Relebactam
- CAS NO.:1174018-99-5
- Empirical Formula: C12H20N4O6S
- Molecular Weight: 348.38
- MDL number: MFCD28502833
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
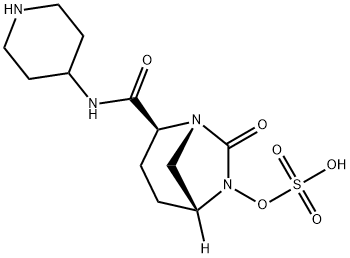
What is Relebactam?
Absorption
Currently, relebactam is only available as an intravenous product; therefore, there is no relevant absorption data in the literature.
Toxicity
If overdose with the combination product which includes relebactam, imipenem and cilastatin occurs, the drug should be stopped immediately and the patient should be provided with supportive care. Relebactam, imipenem, and cilastatin may be removed via hemodialysis; however, the use of hemodialysis to manage cases of overdose has not been studied.
Description
Relebactam (formerly known as MK-7655) is a novel,intravenous,class A and class C B-lactamase inhibitor and is currently under evaluation in combination with imipenem/cilastatin for the treatment of resistant Gram-negative infections.In vitro studies demonstrated that relebactam restored imipenem's activity against KPC-producing Enterobacteriacae,lowering imipenem MICs from 16-64 to 0.12-1mg/L at a concentration of 4 mg/L. Moreover, relebactam is able to lower imipenem MICs for P. aeruginosa,particularly in strains with depressed OprD expression and increased AmpC expression.Conversely, the addition of relebactam to imipenem does not seem to provide any adjunctive benefit against A.baumanii or S.maltophilia or against MBL-producing Enterobacteriacae.A non-inferiority, Phase 3 trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of imipenem/relebactam compared to piperacillin/tazobactam for the treatment of HAP and VAP(ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02493764) is currently recruiting. A Phase 3 study evaluating the efficacy and safety of imipenem/relebactam (200/100-500/250 mg depending on renal function) compared to colistimethate sodium plus imipenem/cilastatin for the treatment of imipenem-resistant bacterial infections,including HAP, VAP, cIAIs and cUTIs, has recently been completed and results are pending(ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCTO2452047).In Phase 2 trials, imipenem/relebactam was well tolerated, with diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and headache being the most commonly reported adverse events.
The Uses of Relebactam
Relebactam is a novel β-lactamase inhibitor in combination with Primaxin. It has also demonstrated the potential to enhance the activity of imipenem against P.aeruginosa, including those strains with depressed OprD expression and increased AmpC expression.
Background
Relebactam is a diazabicyclooctane beta-lactamase inhibitor, similar in structure to avibactam. It includes a piperidine ring which reduces export from bacterial cells by producing a positive charge. It is currently available in a combination product which includes imipenem and cilastatin to treat complicated urinary tract infections (UTIs), pyelonephritis, and complicated intra-abdominal infections in adults. It is considered to be a last-line treatment option and gained FDA approval as part of the combination product Recarbrio? in July 2019.
Indications
Relebactam is indicated in combination with imipenem and cilastatin for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections (including pyelonephritis), and complicated intra-abdominal infections caused by susceptible organisms in adults.
Mechanism of action
Relebactam is a beta-lactamase inhibitor known to inhibit many types of beta-lactamases including Ambler class A and Ambler class C enzymes, helping to prevent imipenem from degrading in the body.Label,Similar to the structurally-related avibactam, first, relebactam binds non-covalently to a beta-lactamase binding site, then, it covalently acylates the serine residue in the active site of the enzyme.In contrast to some other beta-lactamase inhibitors, once relebactam de-acylates from the active site, it can reform it's 5 membered ring and is capable of rebinding to target enzymes.
https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB12377
Pharmacokinetics
Relebactam prevents the hydrolysis of imipenem, allowing it to exert its bactericidal effect.
