POLYOXIN D
- CAS NO.:22976-86-9
- Empirical Formula: C17H23N5O14
- Molecular Weight: 521.39
- MDL number: MFCD00166352
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2022-12-21 16:56:50
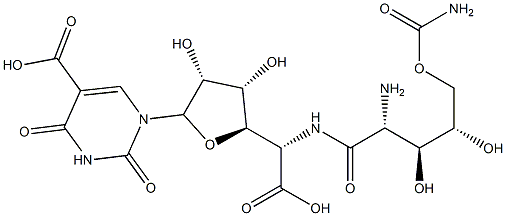
What is POLYOXIN D?
The Uses of POLYOXIN D
Polyoxin D,?Streptomyces cacaoi var. asoensis is a specific inhibitor of fungal chitin synthetase.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of polyoxins that is isolated from the soil organism Streptomyces cacaoi var. asoensis. Polyoxorim exhibits fungicidal properties and may be used on rice, industrial grounds, golf courses and parks.
Enzyme inhibitor
This pyrimidin nucleoside analogue and antifungal antibiotic (FWfree-acid = 521.39 g/mol; CAS 22976-86-9; 33401-46-6 for the zinc salt), produced by soil organisms Streptomyces cacaoi and S. piomogenus, inhibits chitin biosynthesis, Ki = 6 μM, thereby blocking septum formation. The zinc salt of polyyoxin is used to control Rice Sheath Blight, caused by the fungus Rhizoctonia solani, as well as the turfgrass disease Brown Patch, caused by other Rhizoctonia species. Polyoxin D also inhibits Neurospora crassa, but is nontoxic to land mammals, insects, or birds, when applied to plants as the wettable powder form known as Endorse?. Target(s): chitin synthase (1- 24); chitin synthase B; chitin synthase, canChs1A; WdChs4p, a chitin synthase 3 homologue.
Properties of POLYOXIN D
| Melting point: | 173-175 °C (decomp) |
| Density | 1.864±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 2.67±0.10(Predicted) |
Safety information for POLYOXIN D
Computed Descriptors for POLYOXIN D
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8