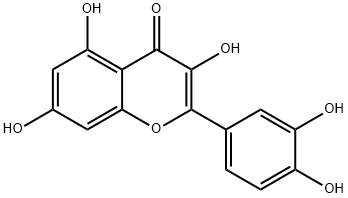
Quercetin
Synonym(s):Quercetin dihydrate;Quercetin hydrate;2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one;3,3′,4′,5,6-Pentahydroxyflavone;3,3′,4′,5,7-Pentahydroxyflavone dihydrate
- CAS NO.:117-39-5
- Empirical Formula: C15H10O7
- Molecular Weight: 302.24
- MDL number: MFCD00006828
- EINECS: 204-187-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-25 11:31:46
What is Quercetin?
Description
The name of quercetin has been used since 1857, which is derived from quercetum
(oak forest) after Quercus. Quercetin is widely found in flowers, leaves, and
fruits of various plants. Vegetables (such as onions, ginger, celery, etc.), fruits (such
as apples, strawberries, etc.), beverages (such as tea, coffee, red wine, fruit juice,
etc.), and more than 100 kinds of Chinese herbal medicines (such as Threevein
Aster, mountain white chrysanthemum, Huai rice, Apocynum, Ginkgo biloba, etc.)
contain this ingredient.
Threevein Aster is a Chinese herbal medicine and used in Jiangxi province,
China, for more than 30 years. Its plant name is three veins Mala, Compositae. It is
rich in drug sources, which can be found in Southern provinces of China. Clinical
practice proved that it has significant anti-inflammatory and expectorant effects, and
it is a good prescription for the treatment of elderly chronic bronchitis.
Description
Quercetin is a flavonoid that occurs in many plant parts including rinds, barks, clover blossoms, and ragweed pollen. Capers are an especially rich source of quercetin. In 1962, S. Rangaswami and co-workers isolated it from?Rhododendron cinnabarinum, a shrub that grows at high altitudes in Southeast Asia.
Quercetin’s bioavailability is poor, but its glycosides are readily absorbed by the body. It has been used to treat conditions ranging from eczema and inflammation to cancer and asthma. No clinical trials, however, have convincingly demonstrated its value; and it has not been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for any use.
Chemical properties
Yellow to green yellow crystalline powde
Physical properties
Appearance: yellow needle-like crystalline powder. Solubility: slightly soluble in water; soluble in ethanol, acetone, pyridine, and acetic acid; easily soluble in ether and methanol. Melting point: 314–317 °C.
History
In 1936, Szent-Gyorgyi firstly reported the separation and identification of biological
activity of quercetin. Usually quercetin is presented in the form of glycosides
such as lutin, quercitrin, and mycoside, which can be hydrolyzed to get the quercetin.
Quercetin has a polyphenol hydroxyl structure, which is of weak lipophilicity and poor hydrophilicity, resulting in its low bioavailability and limiting its clinical application. The synthesis of phenolic derivatives improves its bioavailability,
which are lipid-soluble quercetin derivatives such as 3-O-methylquercetin, hydrophilic
quercetin derivatives such as 3′-ON-carboxymethylformamide quercetin, and quercetin glycosides.
Threevein Aster, having quercetin as one of the main active ingredients, has been used for the domestic clinical treatment for chronic bronchitis in China since 1971.
The Uses of Quercetin
- Quercetin has been used as an antioxidant which reversed the immunosuppressive effects of high glucose and hyperglycemic sera in type 2 diabetic patients.
- It has been used as a detoxifying phytochemical in Apis mellifera.
- It has been used as a positive control in DPPH (2,2- diphenyl-1-picryhydrazyl) radical scavenging assay. It has also been used for the preparation of calibration curve to determine total flavonoid content.
The Uses of Quercetin
Medicine, reported formation of epoxy resins on mixing with epichlorohydrin.
What are the applications of Application
Quercetin is a PI 3-kinase inhibitor, GPR30 activator, and apoptosis inducer
Indications
It is mainly used for the treatment of chronic bronchitis.
Definition
ChEBI: Quercetin is a pentahydroxyflavone having the five hydroxy groups placed at the 3-, 3'-, 4'-, 5- and 7-positions. It is one of the most abundant flavonoids in edible vegetables, fruit and wine. It has a role as an antibacterial agent, an antioxidant, a protein kinase inhibitor, an antineoplastic agent, an EC 1.10.99.2 [ribosyldihydronicotinamide dehydrogenase (quinone)] inhibitor, a plant metabolite, a phytoestrogen, a radical scavenger, a chelator, an Aurora kinase inhibitor and a geroprotector. It is a pentahydroxyflavone and a 7-hydroxyflavonol. It is a conjugate acid of a quercetin-7-olate.
General Description
Yellow needles or yellow powder. Converts to anhydrous form at 203-207°F. Alcoholic solutions taste very bitter.
Air & Water Reactions
Sensitive to exposure to air and light. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
3,3',4',5,7-Pentahydroxyflavone is a strong antioxidant and a metal chelator. Promotes the formation of nitrosamines .
Hazard
Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: When heated to decomposition 3,3',4',5,7-Pentahydroxyflavone emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for 3,3',4',5,7-Pentahydroxyflavone are not available; however, 3,3',4',5,7-Pentahydroxyflavone is probably combustible.
