Quintozine
Synonym(s):PCNB;Pentachloronitrobenzene;Quintozene
- CAS NO.:82-68-8
- Empirical Formula: C6Cl5NO2
- Molecular Weight: 295.33
- MDL number: MFCD00007065
- EINECS: 201-435-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
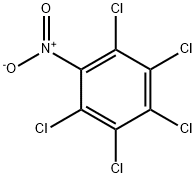
What is Quintozine?
Description
Pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB) is a pesticide and fungicide. Sensitization can occur in farmers and in those working in chemical plants.
Chemical properties
Light green powder
Chemical properties
Quinalphos is an off-white powder. It is stable and incompatible with strong bases and strong oxidizing agents. Quinalphos is uses as a fungicide and herbicide.
Chemical properties
Quintozene is a colorless to cream-colored crystalline material. Musty, mothball odor. Technical-grade PCNB contains an average of 97.8% PCNB, 1.8% hexa- chlorobenzene (HCB), 0.4% 2,3,4,5-tetrachloronitrobenzene (TCNB), and less than 0.1% pentachlorobenzene. Musty odor.
Chemical properties
Pentachloronitrobenzene forms colorless needles. Technical-grade PCNB contains an average of 97.8% PCNB, 1.8% hexachlorobenzene (HCB), 0.4% 2,3,4,5-tetrachloronitrobenzene (TCNB), and less than 0.1% pentachlorobenzene.
The Uses of Quintozine
Fungicide for seed and soil treatment.
The Uses of Quintozine
Quintozene is used against a range of diseases on vegetables, flower crops, cotton, bulbs, potatoes, wheat, rice, peanuts, pulse crops, maize, bananas and turf. It is used in the field and in glasshouses. It is usually applied to soil or as a seed treatment.
The Uses of Quintozine
Pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB) is used as a fungicide to suppress the growth of fungi in selective culture media such as Nash and Snyder medium (NS).
Definition
ChEBI: A C-nitro compound that is nitrobenzene in which every hydrogen has been replaced by a chlorine. A fungicide used on a variety of crops, including cotton, rice and seed grains, it is no longer approved for use within the European Union.
Production Methods
Quintozine is produced by nitration of pentachlorobenzene.
General Description
Crystalline pale yellow to white solid or powder with a musty moth ball odor. Insoluble in water and denser than water. Hence sinks in water.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Quintozine is hydrolyzed by alkalis. Is incompatible with strong oxidizing agnets. Also incompatible with strong bases. Corrosive to unlined metal containers .
Health Hazard
Exposures to quinalphos cause toxicity and adverse health effects. On contact with the skin, quinalphos causes the effects of sensitization.
Fire Hazard
On hazardous decomposition, quintozene releases phosgene, hydrogen chloride, oxides of nitrogen, and chlorine-containing compounds, and other unknown materials may be released in a fire situation. Incomplete combustion may lead to the formation of oxides of carbon.
Agricultural Uses
Soil fungicide, Nematicide, Seed treatment: Quintozene, the common name for PCNB or pentachlkoronitrobenzene, is an organochlorine fungicide used as a seed dressing or soil treatment to control a wide range of fungi species in such crops as potatoes, wheat, onions, lettuce, tomatoes, tulips, garlic, and others. Depending on the producer and the manufacturing procedure, PCNB impurities can include hexachlorobenzene, pentachlorobenzene, and tetrachloronitrobenzene. The fungicide is often used in combination with insecticides and fungicides including carbaryl, imazalil, tridimenol, etridiazole, and fuberidazole. It is available as a dustable or wettable powder, in granular form, emulsifiable concentrate, and seed treatment. Not approved for use in EU countries. Registered for use in the U.S. and Canada. There are more than 35 global suppliers.
