Ranitidine
- CAS NO.:66357-35-5
- Empirical Formula: C13H22N4O3S
- Molecular Weight: 314.4
- MDL number: MFCD00081180
- EINECS: 266-332-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57

What is Ranitidine?
Absorption
Ranitidine is rapidly absorbed with peak concentrations reached within 1-3 hours after administration, and varying greatly among patients. Bioavailability is about 50%-60% due to hepatic metabolism. In a pharmacokinetic study of healthy males, the AUC 0-infinity was about 2,488.6 ng x h/mL and the median Tmax was 2.83 hours. Food or antacids have limited effects on absorption. One clinical study found that the administration of a potent antacid (150 mmol) in subjects in the fasted state led to decreased absorption of ranitidine.
Toxicity
Oral doses of 1,000 mg/kg in mice and rats were not found to be lethal. Intravenous LD50 values in mice and rats were 77 and 83 mg/kg, respectively.
Overdose information
There has been limited experience with ranitidine overdose. Reported acute ingestions of up to 18 grams orally were followed by temporary adverse effects similar to the normal adverse effects of this drug, including tachycardia, bradycardia, dizziness, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, among other effects. Gait abnormalities and hypotension have also been observed. When an overdose with ranitidine is suspected, remove unabsorbed ranitidine from the gastrointestinal tract if possible, and monitor the patient and provide supportive therapy as required.
Description
Ranitidine, a H2-receptor agonist, caused contact dermatitis within the pharmaceutical industry.
The Uses of Ranitidine
Ranitidine (cas# 66357-35-5) was used as a standard for testing the therapeutic effect of brown propolis extract against aspirin and ethanol- induced gastric ulcers.
The Uses of Ranitidine
Antagonist (to histamine H2receptors).
The Uses of Ranitidine
It simultaneously reduces pepsin activity and is used for treating stomach and duodenum ulcers as well as other conditions accompanied by elevated acidity of the gastrointestinal tract. Synonyms of this drug are zantac, azantac, raniplex, ranidil, and others.
Indications
This drug is used alone or with concomitant antacids for the following conditions: short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcer, treating gastric acid hypersecretion due to Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, systemic mastocytosis, and other conditions that may pathologically raise gastric acid levels. It also used in the short term treatment of active benign gastric ulcers and maintenance therapy of gastric ulcers at a reduced dose. In addition to the above, ranitidine can be used for the treatment of GERD symptoms, treatment of erosive esophagitis (endoscopically diagnosed) and the maintenance of gastric or duodenal ulcer healing.
Background
Ranitidine is a commonly used drug, classified as a histamine H2-receptor antagonist, and belongs to the same drug class as cimetidine and famotidine. This drug helps to prevent and treat gastric-acid associated conditions, including ulcers, because of its ability to decrease gastric acid secretion. Ranitidine is often referred to as Zantac, and is available in various forms, including tablet, injection, and effervescent tablet preparations.
The prevalence of GERD is thought to be 10-20% in western countries. Ranitidine has proven to be an effective treatment for relieving uncomfortable symptoms of gastric acid associated conditions and is therefore widely used in GERD and other gastric-acid related conditions.
What are the applications of Application
Ranitidine is a selective and competitive histamine H2 receptor inhibitor
Indications
Ranitidine (Zantac) is another H2 receptor antagonist that does not have the same antiandrogen side effects as cimetidine. Note that both cimetidine and ranitidine inhibit the cytochrome P-450 microsomal enzyme system.
Definition
ChEBI: Ranitidine is a member of the class of furans used to treat peptic ulcer disease (PUD) and gastroesophageal reflux disease. It has a role as an anti-ulcer drug, a H2-receptor antagonist, an environmental contaminant, a xenobiotic and a drug allergen. It is a member of furans, a tertiary amino compound, a C-nitro compound and an organic sulfide.
brand name
Zantac (GlaxoSmithKline).
