Piperazine
Synonym(s):Piperazine anhydrous;Diethylenediamine;1,4-Diazacyclohexane;Anti-4.1B;Anti-C17orf36
- CAS NO.:110-85-0
- Empirical Formula: C4H10N2
- Molecular Weight: 86.14
- MDL number: MFCD00005953
- EINECS: 203-808-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
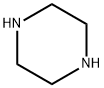
What is Piperazine?
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract
Toxicity
LD50 = 5 g/kg (Human, oral). Symptoms of overdose include muscle fatigue, seizures, and difficulty breathing.
Description
Piperazine is contained in pyrazinobutazone, an equimolecular sah of piperazine and phenylbutazone. Among occupational cases, most were reported in the pharmaceutical industry or laboratory, in nurses and in veterinarians.
Description
Piperazine (Item No. 24019) is an analytical reference standard categorized as a piperazine. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Chemical properties
Piperazine is white to cream-colored needles or powder. Characteristic ammonia-like odor. Combustible solids that do not easily ignite.
Chemical properties
Colorless to yellow solid; salty taste.
The Uses of Piperazine
Labelled Piperazine
The Uses of Piperazine
keratolytic, antiseborheic
The Uses of Piperazine
Piperazine is used as an intermediate in themanufacture of dyes, pharmaceuticals, polymers,surfactants, and rubber accelerators.
Background
Piperazine is an organic compound that consists of a six-membered ring containing two opposing nitrogen atoms. First used as a solvent for uric acid, the use of piperazine as an anthelmintic agent was first introduced in 1953. Upon entry into the systemic circulation, the drug is partly oxidized and partly eliminated as an unchanged compound. Outside the body, piperazine has a remarkable power to dissolve uric acid and producing a soluble urate, but in clinical experience it has not proved equally successful. Piperazine was first introduced as an anthelmintic in 1953. Piperazine compounds mediate their anthelmintic action by generally paralyzing parasites, allowing the host body to easily remove or expel the invading organism.
Indications
Used as alternative treatment for ascariasis caused by Ascaris lumbricoides (roundworm) and enterobiasis (oxyuriasis) caused by Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm). It is also used to treat partial intestinal obstruction by the common roundworm, a condition primarily occurring in children.
What are the applications of Application
Piperazine is a buffer component in chromatography purifications and separations based on pH
Definition
ChEBI: An azacycloalkane that consists of a six-membered ring containing two nitrogen atoms at opposite positions.
Indications
Piperazine (Vermizine) contains a heterocyclic ring that
lacks a carboxyl group. It acts on the musculature of the
helminths to cause reversible flaccid paralysis mediated
by chloride-dependent hyperpolarization of the muscle
membrane. This results in expulsion of the worm.
Piperazine acts as an agonist at gated chloride channels
on the parasite muscle.
Piperazine has been used with success to treat A.
lumbricoides and E. vermicularis infections, although
mebendazole is now the agent of choice. Piperazine is
administered orally and is readily absorbed from the intestinal
tract. Most of the drug is excreted in the urine
within 24 hours.
Piperazine is an appropriate alternative to mebendazole
for the treatment of ascariasis, especially in the
presence of intestinal or biliary obstruction. Cure rates
of more than 80% are obtained following a 2-day regimen.
Side effects occasionally include gastrointestinal distress,
urticaria, and dizziness. Neurological symptoms of
ataxia, hypotonia, visual disturbances, and exacerbations of epilepsy can occur in patients with preexisting
renal insufficiency. It should not be used in pregnant
women because of the formation of a potentially carcinogenic
and teratogenic nitrosamine metabolite.
Concomitant use of piperazine and chlorpromazine or
pyrantel should be avoided.
