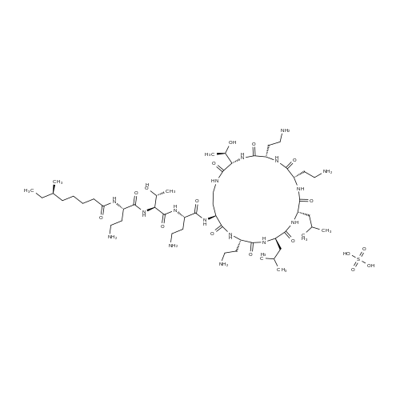
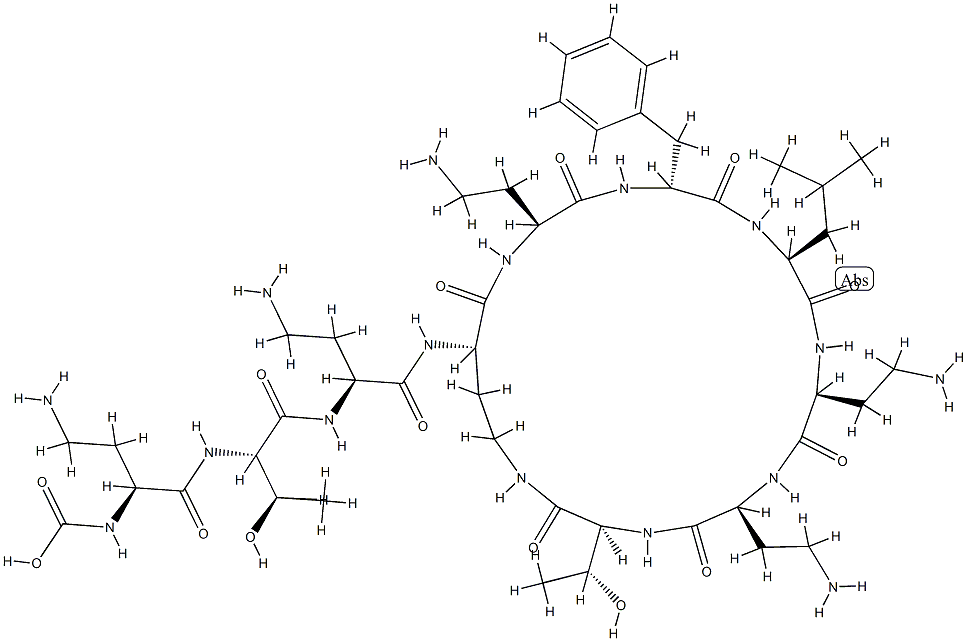
Polymyxin B sulfate
Synonym(s):Polymyxin B sulfate;Polymixin B;Bacillus Cereus;Polymixin;Aerosporin
- CAS NO.:1405-20-5
- Empirical Formula: C56H100N16O17S
- Molecular Weight: 1301.56
- MDL number: MFCD30489731
- EINECS: 215-774-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31

What is Polymyxin B sulfate?
Description
The polymyxins are cationic peptides originally isolated from B. polymyxa. They bind and kill Gram-
Chemical properties
White Solid
The Uses of Polymyxin B sulfate
Polymyxin B sulfate is used as topical antibiotic agent, often used in combination with neomycin; products include ointments, creams, eye, and ear drops.
The Uses of Polymyxin B sulfate
antibacterial
The Uses of Polymyxin B sulfate
Antibiotic with bactericidal action on E. coli. Binds to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Induces pore formation in the membranes of cortex cells from excised sorghum roots. Mixtu re of Polymyxin B1 and B2 sulfate. Biological potency (dry basis): >6000U/mg.
What are the applications of Application
Polymyxin B Sulfate is an antibiotic mixture active against Gram (?) organisms
Indications
Polymyxin B is one of a group of cyclic polypeptides elaborated by Bacillus polymyxa. The drug is a surface-active agent. It is thought to alter the lipoprotein membrane of bacteria so that it no longer functions as an effective barrier, thereby allowing the cell contents to escape. Polymyxin B is effective against Pseudomonas, E. coli, and other gram-negative bacteria except the Proteus and Serratia species. It has little effect on gram-positive organisms.
brand name
(GlaxoSmithKline); Poly-Rx (X Gen).
General Description
Polymyxin (Aerosporin) was discovered in 1947 almost simultaneouslyin three separate laboratories in the UnitedStates and Great Britain. As often happens whensimilar discoveries are made in widely separated laboratories,differences in nomenclature, referring to both theantibiotic-producing organism and the antibiotic itself, appearedin references to the polymyxins. Because the organismsfirst designated as Bacillus polymyxa and B.aerosporus Greer were found to be identical species, thename B. polymyxa is used to refer to all of the strains thatproduce the closely related polypeptides called polymyxins.Other organisms (e.g., see “Colistin” later) also producepolymyxins. Identified so far are polymyxins A, B1,B2, C, D1, D2, M, colistin A (polymyxin E1), colistin B(polymyxin E2), circulins A and B, and polypeptin. Theknown structures of this group and their properties havebeen reviewed by Vogler and Studer. Of these,polymyxin B as the sulfate usually is used in medicine because,when used systemically, it causes less kidney damagethan the others. Polymyxin B sulfate is a nearly odorless, white to buff powder. It is freely soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Polymyxin B?is one of the most important antibiotics used to treat gram-negative bacterial infections, including infections caused by carbapenem-resistant non-fermenters and carbapenem-resistant?Enterobacteriaceae.