General Description
Ranitidine, N-[2-[[[5-(dimethylamino)methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]thiol] ethyl]-N'-methyl-2-nitro-l,1-ethenediamine (Zantac), is a white solid, which inits hydrochloride salt form is highly soluble in water. It is anaminoalkyl furan derivative with pKa values of 2.7 (sidechain) and 8.2 (dimethylamino). Ranitidine is more potentthan cimetidine, but less potent than famotidine. Likeother H2-antagonists, it does not appear to bind to otherreceptors.
Bioavailability of an oral dose of ranitidine is about 50%and is not significantly affected by the presence of food.Some antacids may reduce ranitidine absorption and shouldnot be taken within 1 hour of administration of this drug. Theplasma half-life of the drug is 2 to 3 hours, and it is excretedalong with its metabolites in the urine. Three metabolites, ranitidineN-oxide, ranitidine S-oxide, and desmethyl ranitidine,have been identified. Ranitidine is only a weak inhibitor ofthe hepatic cytochrome isozymes, and recommended doses ofthe drug do not appear to inhibit the metabolism of otherdrugs. However, there have been isolated reports of drug interactions(warfarin, triazolam) that suggest that ranitidinemay affect the bioavailability of certain drugs by someunidentified mechanism, perhaps by pH-dependent effect onabsorption or a change in volume of distribution.
In addition to being available in various dosage forms asthe hydrochloride salt, ranitidine is also available as a bismuthcitrate salt for use with the macrolide antibiotic clarithromycinin treating patients with an active duodenalulcer associated with H. pylori infection. Eradication of H.pylori reduces the risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence.
Biological Activity
Potent, selective and competitive histamine H 2 receptor antagonist (pA 2 = 6.95-7.2). In vivo, inhibits gastric acid secretion induced by histamine, pentagastrin, bethanecol and food. Also inhibits aspirin-induced gastric lesions.
Contact allergens
Ranitidine, an H2-receptor antagonist, can cause contact dermatitis within the pharmaceutical industry and in health care workers, or may induce systemic drug reactions in patients.
Pharmacokinetics
Ranitidine decreases the secretion of gastric acid stimulated by food and drugs. It also reduces the secretion of gastric acid in hypersecretory conditions such as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Marked improvements in the appearance of the esophageal tissues have been observed by endoscopic imaging after ranitidine therapy.
Clinical Use
H2
antagonist:
Conditions associated with hyperacidity
Synthesis
Ranitidine, N[2-[[[5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]thio]ethyl]- N??-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethendiamine (16.2.8), is synthesized from furfuryl alcohol, which undergoes aminomethylation reaction using dimethylamine and paraform, which form 5- (dimethylaminomethyl)furfuryl alcohol (16.2.6). Further reaction with 2-mercaptoethylamine hydrochloride gives a product of substitution of the hydroxyl group in (16.2.6), 5-dimethylaminomethyl-2-(2??-aminoethyl)thiomethylfurane (16.2.7). Reacting this with Nmethyl- 1-methylthio-2-nitroethenaamine gives ranitidine (16.2.8).

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Alpha-blockers: effects of tolazoline antagonised.
Antifungals: absorption of itraconazole and
ketoconazole reduced; concentration of posaconazole
possibly reduced - avoid.
Antivirals: concentration of atazanavir reduced;
concentration of raltegravir possibly increased - avoid;
avoid for 12 hours before and 4 hours after rilpivirine.
Ciclosporin: may increase or not change ciclosporin
levels; nephrotoxicity, additive hepatotoxicity and
thrombocytopenia reported.
Cytotoxics: reduced gefitinib concentration; reduces
concentration of erlotinib and possibly pazopanib,
give at least 2 hours before or 10 hours after
ranitidine; absorption of dasatinib reduced - avoid;
possibly reduced absorption of lapatinib.
Ulipristal: contraceptive effect possibly reduced -
avoid with high dose ulipristal.
Metabolism
The major metabolite in the urine is N-oxide, which represents less than 4% of the dose. Other metabolites of ranitidine include S-oxide (1%) and desmethyl ranitidine (1%). The feces contain the remainder of the excreted ranitidine dose. Liver dysfunction has been shown to cause small, but clinically insignificant, changes in various ranitidine pharmacokinetic parameters.