brand name
Pincets (Marion Merrell Dow); Pinsirup (Marion Merrell Dow);Adelmintex;Adipalis;Adipalit;Adiver;Ancaris thenium;Ancazine;Antelmina;Antepar (b-w);Anterobius;Anthalazine;Anthelmina;Anticucs;Antivermine;Ascalix;Ascarinex;Ascarivet;Asca-trol no.3;Asepar;Askaripar;Averamexan;Bel-zine;Bioxurin;B-piperazine;Brirel;Candizine;Carudol;Ciperazin;Citrazine;Coopane;Dak;Demovermil;Diatesurico;Dicevermin;Digesan;Dilaurazine;Dispermin;Diurazina;Dowzene;Ecosan;Endorid;Entazin;Equizole-a;Escovermin;Esteropipate;Etaphylline (acetyllinate);Gentiazina;Glycopiparsol;Heksapar;Helmacid;Helmezin;Helmicide;Helmifren;Helmipar;Helmirazine (adipate);Helmirazine (citrate);Helmitin;Helmizin;Herb royal round worm treatment;Hexanthelin;Ismiverm;Janes liquid permifu;Jarabe neox;Jetsan supp. (adipate);Justalmin;Kennel-maid;Kihomato;Kontipar;Lamboxil;Lombricida tropico;Lombrifher;Lombrikal;Lombrimade;Mapiprin;Maskito;Noxiurotan;Ogen;Okuside;Optiverm;Oxiril syrup (hydrate);Oxiuran (hydrate);Oxiurasin;Oxiustip elix;Oxivermin;Oxizin;Oxucid;Oxuril;Oxypip;Oxyzin;P.c. (citrate);Padrax;Paravermin;Pariamate;Par-tega;Perin;Piavermit;Pincide;Pipan;Pip-a-ray;Pipenin;Piperacid;Piperamicin;Piperascat;Piperaskat;Piperate;Piperaverm;Piperazinal;Piperazine (adipate);Pipercrean;Piperex;Piperiod;Piperital od;Piperitol;Piper-jodina;Piperol fort;Piperone;Piperoverm;Pipertox;Piperver;Piperzinal;Pipeverm;Pipezol;Pipizan citrate;Pipracid;Piprazid;Piprazyl;Pipricide;Piptelate;Piverma;Polo-verm;Polyquil;Pripsen;Provtovermil;Razinol;Rondelim;Rondoxyl;Santoban;Siropar;Supraverm;Taenifigin;Teniver;Tivazine;Toxocan;Uricida;Uridina;Uroclear (hexamine);Urodan (phosphate);Urosolvina;Uvilon syrup (hydrate);Vanpar (hydrate);Veripar;Vermazine;Vermenter;Vermicompren;Vermidol;Vermifug;Vermilass;Vermipan;Vermiphsarmette;Vermiquimpe;Vermiquimyc;Vermisit;Vermitox;Vermofrik;Verocid;Wairmex;Wurmex;Wurmsirup siegfried Multifuge;Multifuj;Nea-vermiol;Nemafugan;Nemasin;Nematocton;Nematorazine;Neo-ifusa;.
World Health Organization (WHO)
Piperazine was first used as a treatment for gout earlier this century and its anthelminthic activity was discovered in 1949. It is also considerably cheaper than other anthelminthic drugs. In some countries where ascariasis is not endemic and where piperazine was used predominantly for the treatment of pinworm it has been withdrawn from use on the grounds that other more effective and less toxic drugs are now available (see full list). In other such countries, however, piperazine remains available in over-the-counter preparations. Clinical dosages occasionally induce transient neurological signs and concern has been expressed that in some circumstances the drug may generate small amounts of nitrosamine in the stomach. However, it is widely considered that these trace doses are unlikely to give rise to a significant carcinogenic potential. (Reference: (WHODIB) WHO Drug Information Bulletin, 1: 5, , 1983)
General Description
Needle-like white or colorless crystals. Shipped as a solid or suspended in a liquid medium. Very corrosive to skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Solid turns dark when exposed to light. Flash point 190°F. Used as a corrosion inhibitor and as an insecticide.
Air & Water Reactions
Flammable. Absorbs water and carbon dioxide from air. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
1,4-Diazacyclohexane neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Absorbs carbon dioxide from the air, which can cause dry crystals to seem to melt. May generate hydrogen, a flammable gas, in combination with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. 1,4-Diazacyclohexane is sensitive to light; 1,4-Diazacyclohexane absorbs water and carbon dioxide from air. 1,4-Diazacyclohexane may be corrosive to aluminum, magnesium and zinc. .
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Health Hazard
Piperazine is a corrosive substance. The solidand its concentrated aqueous solutions areirritants to the skin and eyes. The irritanteffect in rabbits’ eyes was severe.
