blood pressure and increased sodium retention by the kidney. REN1 is a protein coding gene with 406 aa residues in humans; it forms an aspartyl protease.
Properties of RENNIN
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| form | powder |
| color | slightly brown |
| Merck | 13,8218 |
Safety information for RENNIN
Computed Descriptors for RENNIN
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 7-Bromo-1H-indazole N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid Electrolytic Iron Powder Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 1-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,3-benzotriazole 1-(2-Chlorobenzyl)-4-nitro-1H-pyrazole 1-(2-Nitrophenyl)-4-phenylpiperazineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
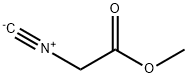
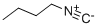

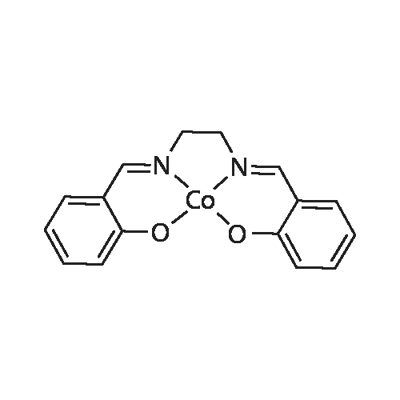
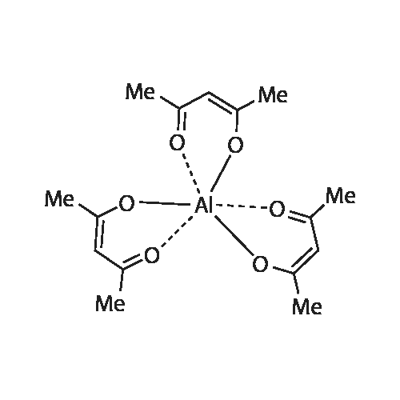
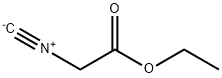
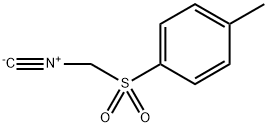
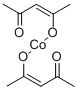
You may like
-
 55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 181228-33-1 99%View Details
181228-33-1 99%View Details
181228-33-1 -
 Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
1169630-40-3 -
 1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 -
 127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5