Clinical Use
Polymyxin B is produced by fermentation of Bacillus polymyxa. It is separated from a mixture of related cyclic peptides and is primarily active against Gram-negative microorganisms. It apparently binds to phosphate groups in bacterial cytoplasmic membranes and disrupts their integrity. It is used IM or IV as a sulfate salt to treat serious urinary tract infections, meningitis, and septicemia, primarily caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, but some other Gram-negative bacteria also will respond. Irrigation of the urinary bladder with solutions of polymyxin B sulfate is employed as well by some to reduce the incidence of infections subsequent to installation of indwelling catheters. Additionally, it is used ophthalmically to treat infections by P. aeruginosa. When given parenterally, the drug is neuro- and nephrotoxic and, therefore, is employed only after other drugs have failed.
in vitro
polymyxin b elicited up-regulation of dendritic cells (dcs) maturation markers, including the increase in the in the expression of co-stimulatory molecule cd86 and hla-class i and ii molecules. polymyxin b induced a progressive increase in the adhesion property of human dcs. in addition, polymyxin b triggered the activation of the erk1/2 pathway and iκb-α/nf-κb pathways [1].
in vivo
male bacteraemia ddy mice were subcutaneously treated with polymyxin b at a dose of 5, 10, 15 or 20 mg/kg for 7 days. polymyxin b, in a dose-dependent fashion, improved the survival both of ou-01062- and ou-98039-infected mice. in polymyxin b-treated mice, except for 5 mg/kg polymyxin b, the viable cell counts had a tendency to reduce steadily in each concentration group. it was showed a rapid and marked decline of bacterial cell count between 3 to 6 h after infection [2].
Storage
Room temperature
References
[1]. valentinis, b., bianchi, a., zhou, d., cipponi, a., catalanotti, f., russo, v., & traversari, c. direct effects of polymyxin b on human dendritic cells maturation: the role of i b- /nf- b and erk1/2 pathways and adhesion. journal of biological chemistry. 2005; 280(14): 14264-14271.
[2]. miyajima, y., hiramatsu, k., mizukami, e., morinaga, r., ishii, h., & shirai, r. et al. in vitro and in vivo potency of polymyxin b against imp-type metallo-β-lactamase-producing pseudomonas aeruginosa. international journal of antimicrobial agents. 2008; 32(5): 437-440.
Properties of Polymyxin B sulfate
| Melting point: | 217-220°C (dec.) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | pKa 8.9 (Uncertain) |
| color | colorless or slightly yellow |
| PH | pH (10g/L, 25℃) : 4.5~7.0 |
| optical activity | [α]/D 20/D (Rotation: -2.3 +/- 0.2 degrees) |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water at 50mg/ml/n |
| Merck | 14,7573 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1405-20-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Polymixin B sulfate (1405-20-5) |
Safety information for Polymyxin B sulfate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Polymyxin B sulfate
| InChIKey | HFMDLUQUEXNBOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Polymyxin B sulfate manufacturer
Sumar biotech LLP
Kavya Pharma
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Polymyxin B Sulphate 99%View Details
Polymyxin B Sulphate 99%View Details -
 Polymyxin B Sulphate (Aerosporin CAS 1405-20-5View Details
Polymyxin B Sulphate (Aerosporin CAS 1405-20-5View Details
1405-20-5 -
 Polymyxin B sulphate CAS 1405-20-5View Details
Polymyxin B sulphate CAS 1405-20-5View Details
1405-20-5 -
 Polymyxin B Sulphate (Aerosporin CAS 1405-20-5View Details
Polymyxin B Sulphate (Aerosporin CAS 1405-20-5View Details
1405-20-5 -
 Polymyxin B Sulfate CAS 1405-20-5View Details
Polymyxin B Sulfate CAS 1405-20-5View Details
1405-20-5 -
 Polymixin B sulphate 97% CAS 1405-20-5View Details
Polymixin B sulphate 97% CAS 1405-20-5View Details
1405-20-5 -
 polymixin b sulphate IP, For Pharma Raw MaterialView Details
polymixin b sulphate IP, For Pharma Raw MaterialView Details
1405-20-5 -
 Polymyxin B Sulfate, For Im/Iv, Grade: A GradeView Details
Polymyxin B Sulfate, For Im/Iv, Grade: A GradeView Details
1405-20-5