The toxic symptoms from ingestion ofpiperazine include nausea, vomiting, excitement,change in motor activity, somnolence,and muscle contraction. The toxicity of thiscompound is low, however. The oral LD50value in rats is 1900 mg/kg. The inhalationtoxicity is very low. The inhalation LC50value in mice is 5400 mg/m3/2 h.
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Flammability and Explosibility
Highly flammable
Pharmaceutical Applications
A synthetic chemical, most commonly formulated as the citrate, but also available as the adipate, edetate calcium and tartrate salts.
Contact allergens
Piperazine is contained in pyrazinobutazone, an equimolar salt of piperazine and phenylbutazone. Among occupational cases, most were reported in the pharmaceutical industry or laboratory workers, in nurses, and in veterinarians.
Mechanism of action
Piperazine increases the resting potential of the somatic musculature of nematodes, especially in the syncytial region, by increasing the permeability of the membrane to chloride ions. This results in flaccid paralysis of the parasites, which are expelled from the intestine .
Pharmacokinetics
Piperazine is an anthelminthic especially useful in the treatment of partial intestinal obstruction caused by Ascaris worms, which is a condition primarily seen in children. Piperazine hydrate and piperazine citrate are the main anthelminthic piperazines.
Pharmacokinetics
Activity against intestinal worms requires that a substantial amount remains in the gut. However, after oral administration a variable amount is rapidly absorbed from the small intestine and subsequently excreted in the urine. Its half-life is extremely variable.
Clinical Use
Ascariasis
Pinworm
Clinical Use
Hexahydropyrazine or diethylenediamine (Arthriticine,Dispermin) occurs as colorless, volatile crystals of the hexahydratethat are freely soluble in water. After the discoveryof the anthelmintic properties of a derivative diethylcarbamazine,the activity of piperazine itself was established.Piperazine is still used as an anthelmintic for the treatmentof pinworm (Enterobius [Oxyuris] vermicularis) and roundworm(Ascaris lumbricoides) infestations. It is available invarious salt forms, including the citrate (official in the USP)in syrup and tablet forms. Piperazine blocks the response of the ascaris muscleto acetylcholine, causing flaccid paralysis in the worm,which is dislodged from the intestinal wall and expelled inthe feces.
Side Effects
Some people develop hypersensitivity, requiring cessation of treatment. Transient, mild gastrointestinal or neurological symptoms may occur.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion, skin contact, intravenous, and subcutaneous routes. Mildly toxic by inhalation. A skin and severe eye irritant. Excessive absorption can cause urticaria, vomiting, diarrhea, blurred vision, and weakness. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame; can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. Explodes on contact with dicyanofurazan. To fight fire, use alcohol foam, mist, dry chemical, water spray. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of NOx.
Synthesis
Piperazine (38.1.12) is a bulk product in organic synthesis. It is made from ethanolamine by heating it in ammonia at a temperature of 150¨C220??C and a pressure of 100¨C250atm. It is used as a drug in the form of a salt, and as a rule, in the form of adipinate.

Potential Exposure
(Piperazine): Primary irritant (w/o allergic reaction),
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Piperazine is used for the treatment of ascarids in dogs, cats, horses, swine and poultry. Piperazine is considered safe to use in animals with concurrent gastroenteritis and during pregnancy.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Pyrantel: antagonises effect of piperazine.
Carcinogenicity
No increase in lung adenomas was produced in mice administered 0.69–18.75mg of piperazine/ kg in drinking water for 20–25 weeks and sacrificed 10–13 weeks later. Mice fed the equivalent of 938 mg/kg in the diet for 28 weeks and sacrificed at 40 weeks failed to show any significant increase in the incidence of lung adenomas. An increase in lung adenomas was produced in this bioassay by administration of piperazine together with sodium nitrate, suggesting the formation of the active nitroso derivative. Sodium ascorbate inhibited tumor formation, in theory, by preventing piperazine nitrosation (304). Coadministration of 250 ppm piperazine and 500 ppm sodium nitrate in drinking water did not produce tumors in rats. None of these studies were conducted using currently accepted methods for evaluating carcinogenic potential but piperazine alone, in these assays, was noncarcinogenic.