Metabolism
Ranitidine is not extensively metabolised. A small
proportion of ranitidine is metabolised in the liver to
the N-oxide, the S-oxide, and desmethylranitidine; the
N-oxide is the major metabolite but accounts for only
about 4-6% of a dose.
The fraction of the dose recovered as metabolites is
similar after both oral and IV dosing; and includes 6%
of the dose in urine as the N-oxide, 2% as the S-oxide,
2% as desmethylranitidine and 1-2% as the furoic acid
analogue. There is also some excretion in the faeces.
Dosage forms
150 mg b.i.d.
Properties of Ranitidine
| Melting point: | 69-70°C |
| Boiling point: | 437.1±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.184±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Desiccate at +4°C |
| solubility | H2O: 1.8 mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | pKa 2.19±0.04 (Uncertain) |
| color | tan |
| Water Solubility | 24.7 mg/mL |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 66357-35-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ranitidine(66357-35-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,1-Ethenediamine, N-[2-[[[5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]thio]ethyl]-N'-methyl-2-nitro- (66357-35-5) |
Safety information for Ranitidine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P362:Take off contaminated clothing and wash before reuse. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Ranitidine
Ranitidine manufacturer
Molsyns Research
Alfa Omega Pharma
New Products
1-Amino-1-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid Cycloleucine 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 7-Bromo-1H-indazole ELECTROLYTIC IRON POWDER 2-Methyl-2-phenylpropyl acetate 1-Aminocyclobutanecarboxylic acid 1-(2-Ethoxyethyl)-2-(piperidin-4-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole hydrochloride Decanonitrile tert-butyl 4-(1H-benzo[d]iMidazol-2-yl)piperidine-1-carboxylate 4-Ethylbenzylamine Methyl 5-bromo-2-chloro-3-nitrobenzoate N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 2-Chloro-3-nitropyridine 5-Bromo-2,3-dimethoxypyridine methyl 6-chloro-2-(chloromethyl)nicotinate 2-methoxy-4-methyl-5-nitro pyridine 2-iodo-5-bromo pyridine 2-amino-4-methyl-5-nitro pyridine 5-Fluoro-2-Oxindole methyl L-alaninate hydrochloride diethyl L-glutamate hydrochloride Ethyl tosylcarbamateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
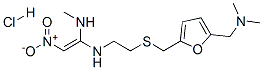
![2,2'-Methylene Bis[Ranitidine]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/207592-21-0.gif)
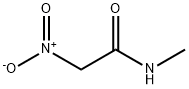

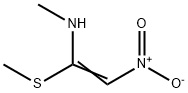
![RANITIDINE RELATED COMPOUND A 5-[[(2-AMINOETHYL)THIO]METHYL]-N,N-DIMETHYL-2-FURANMETHANAMINE HEMIFUMARATE USP(CRM STANDARD)](https://img.chemicalbook.in/)
![RANITIDINE IMPURITY AN,N'-BIS[2-[[[5-[(DIMETHYLAMINO)METHYL]FURAN-2-YL]METHYL]THIO]ETHYL]-2-NITROETHENE-1,1-DIAMINE EPR(CRM STANDARD)](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure22/GIF/CB0994743.gif)
You may like
-
 66357-35-5 Ranitidine 98%View Details
66357-35-5 Ranitidine 98%View Details
66357-35-5 -
 66357-35-5 99%View Details
66357-35-5 99%View Details
66357-35-5 -
 Ranitidine 66357-35-5 98%View Details
Ranitidine 66357-35-5 98%View Details
66357-35-5 -
 Ranitidine 98%View Details
Ranitidine 98%View Details
66357-35-5 -
 Ranitidine 66357-35-5 98%View Details
Ranitidine 66357-35-5 98%View Details
66357-35-5 -
 66357-35-5 Ranitidine 98%View Details
66357-35-5 Ranitidine 98%View Details
66357-35-5 -
 Ranitidine 96% CAS 66357-35-5View Details
Ranitidine 96% CAS 66357-35-5View Details
66357-35-5 -
 66357-35-5 Ranitidine Reference Standard 98%View Details
66357-35-5 Ranitidine Reference Standard 98%View Details
66357-35-5