Trade name
(EPA lists 290 active and canceled or transferred products) AVICOL (PESTICIDE)®; BOTRILEX®; BLOCKER 4F®; BOTRILEX®; BRASSICOL®; BRASSICOL EARTHCIDE®; BRASSICOL 75®; BRASSICOL SUPER®; CHINOZAN®; EARTHCIDE®; FARTOX®; FOLOSAN®; FOMAC 2®; FUNGICHLOR®; GC 3944-3-4®; KOBU®; KOBUTOL®; KODIAK A-T FUNGICIDE®; KP 2®; MARISAN FORTE®; MEFENOXAM®; PARFLO®; PENTAGEN®; PHOMASAN®; PKhNB®; RTU 1010®; SANICLOR 30®; TERRACHLOR®; TERRACLOR®; TERRACLOR 30G®; TERRA-COAT®; TERRAFUN®; TERRAZAN®; TILCAREX®; TRIPCNB®; TRIQUINTAM®; TRITISAN®; TUBERGRAN®; TURFCIDE®; VITAVAX® Quintozene
Contact allergens
Pentachloronitrobenzene is a pesticide and a fungicide. Sensitization can occur in farmers or in chemical plants.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. An experimental teratogen. Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic data. Mutation data reported. Used as a fungcide. Dangerous; when heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of NO, and Cl-. See also NITRO COMPOUNDS OF AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS
Potential Exposure
Those engaged in manufacture, formulation and application of this soil fungicide and seed treatment chemical. Peracetic acid is often used as a sterilizing agent in the medical, food service and pharmaceutical industries in combination hydrogen peroxide and acetic acid.
Environmental Fate
Biological. Pentachloronitrobenzene is rapidly degraded in flooded soils forming pentachloroaniline. When pentachloronitrobenzene was incubated in a submerged soil and
moist soil for 3 weeks, the percentages of the applied dosage remaining were <1 and 82%,
respectively. Chacko et al. (1966) reported microorganisms can convert pentachloronitrobenzene to pentachloroaniline and pentachlorothioanisole
Soil. The half-lives of pentachloronitrobenzene in a Columbia fine sandy loam, Sacramento clay and Staten peaty muck from California were 4.7, 7.6 and 9.7 months,
respectively. Degradation products were pentachloroaniline and pentachlorothioanis
When heated to decomposition (330°C), emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides and
chlorine (Sax and Lewis, 1987)
Metabolic pathway
Renner (1981) has reviewed the metabolism of quintozene. Fate in soil, plants, several animal species and fish has been reported. The nitro group provides a reactive centre, which allows rapid metabolism via three primary routes: nitro reduction, glutathione-dependent denitration and dechlorination. Thus a very complex array of metabolites is formed. Quintozene is relatively persistent in soil in comparison with plants and animals. It was one of the compounds which stimulated the study and understanding of the catabolism of glutathione conjugates in plants and animals and this was properly elucidated for the first time using such compounds. Nitro reduction and nitro displacement is quite rapid and therefore quintozene is much less persistent than is hexachlorobenzene. The latter shares one of the primary metabolites [ S-(pentachlorophenyl)glutathione] with quintozene and many of the sulfur-containing metabolites are common to both compounds.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required. UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from EtOH. [Beilstein 5 H 247, 5 II 188, 5 III 618.]
Degradation
Quintozene is a stable compound. It is stable in acidic media but is hydrolysed in base (PM). The nitro group is liable to displacement by thiolysis.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explo- sions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Thermal decomposition products may include nitrogen oxides and hydrogen chlo- ride. Corrosive to unlined metal containers .
Waste Disposal
Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant or consult with envi- ronmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste contain- ing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform to EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal.
Properties of Quintozine
| Melting point: | 140-143 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 328°C |
| Density | 1.718 |
| vapor pressure | 1.27 x l0-2Pa (25 °C) |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| solubility | toluene: soluble50mg/mL, clear, faintly to slightly yellow |
| form | powder |
| color | yellow to tan |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble |
| Merck | 8080 |
| BRN | 1914324 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong bases, strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 82-68-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 5, Sup 7) 1987 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzene, pentachloronitro-(82-68-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Pentachloronitrobenzene (82-68-8) |
Safety information for Quintozine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Quintozine
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Pentachloronitrobenzene 95% CAS 82-68-8View Details
Pentachloronitrobenzene 95% CAS 82-68-8View Details
82-68-8 -
 Quintozene CAS 82-68-8View Details
Quintozene CAS 82-68-8View Details
82-68-8 -
 Pentachloronitrobenzene CAS 82-68-8View Details
Pentachloronitrobenzene CAS 82-68-8View Details
82-68-8 -
 Pentachloronitrobenzene solution CAS 82-68-8View Details
Pentachloronitrobenzene solution CAS 82-68-8View Details
82-68-8 -
 Quintozene CAS 82-68-8View Details
Quintozene CAS 82-68-8View Details
82-68-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1