POLY(2,6-DIMETHYL-1,4-PHENYLENE OXIDE)
Synonym(s):2,6-Dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether homopolymer;2,6-Dimethylphenol homopolymer;2,6-Dimethylphenol polymer;Poly(2,6-dimethylphenylene oxide);Poly(2,6-xylenol)
- CAS NO.:25134-01-4
- Empirical Formula: C8H10O
- Molecular Weight: 122.1644
- MDL number: MFCD00084368
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
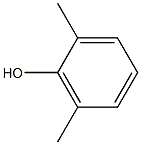
What is POLY(2,6-DIMETHYL-1,4-PHENYLENE OXIDE)?
Chemical properties
white to off-white powder
Chemical properties
Poly(2,6-dimethyl-l,4-phenylene oxide) is characterized by high tensile
strength, stiffness, impact strength and creep resistance; it also has good
dielectric properties. These properties are maintained over a broad temperature
range (about -45-120°C). The polymer is self-extinguishing. The polymer
has a high glass-transition temperature (Tg = 208°C) which restricts
crystallization in normal moulding techniques. Crystalline material may be
obtained by heating the amorphous material or from solutions. One notable
feature of the polymer is its good dimensional stability; it has a very low
coefficient of thermal expansion and low water absorption.
Poly(2,6-dimethyl-l,4-phenylene oxide) is soluble in aromatic hydrocarbons
and chlorinated solvents and several aliphatic hydrocarbons cause
environmental stress cracking. The polymer is outstandingly resistant to
most aqueous reagents, being unaffected by acids, alkalis and detergents.
The Uses of POLY(2,6-DIMETHYL-1,4-PHENYLENE OXIDE)
Imidazolium modified PPO with liquid ionic graphene oxide can be used as an anion exchange membrane (AEM) composite with a peak power density of 136 mW cm?2 for use in the fabrication of high performance fuel cells. It may also be sulfonated to form a long chained polymeric structure with an efficiency of 81.8% at a current density of 120 mA cm?2 for potentiall use in vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs) as effective energy storage systems. It may also be used in the formation of AEMs, which can be used in the development of microbial desalination cell system (MDCS).
The Uses of POLY(2,6-DIMETHYL-1,4-PHENYLENE OXIDE)
At the present time, most poly(2,6-dimethyl-l,4-phenylene oxide) intended for commercial use is blended with polystyrene (principally in the form of high-impact polystyrene). The two materials are miscible over the complete composition range. The effect of blending is to facilitate melt-processing (by lowering melt viscosity) and to lower cost whilst the desirable properties of the straight polymer are largely retained. In one recent product, the polystyrene is grafted on to the polyether. Polystyrene-modified poly(2,6- dimethyl-l,4-phenylene oxide) (commonly referred to as PPO) has found a variety of uses, which include telecommunication and business equipment housings and components and automotive parts.
Preparation
Oxidative coupling is readily accomplished by passing oxygen into a reaction
mixture containing 2,6-xylenol, pyridine and cuprous chloride. (The molar
ratio of pyridine to cuprous ion is generally in the range 10: 1 to 100: 1.)
External heating is unnecessary; during the course of the reaction the
temperature rises to about 70??C. The polymer is precipitated with dilute
hydrochloric acid and collected by filtration.
It is generally accepted that aryloxy radicals are intermediates in the
polymerization reaction since ESR studies have shown the presence of both
monomeric and polymeric aryloxy radicals in polymerizing solutions of 2,6-
xylenol. The simplest mechanism that can be suggested for the reaction is
aromatic substitution:

Definition
ChEBI: 2,6-Dimethylphenol is a hydroxytoluene.
General Description
Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) (PPO) is an anion exchange membrane (AEM) material that is mainly used as a cross-linker in which the methyl groups are used to bond with ultraviolet (UV) excited ketones.
Properties of POLY(2,6-DIMETHYL-1,4-PHENYLENE OXIDE)
| Melting point: | 258-261 °C |
| Density | 1.06 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| form | powder |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phenol, 2,6-dimethyl-, homopolymer (25134-01-4) |
Safety information for POLY(2,6-DIMETHYL-1,4-PHENYLENE OXIDE)
Computed Descriptors for POLY(2,6-DIMETHYL-1,4-PHENYLENE OXIDE)
Related products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) pellets CAS 25134-01-4View Details
Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) pellets CAS 25134-01-4View Details
25134-01-4 -
 Poly(p-phenylene oxide) CAS 25134-01-4View Details
Poly(p-phenylene oxide) CAS 25134-01-4View Details
25134-01-4 -
 Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) powder CAS 25134-01-4View Details
Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) powder CAS 25134-01-4View Details
25134-01-4 -
 Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) CAS 25134-01-4View Details
Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) CAS 25134-01-4View Details
25134-01-4 -
 Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) CAS 25134-01-4View Details
Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) CAS 25134-01-4View Details
25134-01-4 -
 25134-01-4 Polyphenylene oxide 98%View Details
25134-01-4 Polyphenylene oxide 98%View Details
25134-01-4 -
 Pyrrolidine 99.00%View Details
Pyrrolidine 99.00%View Details
123-75-1 -
 12029-98-0 99.00%View Details
12029-98-0 99.00%View Details
12029-98-0