Clinical Use
Recently, another carbapenem-β-lactamase inhibitor, imipenem/cilastatin-relebactam (RecarbrioTM), was approved by the FDA. Relebactam, a bicyclic diazabicyclooctane, is structurally related to avibactam but differs by the addition of a piperidine ring to the 2-position carbonyl group. Like meropenem- vaborbactam (VabomereTM), imipenem-relebactam(RecarbrioTM) is active against class A and class C carbapenemases and is approved for the treatment of multidrug-resistant intraabdominal infections secondary to Bacteroides caccae, Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides ovatus, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Bacteroides uniformis, Bacteroides vulgatus, Bifidobacterium stercoris, Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Fusobacterium nucleatum, Klebsiella aerogenes, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Parabacteroides distasonis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa and multidrug-resistant complicated urinary tract infections secondary to E. cloacae, E. coli, K. aerogenes, K. pneumoniae and P. aeruginosa.
Synthesis
Relebactam is a β-lactamase inhibitor in clinical trials as a combination therapy for the treatment of bacterial infection resistant to β-lactam antibiotics. Its unusual structural challenges have inspired a rapid synthesis featuring an iridium-catalyzed N–H insertion and a series of late stage transformations designed around the reactivity of the labile bicyclo[3.2.1]urea at the core of the target.
In 2014, Qualified Infectious Disease Product (QIDP) and Fast Track designations were assigned by the FDA for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections, complicated intra-abdominal infections and hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia/ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia.
A Concise Synthesis of a β-Lactamase Inhibitor
Metabolism
Relebactam does not undergo significant metabolism and can be found mostly unchanged in human plasma.
Properties of Relebactam
| Melting point: | >252°C (dec.) |
| Density | 1.59 |
| storage temp. | Hygroscopic, -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | -4.59±0.18(Predicted) |
| color | Off-White to Light Yellow |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C12H20N4O6S/c17-11(14-8-3-5-13-6-4-8)10-2-1-9-7-15(10)12(18)16(9)22-23(19,20)21/h8-10,13H,1-7H2,(H,14,17)(H,19,20,21)/t9-,10+/m1/s1 |
Safety information for Relebactam
Computed Descriptors for Relebactam
| InChIKey | SMOBCLHAZXOKDQ-ZJUUUORDSA-N |
| SMILES | S(O)(ON1C(=O)[N@@]2C[C@@]1([H])CC[C@H]2C(NC1CCNCC1)=O)(=O)=O |
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium 3-Bromopyrazole (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-hexahydro-5-Triethyl silyloxy-4-((E)-3-oxo-5-phenylpent-1- enyl)cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one. 1-Chlorocarbonyl-4-piperidinopiperidine 1-Bromo-4-phenyl-2-Butanone 4-Amino-2-fluoro-N-methylbenzamide 1,1'-Carbonyldiimidazole SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTIONRelated products of tetrahydrofuran





You may like
-
![Dimethyl [2-oxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propyl]phosphonate 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) Dimethyl [2-oxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propyl]phosphonate 99%View Details
Dimethyl [2-oxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propyl]phosphonate 99%View Details
54094-19-8 -
 85-81-4 99%View Details
85-81-4 99%View Details
85-81-4 -
 Cyclopentane carboxxylic acid 3400-45-1 99%View Details
Cyclopentane carboxxylic acid 3400-45-1 99%View Details
3400-45-1 -
![208111-98-2 (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-5-(Benzoyloxy)hexahydro-4-[(1E)-3-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-1-buten- 1-yl]-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 208111-98-2 (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-5-(Benzoyloxy)hexahydro-4-[(1E)-3-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-1-buten- 1-yl]-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one 99%View Details
208111-98-2 (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-5-(Benzoyloxy)hexahydro-4-[(1E)-3-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-1-buten- 1-yl]-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one 99%View Details
208111-98-2 -
 2033-24-1 99%View Details
2033-24-1 99%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 Meldrums acid 2033-24-1 99%View Details
Meldrums acid 2033-24-1 99%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 Cyaclopentane carboxylic acid 99%View Details
Cyaclopentane carboxylic acid 99%View Details
3400-45-1 -
 2-Aminopyridine 504-29-0 99%View Details
2-Aminopyridine 504-29-0 99%View Details
504-29-0