Phenylboronic acid
Synonym(s):Benzeneboronic acid;Dihydroxyphenylborane;Phenylboric acid;Phenyl-boric acid;Phenyldihydroxyborane
- CAS NO.:98-80-6
- Empirical Formula: C6H7BO2
- Molecular Weight: 121.93
- MDL number: MFCD00002103
- EINECS: 202-701-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-07 19:09:50
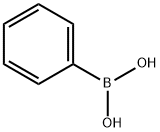
What is Phenylboronic acid?
Description
Phenylboronic acid, also known as benzeneboronic acid, is synthesized through the reaction of the Grignard reagent PhMgBr with B(OMe)3. This compound and its derivatives with aryl substitutions are widely recognized as essential building blocks in the field of synthetic organic chemistry. They are particularly prominent in the Suzuki coupling reaction, where a boronic acid reacts with an organic halide to form a carbon-carbon bond. Additionally, the reactions of boronic acids with 1,2- and 1,3-diols are significant for saccharide recognition, highlighting their versatility in chemical applications.
Chemical properties
white to light yellow crystal powder. Insoluble in water and benzene, easily soluble in ether and methanol. When exposed to air or under heating conditions, it is easy to dehydrate and form a three-molecular polymer.
The Uses of Phenylboronic acid
Phenylboronic Acid is a compound used in organic synthesis of various pharmaceutical goods.
Phenylboronic acid (PBA) and its derivatives can bind sugars and other diol compounds to form cyclic boronate esters. These esters bear negative charges. Due to this reaction, sugars can be detected by means of electrochemical and optical techniques.
PBA modified electrodes have been constructed as reagentless electrochemical sensors. There, PBA is absorbed on the electrode surface either as a self- assembled monolayer film ore a polymer thin film. Basically, for optical detection techniques for the detection of sugars, PBA is modified with a chromophore that should change its properties on reaction with a sugar.

Reaction of Phenylboronic acid with a sugar
The Uses of Phenylboronic acid
Reagent used for• ;Rhodium-catalyzed intramolecular amination1 • ;Pd-catalyzed direct arylation2 • ;Mizoroki-Heck and Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions catalyzed by palladium nanoparticles3 • ;Palladium-catalyzed stereoselective Heck-type reaction4 • ;Highly effective Palladium-catalyzed arylation Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling in water5 Reagent used in Preparation of• ;Ni(II) pincer complex and Pd(II) pyridoxal hydrazone metallacycles as catalysts for the Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions6,7• ;N-type polymers for all-polymer solar cells8 •
The Uses of Phenylboronic acid
Phenylboronic acid is a versatile compound that is soluble in water, allowing for coupling reactions to be performed in aqueous environments. This solubility, along with its compatibility with various organic substituents such as esters, ketones, and alcohols, makes it a preferred choice over Grignard reagents in certain coupling reactions.
Furthermore, phenylboronic acid and its derivatives have the ability to form complexes with polyol compounds, including saccharides and poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA). This property is particularly useful in the development of glucose-sensitive materials. For instance, a copolymer containing phenylboronic acid moieties can be synthesized through the copolymerization of 4V-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone (NVP) and 3-(acryl-amide)phenylboronic acid (PBA). The formation of complexes between this NVP-PBA copolymer and PVA is crucial for constructing glucose-sensitive insulin release systems. These systems are designed to dissociate in response to changes in glucose concentration, providing a mechanism for controlled insulin delivery.
The utility of phenylboronic acid in the creation of glucose-sensitive hydrogels and its role as a ligand for glucose targeting exemplify its importance in the development of advanced materials for healthcare applications.
Definition
ChEBI: Phenylboronic acid is a member of boronic acids. It is functionally related to a boronic acid.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 4, p. 68, 1963
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 49, p. 5237, 1984 DOI: 10.1021/jo00200a045
General Description
Phenylboronic acid (PBA) is an organoboronic acid with unique properties. It functions as a molecular receptor, capable of binding to compounds that contain a cis-diol group. This ability makes it a valuable component in various chemical reactions.
One notable application is in the microwave-assisted Suzuki coupling process, where aryl chlorides are coupled with phenylboronic acid. This reaction takes place in the presence of a Pd/C catalyst and uses water as the solvent, offering an efficient and environmentally friendly method for synthesizing biaryls.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous andintraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion.Mildly toxic by skin contact. When heated to decomposition it emitsacrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Properties of Phenylboronic acid
| Melting point: | 216-219 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 265.9±23.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.13±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 8.83(at 25℃) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | 10 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,1068 |
| BRN | 970972 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 98-80-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Boronic acid, phenyl- (98-80-6) |
Safety information for Phenylboronic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Phenylboronic acid
| InChIKey | HXITXNWTGFUOAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Phenylboronic acid manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Sainor Laboratories Pvt Ltd Unit III
ASM Organics
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 98-80-6 98%View Details
98-80-6 98%View Details
98-80-6 -
 Phenylboronic acid CAS 98-80-6View Details
Phenylboronic acid CAS 98-80-6View Details
98-80-6 -
 Phenylboronic Acid extrapure CAS 98-80-6View Details
Phenylboronic Acid extrapure CAS 98-80-6View Details
98-80-6 -
 Phenylboronic Acid (contains varying amounts of Anhydride) CAS 98-80-6View Details
Phenylboronic Acid (contains varying amounts of Anhydride) CAS 98-80-6View Details
98-80-6 -
 Phenylboronic acid 98% CAS 98-80-6View Details
Phenylboronic acid 98% CAS 98-80-6View Details
98-80-6 -
 Phenylboronic acid CAS 98-80-6View Details
Phenylboronic acid CAS 98-80-6View Details
98-80-6 -
 Phenylboronic acid CAS 98-80-6View Details
Phenylboronic acid CAS 98-80-6View Details
98-80-6 -
 98-80-6 98%View Details
98-80-6 98%View Details
98-80-6
