REMIFENTANIL
- CAS NO.:132875-61-7
- Empirical Formula: C20H28N2O5
- Molecular Weight: 376.45
- MDL number: MFCD00864324
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-04 15:16:44
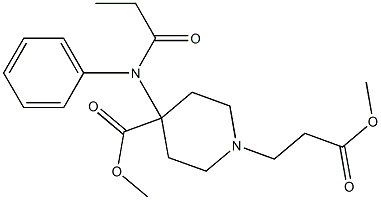
What is REMIFENTANIL?
The Uses of REMIFENTANIL
Analgesic.
Background
Remifentanil (marketed by Abbott as Ultiva) is a potent ultra short-acting synthetic opioid given to patients during surgery for pain relief and adjunctive to an anaesthetic. Remifentanil is a specific mu-type-opioid receptor agonist which means it reduces sympathetic nervous system tone, and causes respiratory depression and analgesia.
Indications
For use during the induction and maintenance of general anesthesia.
Definition
ChEBI: A piperidinecarboxylate ester that is methyl piperidine-4-carboxylate in which the hydrogen attached to the nitrogen is substituted by a 3-methoxy-3-oxopropyl group and the hydrogen at position 4 is substituted the nitrogen of N-propanoy aniline.
brand name
Ultiva (Abbott).
World Health Organization (WHO)
Remifentanil is defined as an opioid narcotic with an addictionforming and addiction-sustaining liability similar to morphine.
General Description
Remifentanil (Ultiva) was designed as a “soft drug.” Softdrugs are designed to undergo metabolism quickly and thushave ultrashort durations of action. In place of the ethylaromatic ring seen on the other piperidine opioids, remifentanilhas an ester group. This ester group is metabolizedby esterases in the blood and tissue to a weaklyactive metabolite (1:300–1:1,000 the potency of remifentanil). The n-octanol/water partition coefficient ofremifentanil is 17.9. The pKa of remifentanil is 7.07, thus itis predominately unionized at physiological pH. Both ofthese properties account for its rapid distribution across theblood-brain barrier (<1 minute). The ester hydrolysis leadsto a quick recovery (5–10 minutes) independent of durationof drug administration, renal, or liver function. The favorablepharmacodynamics of remifentanil have led to its usefor induction and maintenance of surgical anesthesia.
Pharmacokinetics
Remifentanil is an opioid agonist with rapid onset and peak effect and ultra-short duration of action. The opioid activity of remifentanil is antagonized by opioid antagonists such as naloxone. The analgesic effects of remifentanil are rapid in onset and offset. Its effects and side effects are dose dependent and similar to other opioids. Remifentanil in humans has a rapid blood-brain equilibration half-time of 1 ± 1 minutes (mean ± SD) and a rapid onset of action.
Pharmacology
Remifentanil is a MOP agonist with a similar potency to fentanyl and
approximately 20 times more than alfentanil. It has a rapid blood–brain
equilibration time of just over 1min, with a short context-sensitive half-life of
3–5min, which is unaffected by duration of infusion. This makes it ideally
suited for infusion during anaesthesia and in critical care. It may be titrated
rapidly to achieve the desired effect. Remifentanil is available as a lyophilised
white crystalline powder containing glycine; it should not be administered
via the epidural or intrathecal routes. There may be increased opioid
sensitivity in hepatic disease, resulting in a lower dosage requirement. Other
situations requiring a reduction in dose include haemorrhage and shock and
when administering in elderly patients. The high clearance and low VD imply
that the offset of effect is caused by metabolism rather than redistribution.
Hypothermia, such as may occur in cardiac surgery, may reduce clearance by
up to 20%.
There is some evidence to suggest that acute opioid tolerance and
hyperalgesia may occur, particularly after remifentanil infusions. If high
doses are used without neuromuscular blockade, muscle rigidity may be a
problem, though this is less likely if using a concentration of 100 μgml-1 or
less and an infusion rate of 0.2–0.5μgkg-1 min-1. Bradycardia has also been
reported.
Clinical Use
Analgesic
Induction of anaesthesia
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anti-arrhythmics: delayed absorption of mexiletine.
Antidepressants: possible CNS excitation or depression
(hypertension or hypotension) in patients also receiving
MAOIs (including moclobemide) - avoid; possibly
increased sedative effects with tricyclics.
Antihistamines: sedative effects possibly increased
with sedating antihistamines.
Antipsychotics: enhanced sedative and hypotensive
effect.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir (risk of toxicity) - avoid.
Dopaminergics: avoid with selegiline.
Nalmefene: avoid concomitant use.
Sodium oxybate: enhanced effect of sodium oxybate
- avoid.
Metabolism
By hydrolysis of the propanoic acid-methyl ester linkage by nonspecific blood and tissue esterases.
Metabolism
Remifentanil is an esterase metabolised opioid that is susceptible to metabolism by non-specific blood and tissue esterases. The metabolism of remifentanil results in the formation of an essentially inactive carboxylic acid metabolite (1/4600th as potent as remifentanil). About 95% of a dose of remifentanil is excreted in the urine as the metabolite.
Properties of REMIFENTANIL
| Boiling point: | 487.8±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.171±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 6.65±0.20(Predicted) |
Safety information for REMIFENTANIL
Computed Descriptors for REMIFENTANIL
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1