PHENYLMERCURIC ACETATE
Synonym(s):Mercury phenyl acetate;Phenylmercury acetate
- CAS NO.:62-38-4
- Empirical Formula: C8H8HgO2
- Molecular Weight: 336.74
- MDL number: MFCD00008691
- EINECS: 200-532-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
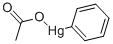
What is PHENYLMERCURIC ACETATE?
Chemical properties
white crystalline powder
Chemical properties
Phenylmercury acetate is a white or yellow crystalline solid.
Chemical properties
Phenylmercuric acetate occurs as a white to creamy white, odorless or almost odorless, crystalline powder or as small white prisms or leaflets.
The Uses of PHENYLMERCURIC ACETATE
Phenylmercuric acetate is used as catalyst; fungicide; herbicide; algicide; preservative in antibiotic eye drops, eye cosmetics, shampoos, etc.
The Uses of PHENYLMERCURIC ACETATE
antiulcer
The Uses of PHENYLMERCURIC ACETATE
Herbicide; fungicide.
Production Methods
Phenylmercuric acetate is readily formed by heating benzene with mercuric acetate.
Definition
ChEBI: Phenylmercury acetate is an arylmercury compound and a member of benzenes.
General Description
Small lustrous prisms. Toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. May severely irritate skin and eyes. Used as an herbicide and fungicide. as such, is mixed with organic solvent for the purpose of application.
Reactivity Profile
PHENYLMERCURIC ACETATE may react with strong oxidizing agents .
Health Hazard
Extremely toxic. The probable oral lethal dose for humans is 5-50 mg/kg, between 7 drops and 1 teaspoonful for a 70 kg (150 lb.) person.
Fire Hazard
Fire may produce irritating or poisonous gases. When heated to decomposition, very toxic mercuric fumes may be given off. Phenylmercuric ion is incompatible with halides, with which precipitates are formed.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Phenylmercuric acetate is used as an alternative antimicrobial
preservative to phenylmercuric borate or phenylmercuric nitrate in
a limited range of cosmetics (in concentrations not exceeding
0.007% of mercury calculated as the metal) and pharmaceuticals. It
may be used in preference to phenylmercuric nitrate owing to its
greater solubility.
Phenylmercuric acetate is also used as a spermicide;
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intravenous, intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, and possibly other routes. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. See also MERCURY COMPOUNDS. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Hg.
Safety
Phenylmercuric acetate is mainly used as an antimicrobial
preservative in topical pharmaceutical formulations. A number of
adverse reactions to mercury-containing preservatives have been
reported; see Phenylmercuric Nitrate.
LD50 (chicken, oral): 60 mg/kg
LD50 (mouse, IP): 13 mg/kg
LD50 (mouse, IV): 18 mg/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): 13 mg/kg
LD50 (mouse, SC): 12 mg/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 41 mg/kg
Potential Exposure
Phenylmercury acetate is used as an antiseptic, fungicide; for fungal and bacterial control; herbicide and control of crabgrass; mildewcide for paints; slimicide in paper mills. It was also used in contraceptive gels and foams.
Environmental Fate
If released into air, soil, or water, phenylmercuric acetate is unlikely to volatilize and is instead expected to be bound to particulates based on a low vapor pressure (6 × 10-6 mm Hg) and low Henry’s constant (5.66 × 10-10 atmm3 mol -1). Photolysis has the potential to degrade phenylmercuric acetate, releasing inorganic mercury which can volatilize and enter the atmosphere from superficial soils or water. If released into soil, the mobility of parent phenylmercuric acetic acid is expected to be high based on a Koc of 60. Water releases would result in quick dispersion since water solubility is high (4370 mg l-1). Once in solution, especially with harder water, it will dissociate into a salt. The cation will adsorb to particulates or humics suspended in the water column or in sediment, with little bioconcentration in aquatic species.
storage
As for other phenylmercuric salts; see Phenylmercuric Nitrate.
