Pendimethalin
- CAS NO.:40487-42-1
- Empirical Formula: C13H19N3O4
- Molecular Weight: 281.31
- MDL number: MFCD00055332
- EINECS: 254-938-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
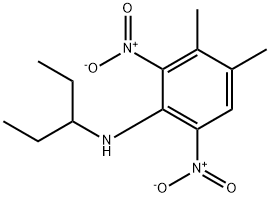
What is Pendimethalin?
Chemical properties
Brown Solid
Chemical properties
Yellow-orange crystalline solid. Mild nut-like odor. Commercial product is available as an emulsifiable concentrate.
The Uses of Pendimethalin
Herbicide used to control the spread of weedgrass.
The Uses of Pendimethalin
Herbicide.
The Uses of Pendimethalin
used to control many annual grasses and broad-leaved weeds in crops such as corn, cotton, peanuts, potatoes, rice, sorghum, sunflower and tobacco.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of substituted anilines that is N-(pentan-3-yl)aniline bearing two additional nitro substituents at positions 2 and 6 as well as two methyl substituents at positions 3 and 4. A herbicide used to control most annual rasses and many annual broad-leaved weeds.
General Description
Orange-yellow crystals. Non corrosive. Used as an herbicide.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
A dinitroaniline derivative.
Agricultural Uses
Herbicide: Pendimethalin is a selective pre-emergence and post-emergence herbicide used on various agricultural and non-agricultural sites to control broadleaf weeds and grassy weeds in crops such as apricot, carrot, cherry, corn, cotton, fig, garbanzos, garlic, olive, onion, nectarine, peach, pear, pecan, plum, rice and prune, and noncrop areas. It is applied to soil preplant, pre-emergence, and post-emergence with ground and aerial equipment.
Trade name
AC 92553®; ACCOTAB®; BULLET® (pendimethalin + cyanazine); GO-GO-SAN®; HERBADOX®; PAY-OFF®; PENOXALIN®; PENOXALINE®; PROWL®; SIPAXOL®; SQUADRON® (with imazaquin); STOMP®; TATA PANIDA®; VALOR®; WAY-UP®
Potential Exposure
Pendimethalin is a selective preemergence and postemergence 2,6-dinitroaniline herbicide used on various agricultural and non-agricultural sites to control broadleaf weeds and grassy weeds in crops such as apricot, carrot, cherry, corn, cotton, fig, garbanzos, garlic, olive, onion, nectarine, peach, pear, pecan, plum, rice and prune, and noncrop areas. It is applied to soil preplant, pre-emergence, and postemergence with ground and aerial equipment.
Environmental Fate
Biological. In an in vitro study, the soil fungi Fusarium oxysporum and Paecilomyces
varioti degraded pendimethalin to N-(1-ethylpropyl)-3,3-dimethyl-2-nitrobenzene-1,6-
diamine and 3,4-dimethyl-2,6-dinitroaniline. The latter compound was the only metabolite
identified by another soil fungus; namely, Rhizoctonia bataticola (Singh and Kulshrestha,
1991)
Kole et al. (1994) studied the degradation of pendimethalin by an unadapted strain of
Azotobacter chroococcum Beijerinck in pure culture condition. Degradation was rapid —
45 and 55% of the parent compound was degraded after 10 and 20 days, respectively.
xylidine. At the C-3 position on the parent compound, the methyl group oxidized to
-CH2OH which underwent partial reduction of the 2-nitro group and N-dealkylation followed by oxidative cyclization to give 2-methyl-4-nitro-5-N-(1-cyclopropyl)-6-nitrosobe
Soil/Plant. In soil, the 4-methyl group on the benzene ring is oxidized to a hydroxy
group which undergoes further oxidation to the carboxylic acid. The major plant metabolite
is 4-(1-ethylpropyl)amino-2-methyl-3,5-dinitrobenzyl alcohol (Hartley and Kidd, 1987).
Kulshrestha and Singh (1992) investigated the influence of soil moisture and microbial
activity on the degradation of pendimethalin in a sandy loam soil. In both nonsterile,
nonflooded and flooded soils, degradation followed first-order kinetics. The observed halflives in flooded and nonflooded conditions in nonsterile and sterile soils were 33 and 45;
52 and 67 days, respectively. In the nonsterile, nonflooded soil, pendimethalin underwent
N-dealkylation and reduction of the less hindered nitro group affording N-(1-ethylpropyl)-
3,4-dimethyl-2-nitrobenzene-1,6-diamine and 3,4-dimethyl-2,6-dinitroaniline as major
products. Under flooded conditions, only one degradation product was formed: N-(1-
ethylpropyl)-5,6-dimethyl-7-nitrobenzimidazole. Under flooded conditions, pendimethalin
was completely degraded after 4 days (Kulshrestha and Singh, 1992)
The reported half-lives of pendimethalin in a Sharkey clay soil and Bosket silt loam
are 6 and 4 days, respectively (Savage and Jordan, 1980).