Environmental Fate
This molecule has a simple chemical structure and molecular weight of 86.14. It has a strong alkaline base soluble in water (1:18), glycerol, and glycols, but is only sparingly soluble in alcohol and insoluble in ether. Piperazine is not expected to hydrolyze in water. The photodegradation half-life is approximately 0.8 h. The piperazine molecule is easily denaturalized by diverse environmental factors and has a low potential for bioaccumulation or biomagnification. To improve its stability, it is usually formulated as different salts such as adipate, citrate, phosphate, hexahydrate, and sulfate. Most piperazine salts are white crystalline powders that are readily soluble in water.Exceptions are adipates, which dissolve to only a maximum concentration of 5% in water, and phosphate, which is insoluble.
Metabolism
About 25% is metabolized in the liver. Piperazine is nitrosated to form N -mononitrosopiperazine (MNPz) in gastric juice, which is then metabolized to N-nitroso-3-hydroxypyrrolidine (NHPYR).
Metabolism
About 25% is metabolised in the liver. Piperazine is
nitrosated to form N -mononitrosopiperazine (MNPz)
in gastric juice, which is then metabolised to N-nitroso-3-
hydroxypyrrolidine (NHPYR).
It is excreted in the urine mainly as metabolites.
Shipping
UN2579 Piperazine, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
Purification Methods
Piperazine crystallises from EtOH or anhydrous *benzene and is dried at 0.01mm. It can be sublimed under vacuum and purified by zone melting. The hydrochloride has m 172-174o (from EtOH), and the dihydrochloride crystallises from aqueous EtOH and has m 318-320o (dec, sublimes at 295-315o). The picrate has m ~200o, and the picrolonate crystallises from dimethylformamide ( m 259-261o). [Beilstein 23 H 4, 23 I 4, 23 II 3, 23 III/IV 15, 23/1 V 30.]
Toxicity evaluation
Piperazine blocks transmission by hyperpolarizing nerve membranes at the neuromuscular junction, leading to parasite immobilization by flaccid paralysis and consequent removal from predilection and death. Piperazine is a selective agonist of GABA receptors, resulting in the opening of chloride channels and hyperpolarization of the membrane of the muscle cells of nematode parasites.
Incompatibilities
Aqueous solution is a strong base. Violent reaction with strong oxidizers and dicyanofurazan. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, nitrogen compounds, carbon tetrachloride. Attacks aluminum, copper, nickel, magnesium and zinc.
Properties of Piperazine
| Melting point: | 109-112 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 145-146 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1,1 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 0.8 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4460 |
| FEMA | 4250 | PIPERAZINE |
| Flash point: | 65 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Crystalline Flakes |
| pka | 9.83(at 23℃) |
| color | White to slightly yellow |
| PH | 11.0-12.5 (25℃, 0.1M in H2O) |
| Odor | at 0.10 % in dipropylene glycol. ammoniacal |
| explosive limit | 14% |
| Water Solubility | 150 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive & Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.035 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.010 |
| JECFA Number | 1615 |
| Merck | 14,7464 |
| BRN | 102555 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.03 ppm |
| Stability: | Stable. Hygroscopic. Light sensitive. Flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 110-85-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Piperazine(110-85-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Piperazine (110-85-0) |
Safety information for Piperazine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Piperazine
| InChIKey | GLUUGHFHXGJENI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Piperazine manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![Ethyl (S)-9,10-difluoro-3-methyl-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7H-pyrido[1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/106939-34-8.gif)

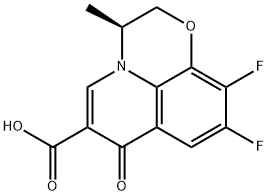
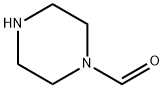
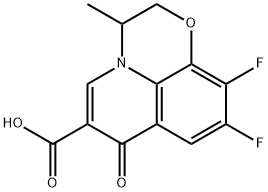
You may like
-
 Piperazine 98%View Details
Piperazine 98%View Details -
 Piperazine Anhydrous CASView Details
Piperazine Anhydrous CASView Details -
 Piperazine Anhydrous pure CAS 110-85-0View Details
Piperazine Anhydrous pure CAS 110-85-0View Details
110-85-0 -
 Anti-KCTD11 antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details
Anti-KCTD11 antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details -
 Anti-EPB41L3 antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details
Anti-EPB41L3 antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details -
 Piperazine Anhydrous PureView Details
Piperazine Anhydrous PureView Details
110-85-0 -
 Piperazine AnhydrousView Details
Piperazine AnhydrousView Details
110-85-0 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0