Phenylmercuric acetate should be stored in a well-closed
container, protected from light, in a cool, dry place.
Shipping
UN1674 Phenylmercuric acetate, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
It forms small colourless lustrous prisms from EtOH. Its solubility in H2O is 0.17%, but it is more soluble in EtOH, Me2CO and *C6H6. [Maynard J Am Chem Soc 46 1510 1925, Coleman et al. J Am Chem Soc 59 2703 1937, J Am Pharm Assoc 25 752 1936, Beilstein 16 IV 1720.] See PhHgOH below.
Toxicity evaluation
Toxic effects of phenylmercuric acetate are correlated with its rapid metabolic breakdown into the mercuric ion. Generally, mercury interferes with cellular enzymatic mechanisms by combining with sulfhydryl (–SH) groups of different enzymes and thereby produces nonspecific cell injury or death.
Incompatibilities
A strong reducing agent. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, halogens.
Incompatibilities
As for other phenylmercuric salts; see Phenylmercuric Nitrate.
Incompatible with: halides; anionic emulsifying agents and
suspending agents; tragacanth; starch; talc; sodium metabisulfite;
sodium thiosulfate; disodium edetate; silicates; aluminum and other
metals; amino acids; ammonia and ammonium salts; sulfur
compounds; rubber; and some plastics.
Phenylmercuric acetate is reported to be incompatible with
cefuroxime and ceftazidime.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. React to produce soluble nitrate form, precipitate as mercuric sulfide. Return to supplier.
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (ophthalmic
ointments; topical emulsions/creams; vaginal emulsions/creams).
Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal
Ingredients (ophthalmic, nasal and otic preparations up to
0.004%; there must be no other suitable alternative preservative
available).
Phenylmercuric acetate is no longer permitted to be used as a
pesticide in the USA. Its use in cosmetic products in the USA is
limited to eye area cosmetics at not more than 0.0065% provided
that there is no other suitable available preservative. It is specifically
prohibited in vaginal contraceptive drug products and antimicrobial
diaper rash drug products in the USA. Phenylmercuric
compounds are prohibited from use in cosmetic products in
Canada.
In Europe, use in cosmetic products is limited to eye makeup and
eye makeup remover at concentrations not exceeding 0.007%
mercury alone or in combination with other permitted mercurial
compounds.In France, a maximum concentration of 0.01% is
permitted for use in pharmaceuticals. The use of mercurial
compounds in cosmetics in Japan is limited to concentrated
shampoo or cream at not more than 0.003% Hg and eye makeup
at not more than 0.0065% Hg.
Properties of PHENYLMERCURIC ACETATE
| Melting point: | 148-151 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 2,4 g/cm3 |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| solubility | Slightly soluble in water, soluble in acetone and in alcohol. |
| form | Powder |
| color | white |
| Specific Gravity | 2.4 |
| Odor | Acetic acid odor |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, benzene and glacial acetic acid. Slightly soluble in water. |
| Merck | 14,7300 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 62-38-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phenylmercury acetate (62-38-4) |
Safety information for PHENYLMERCURIC ACETATE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H300:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for PHENYLMERCURIC ACETATE
PHENYLMERCURIC ACETATE manufacturer
Anand Agencies
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

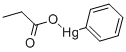
You may like
-
 Phenylmercuric Acetate (PMA) pure CAS 62-38-4View Details
Phenylmercuric Acetate (PMA) pure CAS 62-38-4View Details
62-38-4 -
 Phenylmercury acetate, 99% CAS 62-38-4View Details
Phenylmercury acetate, 99% CAS 62-38-4View Details
62-38-4 -
 PHENYL MERCURY ACETATE For Synthesis CAS 62-38-4View Details
PHENYL MERCURY ACETATE For Synthesis CAS 62-38-4View Details
62-38-4 -
 Phenylmercuric acetate CAS 62-38-4View Details
Phenylmercuric acetate CAS 62-38-4View Details
62-38-4 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1