Metabolic pathway
Irradiation of pendimethalin in methanol yields, in addition to the minor dealkylated product, the major products 2-amino-6-nitro-N-(1-ethylpropyl)-3,4-xylidine and 2-nitroso-6-nitro-3,4-xylidine. Pendimethalin degrades rapidly through reductive cyclization of the amino group and adjacent N-ethylpropyl to give a cyclized benzimidazole product. The photodecomposition of pendimethalin involves oxidative dealkylation, nitro reduction, and cyclization. By soil bacteria, pendimethalin degrades through different pathways from the photodegradation reaction, resulting in benzimidazole and hydroxylated products of the N-alkyl and xylyl methyl groups. The major metabolic routes of pendimethalin by rats involves hydroxylation of the 4-methyl and the N-ethyl group, oxidation of these alkyl groups to carboxylic acids, nitro reduction, cyclization, and conjugation in the urine and the tissues. Products of cyclization reactions giving methylbenzimidazole-carboxylic acids are unique metabolites to the liver and kidney.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Reacts with oxidizers, acids and alkaline materials. Contact with strong oxidizers may cause fire and explosions.
Waste Disposal
It is the responsibility of chemical waste generators to determine if a discarded chemical is classified as a hazardous waste. See 40 CFR Parts 261.3 for United States Environmental Protection Agency guidelines for the classification determination. Additionally, in order to ensure complete and accurate classification, waste generators must consult state and local hazardous waste regulations. Organic pesticides, whether of botanical or synthetic origin, can be destroyed by incineration equipped with scrubbers to remove acid wastes.
Properties of Pendimethalin
| Melting point: | 56-57°C |
| Boiling point: | 330°C |
| Density | 1.17 |
| refractive index | 1.5700 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| solubility | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (355.48 mM) |
| pka | -2.24±0.33(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Yellow-orange brown |
| Water Solubility | <0.5 mg/L |
| Merck | 14,7084 |
| BRN | 2157711 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Penoxaline(40487-42-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Pendimethalin (40487-42-1) |
Safety information for Pendimethalin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Pendimethalin
| InChIKey | CHIFOSRWCNZCFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Pendimethalin manufacturer
ENTOMIC CHEMICALS
Unique Farm Aid Pvt Ltd
Shree Vallabh Chemicals
New Products
p-Toluenesulfonyl hydrazide N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one ELECTROLYTIC IRON POWDER 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE 4-Bromopyrazole 1-Boc-4-cyanopiperidine 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone Cycloleucine 1-Aminocyclobutanecarboxylic acid 1-Amino-1-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid 1-(2-Ethoxyethyl)-2-(piperidin-4-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole hydrochloride TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE Ethyl 2-cyano-2-(hydroxyimino)acetate (S)-1-Benzyl 2-methyl pyrrolidine-1,2-dicarboxylate 2-Amino-3-nitrobenzoic acid methyl ester N1,N2-Dibenzylethane-1,2-diamine 3-(4-Morpholinyl)aniline 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 40487-42-1 Pendimethalin 98%View Details
40487-42-1 Pendimethalin 98%View Details
40487-42-1 -
 40487-42-1 99%View Details
40487-42-1 99%View Details
40487-42-1 -
 40487-42-1 Pendimethalin 98%View Details
40487-42-1 Pendimethalin 98%View Details
40487-42-1 -
 Pendimethalin CAS 40487-42-1View Details
Pendimethalin CAS 40487-42-1View Details
40487-42-1 -
 Pendimethalin CAS 40487-42-1View Details
Pendimethalin CAS 40487-42-1View Details
40487-42-1 -
 Pendimethalin 98%View Details
Pendimethalin 98%View Details
40487-42-1 -
 Pendimethalin CAS 40487-42-1View Details
Pendimethalin CAS 40487-42-1View Details
40487-42-1 -
 Pendimethalin solution CAS 40487-42-1View Details
Pendimethalin solution CAS 40487-42-1View Details
40487-42-1