Biological Activity
Anti-tumor agent; induces apoptosis and inhibits synthesis of heat shock proteins. Inhibits many enzyme systems including tyrosine protein kinase, phospholipase A 2 , phosphodiesterases, mitochondrial ATPase, PI 3-kinase and protein kinase C. Can also activate Ca 2+ and K + channels and behaves as an agonist at estrogen (GPR30) receptors.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Quercetin is a flavonoid with anticancer activity. Quercetin is a mitochondrial ATPase and phosphodiesterase inhibitor. It Inhibits PI3-kinase activity and slightly inhibits PIP kinase activity. Quercetin has antiproliferative effects on cancer cell lines, reduces cancer cell growth via type II estrogen receptors, and arrests human leukemic T cells in late G1 phase of the cell cycle. Quercetin may also inhibit fatty acid synthase activity.
Pharmacology
Experimental studies showed that quercetin had antitumor, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidation, hypoglycemic, anti-obesity, antidepressant, and other effects. In vitro cell experiments and in vivo animal experiments have shown that quercetin could
inhibit the growth of various malignant tumor cells such as human ovarian cancer,
breast cancer, gastrointestinal tumor cells, and leukemia, and it could induce cancer
cell apoptosis and had a reversal of tumor multidrug resistance (MDR) effect, while,
combined with other anticancer drugs, it could enhance the effect of anticancer
drugs.
Quercetin could alleviate the inflammatory response that was aggravated by the activation of the central granulocytes. In the experimental study on the treatment of non-bacterial prostatitis and acute gouty arthritis, quercetin also showed a good
anti-inflammatory effect.
The experimental results showed that quercetin had a good direct scavenging effect on free radicals and exhibited antioxidant activity. In addition, it also had the anti-hepatic fibrosis, pulmonary fibrosis, keloid hyperplasia and glaucoma filtering bubble scarring and other effects, its mechanism involving the inhibition of fibroblast proliferation, inhibition of collagen synthesis, preventing oxidative damage and so on. Moreover, studies have shown that quercetin also had antibacterial, antiaging, antidepressant, antileukemia, antidiabetic, and other pharmacological effects.
Clinical Use
Since the first clinical phase I trial of quercetin in 1996 found that it had antitumor
activity, quercetin has also been reported in early clinical trials of cardiovascular
disease, diabetes, and other diseases. However, there is still insufficient evidence shown that quercetin has a significant effect on the treatment of the disease in clinic.The US FDA has issued a warning, emphasizing that quercetin is not a definite
nutrient, unable to determine its content in the diet, nor can it be used as a drug.
China’s Threevein Aster consists of a single Chinese herb, which was released by
the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (1977) Part I. One of the main active ingredients obtained following the hydrolysis of Threevein Aster is quercetin, which has the function of relieving cough and eliminating phlegm and can be used for the treatment of chronic bronchitis. The anti-inflammatory effect of Threevein Aster is poor. Side effects after use include stomach discomfort, dizziness, and abdominal pain, while withdrawal can make them disappear.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, and intravenous routes. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplastigenic, and tumorigenic data. Human mutation data reported. Used as a pharmaceutical and veterinary drug. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes
in vivo
studies showed that administration of quercetin before the initiation stage of carcinogenesis dramatically reduced various chemical agents induced tumor burden in mice models, including benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung tumor burden, azoxymethane-induced preneoplastic lesions in rat colon and n-nitrosodiethylamine-induced hepatocarcinoma etc. [5].
Storage
Room temperature
References
quercetin and cancer chemoprevention. evid based complement alternat med. 2011;2011:591356. doi: 10.1093/ecam/neq053. epub 2011 apr 14.food-derived polyphenols inhibit pancreatic cancer growth through mitochondrial cytochrome c release and apoptosis. int j cancer. 2002 apr 10;98(5):761-9.stabilization of p53 is involved in quercetin-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in hepg2 cells. bioscience, biotechnology and biochemistry. 2008;72(3):797–804.survivin and p53 modulate quercetin-induced cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in human lung carcinoma cells. the journal of biological chemistry. 2004the effects of quercetin on antioxidant status and tumor markers in the lung and serum of mice treated with benzo(a)pyrene. biological and pharmaceutical bulletin. 2007
Properties of Quercetin
| Melting point: | 316.5 °C |
| Boiling point: | 363.28°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3616 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4790 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥15.1 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥3.28 mg/mL in EtOH |
| form | solid |
| pka | 6.31±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | Yellowish |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 21 ºC |
| Merck | 13,8122 |
| BRN | 317313 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 117-39-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. Sup 7, 73) 1999 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Quercetin (117-39-5) |
Safety information for Quercetin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Quercetin
| InChIKey | REFJWTPEDVJJIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Quercetin manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Quercetin 95% (HPLC) CAS 117-39-5View Details
Quercetin 95% (HPLC) CAS 117-39-5View Details
117-39-5 -
 Quercetin 97% CAS 117-39-5View Details
Quercetin 97% CAS 117-39-5View Details
117-39-5 -
 Quercetin CAS 117-39-5View Details
Quercetin CAS 117-39-5View Details
117-39-5 -
 Quercetin 95 Powder, 1 kg, Packaging Type: DRUMView Details
Quercetin 95 Powder, 1 kg, Packaging Type: DRUMView Details
117-39-5 -
 Quercetin 117-39-5 QuercetinView Details
Quercetin 117-39-5 QuercetinView Details
117-39-5 -
 Quercetin Powder 98, 25 KGSView Details
Quercetin Powder 98, 25 KGSView Details
117-39-5 -
 Quercetin 250 Mg, 6*10 CapsulesView Details
Quercetin 250 Mg, 6*10 CapsulesView Details
117-39-5 -
 Quercetin 250 mg, Packaging Type: BottleView Details
Quercetin 250 mg, Packaging Type: BottleView Details
117-39-5
