Remoxipride
- CAS NO.:80125-14-0
- Empirical Formula: C16H23BrN2O3
- Molecular Weight: 371.27
- MDL number: MFCD00869705
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 16:48:35
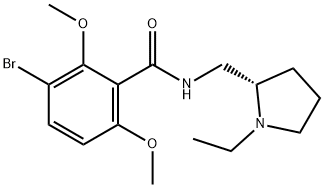
What is Remoxipride?
Absorption
Remoxipride is approximately 90% bioavailable. In patients with normal creatinine clearance, remoxipride reaches a Cmax of 5.5 ± 1.1 μmol/L, with a Tmax of 0.8 ± 0.2 h, and an AUC of 39 ± 9 μmol*h/L. In patients with moderate renal impairment, remoxipride reaches a Cmax of 7.7 ± 2.7 μmol/L, with a Tmax of 0.9 ± 0.4 h, and an AUC of 63 ± 34 μmol*h/L. In patients with severe renal impairment, remoxipride reaches a Cmax of 9.3 ± 2.3 μmol/L, with a Tmax of 1.4 ± 0.9 h, and an AUC of 123 ± 60 μmol*h/L.
Toxicity
Remoxipride was withdrawn from the market after 8 cases of aplastic anemia were reported. Of those 8 cases, 2 were fatal.
The Uses of Remoxipride
Antipsychotic.
Background
Remoxipride is an atypical antipsychotic agent that is specific for dopamine D2 receptors. It gained approval in the UK in 1989 but was withdrawn in 1993 after it was found to be associated with an increased incidence of aplastic anemia.
Indications
Remoxipride is an atypical antipsychotic once used for the treatment of schizophrenia.
Definition
ChEBI: 3-bromo-N-[[(2S)-1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl]methyl]-2,6-dimethoxybenzamide is a dimethoxybenzene.
General Description
Remoxipride is a D2 receptorblocker.It is as effective as haloperidol with fewer EPS andautonomic side effects. Negative symptoms of schizophreniaare diminished. The drug is classed as an atypical antipsychotic.Life-threatening aplastic anemia was reported with itsuse, which prompted its withdrawal from the market.
With respect to the atypical antipsychotics, two eventslong in the past may shed some light on the events of today.
The field of reuptake-inhibiting antidepressants arose whenonly a very small structural change was made in an antipsychoticdrug, and the new activity noted. (The antipsychoticactivity remained.) Therefore, small changes in structurecan produce antipsychotics that are active against depressivesymptoms. Likewise, small changes in structure could provideselectivity among D2 receptors.
Pharmacokinetics
Remoxipride is a weak selective dopamine D2 receptor antagonist that was once used in the treatment of schizophrenia. It has a moderate therapeutic index and duration of action. Remoxipride was withdrawn due to deaths associated with aplastic anemia.
Metabolism
Remoxipride can be N-dealkylated to FLA 853, oxidized to FLA 850, or N-deethylated to FLA 838. FLA 838 can be oxidized to NCL 118 which is further hydroxylated to NCM 009. FLA 850 can be N-deethylated to NCL 118 or hydroxylated to NCM 001. NCM 001 is further N-deethylated to NCM 009. None of these metabolites have measurable activity on dopamine D2 receptors.
Properties of Remoxipride
| alpha | D20 -64° (c = 2 in ethanol) |
| Boiling point: | 439.9±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.292 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| pka | pKa 8.9 (Uncertain) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 80125-14-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Remoxipride(80125-14-0) |
Safety information for Remoxipride
Computed Descriptors for Remoxipride
Remoxipride manufacturer
New Products
Tetrabutylammonium iodide (3,3-DIFLUOROCYCLOBUTYL)METHANOL 4,4-DIFLUOROCYCLOHEXANAMINE Cyclobutylamine (S)-3-Fluoro-pyrrolidine hydrochloride 3-Oxocyclobutanecarboxylic acid N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide L-tert-Leucine,97% 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% Aluminum oxide, basic Calcium hydroxide, 95% Diallylamine, 99% 2-Iodobenzoic Acid 3-Methoxybenzonitrile Pentachlorobenzonitrile Chloral Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide O-Benzylhydroxylamine Hydrochloride 2-Nitrobenzaldehyde 2-Picolylamine (2-Aminomethylpyridine) 2-Venylpyridine Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 4-Dimethylamine PyridineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 1126-74-5 3-Pyridineacrylic acid 98+View Details
1126-74-5 3-Pyridineacrylic acid 98+View Details
1126-74-5 -
 3859-41-4 1,3-Cyclopentanedione 98+View Details
3859-41-4 1,3-Cyclopentanedione 98+View Details
3859-41-4 -
 tert-Butyl carbazate 98+View Details
tert-Butyl carbazate 98+View Details
870-46-2 -
 99-32-1 98+View Details
99-32-1 98+View Details
99-32-1 -
 TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 10442-39-4 98+View Details
TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 10442-39-4 98+View Details
10442-39-4 -
 91419-52-2 98+View Details
91419-52-2 98+View Details
91419-52-2 -
 85909-08-6 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE 98+View Details
85909-08-6 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE 98+View Details
85909-08-6 -
 19752-84-2 TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 98+View Details
19752-84-2 TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 98+View Details
19752-84-2
