Pivalic acid
Synonym(s):2,2-Dimethylpropionic acid;Neopentanoic acid, 2,2-Dimethylpropionic acid, Trimethylacetic acid;Pivalic acid;Trimethylacetic acid
- CAS NO.:75-98-9
- Empirical Formula: C5H10O2
- Molecular Weight: 102.13
- MDL number: MFCD00004194
- EINECS: 200-922-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-26 17:40:57
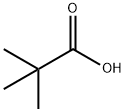
What is Pivalic acid ?
Chemical properties
white crystalline low melting mass
The Uses of Pivalic acid
Pivalic Acid is a metabolite of oral cephem (β-lactam) antibiotics such as S-1108, containing pivaloyl moieties.
The Uses of Pivalic acid
Pivalic acid can be employed:
- As a co-catalyst with palladium for the arylation of unactivated arenes and N-heterocycles.
- As an additive to facilitate the carbonylative suzuki reactions to synthesize biaryl ketones from aryl iodides and arylboronic acids by using palladium nanoparticles as catalyst.
- In the cyclization reaction of benzamides with alkynes to synthesize isoquinolones in the presence of 8-aminoquinoline ligand and cobalt catalyst.
The Uses of Pivalic acid
Valuable building block offered as a solution in dichloromethane for more convenient handling.
Definition
ChEBI: Pivalic acid is a branched, short-chain fatty acid composed of propanoic acid having two methyl substituents at the 2-position. It is a branched-chain saturated fatty acid, a methyl-branched fatty acid and a short-chain fatty acid. It is a conjugate acid of a pivalate.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 98, p. 1275, 1976 DOI: 10.1021/ja00421a046
Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 1, p. 524, 1941
General Description
Pivalic acid is a colored crystalline solid of low toxicity that is soluble in water, ethyl alcohol and diethyl ether.
Air & Water Reactions
With mixing, water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Pivalic acid is a carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acids donate hydrogen ions if a base is present to accept them. They react in this way with all bases, both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic. Their reactions with bases, called "neutralizations", are accompanied by the evolution of substantial amounts of heat. Neutralization between an acid and a base produces water plus a salt. Carboxylic acids with six or fewer carbon atoms are freely or moderately soluble in water; those with more than six carbons are slightly soluble in water. Soluble carboxylic acid dissociate to an extent in water to yield hydrogen ions. The pH of solutions of carboxylic acids is therefore less than 7.0. Many insoluble carboxylic acids react rapidly with aqueous solutions containing a chemical base and dissolve as the neutralization generates a soluble salt. Carboxylic acids in aqueous solution and liquid or molten carboxylic acids can react with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Such reactions occur in principle for solid carboxylic acids as well, but are slow if the solid acid remains dry. Even "insoluble" carboxylic acids may absorb enough water from the air and dissolve sufficiently in Pivalic acid to corrode or dissolve iron, steel, and aluminum parts and containers. Carboxylic acids, like other acids, react with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. The reaction is slower for dry, solid carboxylic acids. Insoluble carboxylic acids react with solutions of cyanides to cause the release of gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat are generated by the reaction of carboxylic acids with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Carboxylic acids, especially in aqueous solution, also react with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Their reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates generates a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still heat. Like other organic compounds, carboxylic acids can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents. These reactions generate heat. A wide variety of products is possible. Like other acids, carboxylic acids may initiate polymerization reactions; like other acids, they often catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions.
Health Hazard
CALL FOR MEDICAL AID. SOLID: Irritating to eyes and skin. Harmful if swallowed. IF IN EYES OR ON SKIN, flush with running water for at least 15 minutes; hold eyelids open if necessary. Wash skin with soap and water. Remove and isolate contaminated clothing and shoes at the site. If SWALLOWED and victim is UNCONSCIOUS OR HAVING CONVULSIONS, do nothing except keep victim warm. Because of low volatility, it is relatively harmless when inhaled at normal ambient temperature (around 20°C). It is slightly toxic by ingestion or skin absorption. The vapor is irritating at elevated temperatures. Can cause considerable discomfort by oral routes; may cause reversible or irreversible changes to exposed tissue, not permanent injury or death.
Fire Hazard
COMBUSTIBLE. Produces vapors irritating to eyes and skin. Decomposes to produce acrid smoke and fumes.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion and skin contact. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Purification Methods
Fractionally distil the acid under reduced pressure, then fractionally crystallise it from its melt. Recrystallise it from *benzene. [Beilstein 2 IV 908.]
Properties of Pivalic acid
| Melting point: | 32-35 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 163-164 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.889 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.6 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 9.75 mm Hg ( 60 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.393 |
| Flash point: | 147 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 25g/l |
| form | Powder, Crystals and/or Chunks |
| pka | 5.03(at 25℃) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.121 |
| color | Yellow to orange to tan |
| PH | 4.04(1 mM solution);3.52(10 mM solution);3.02(100 mM solution) |
| explosive limit | 1.6%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 25 g/L (20 ºC) |
| FreezingPoint | 32.0 to 36.0 ℃ |
| Merck | 14,7511 |
| BRN | 969480 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75-98-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Pivalic acid(75-98-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Pivalic acid (75-98-9) |
Safety information for Pivalic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Pivalic acid
| InChIKey | IUGYQRQAERSCNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Pivalic acid manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Pivalic acid 98%View Details
Pivalic acid 98%View Details
75-98-9 -
 Pivalic Acid CAS 75-98-9View Details
Pivalic Acid CAS 75-98-9View Details
75-98-9 -
 Pivalic acid CAS 75-98-9View Details
Pivalic acid CAS 75-98-9View Details
75-98-9 -
 Pivalic acid 99% CAS 75-98-9View Details
Pivalic acid 99% CAS 75-98-9View Details
75-98-9 -
 Pivalic acid CAS 75-98-9View Details
Pivalic acid CAS 75-98-9View Details
75-98-9 -
 TRIMETHYLACETIC ACID CAS No. 75-98-9View Details
TRIMETHYLACETIC ACID CAS No. 75-98-9View Details
75-98-9 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
