Palmitic acid
Synonym(s):Palmitic acid;Hexadecanoic acid;C16:0;Cetylic acid;1-Pentadecanecarboxylic acid
- CAS NO.:57-10-3
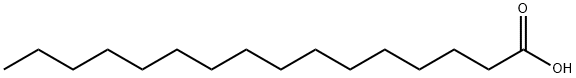
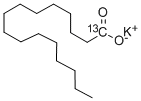
- Empirical Formula: C16H32O2
- Molecular Weight: 256.42
- MDL number: MFCD00002747
- EINECS: 200-312-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18
What is Palmitic acid?
Toxicity
Acute oral toxicity (LD50) in rat is >10000 mg/kg
Description
Palmitic acid is a kind of common saturated fatty acid of a 16-carbon backbone, which is contained in fats and waxes. It naturally exists in palm oil and palm kernel oil, and can also be found in butter, cheese, milk, meat, cocoa butter, soybean oil and sunflower oil. It can be produced by many kinds of plants and organisms. It can be used for the production of soap, cosmetics, and industrial mold release agents. It is also a food processing aid. It can also be used to produce cetyl alocohol which is useful in the production of detergents and cosmetics. Recently, it has been also used for the manufacture of a long-acting antipsychotic medication, paliperidone palmitate.
Chemical properties
Palmitic acid occurs as white crystalline scales with a slight characteristic odor and taste. It is one of the most common saturated fatty acids found in animals and plants. It is a mixture of solid organic acids obtained from fats consisting chiefly of palmitic acid (C16H35O2) with varying amounts of stearic acid (C16H36O2). As its name tells us, it is found in palm oil but also in butter, cheese, milk and meat.
Occurrence
Reported found in apple, beef fat, preferments of bread, celery, cheddar cheese, blue cheese, roquefort cheese, other cheeses, roasted cocoa bean, cognac, country cured ham, essential oil of lemon, heated milk, essential oil of sweet orange, pork fat, potato, black tea, tomato, banana, grapefruit juice, cranberry, guava, grapes, melon, papaya, pear, raspberry, strawberry, cinnamon, ginger, saffron, milk powder, fatty fish, chicken, lamb, hop oil, beer, rum, whiskies, grape wines, peanut oil, popcorn, soybean, coconut meat, avocado, cloudberry, plums, beans, mushroom, starfruit, marjoram, fenugreek, mango, tamarind, fig, kelp, cardamom,rice, prickly pear, dill, licorice, sake, buckwheat, corn oil, malt, wort, roasted chicory root, lemon balm, shrimp, crab, clam, scallop, Chinese quince, pawpaw and sweet grass oil.
The Uses of Palmitic acid
Palmitic Acid is a common fatty acid found in plants and animals. The body converts excess carbohydrates into Palmitic Acid, thus Palmitic Acid is the first fatty acid produced during fatty acid synt hesis as well as a precursor for longer fatty acids.
The Uses of Palmitic acid
palmitic acid is one of the skin’s major fatty acids produced by the sebaceous glands. In cosmetic preparations, it is used as a formula texturizer. This acid is naturally occurring in allspice, anise, calamus oil, cascarilla bark, celery seed, coffee, tea, and many animal fats and plant oils. It is obtained from palm oil, Japan wax, or Chinese vegetable tallow.
The Uses of Palmitic acid
Palmitic Acid is a fatty acid which is a mixture of solid organic acids from fats consisting principally of palmitic acid with varying amounts of stearic acid. it functions as a lubricant, binder, and defoaming agent.
What are the applications of Application
Palmitic Acid is a saturated fatty acid that targets proteins to cell membranes
Background
A common saturated fatty acid found in fats and waxes including olive oil, palm oil, and body lipids.
Definition
ChEBI: Palmitic acid is a saturated long-chain fatty acid with a 16-carbon backbone. It is a metabolite found in the aging mouse brain. It is found naturally in palm oil and palm kernel oil, as well as in butter, cheese, milk and meat.
Production Methods
Palmitic acid occurs naturally in all animal fats as the glyceride, palmitin, and in palm oil partly as the glyceride and partly uncombined. Palmitic acid is most conveniently obtained from olive oil after removal of oleic acid, or from Japanese beeswax. Synthetically, palmitic acid may be prepared by heating cetyl alcohol with soda lime to 270°C or by fusing oleic acid with potassium hydrate.
What are the applications of Application
Palmitic acid is mainly used to produce soaps, cosmetics, and release agents. These applications utilize sodium palmitate, which is commonly obtained by saponification of palm oil. To this end, palm oil, rendered from the coconut palm nut, is treated with sodium hydroxide (in the form of caustic soda or lye), which causes hydrolysis of the ester groups. This procedure affords glycerol and sodium palmitate.
Because it is inexpensive and adds texture to processed foods (convenience food), palmitic acid and its sodium salt find wide use including foodstuffs. Sodium palmitate is permitted as a natural additive in organic products.
Hydrogenation of palmitic acid yields cetyl alcohol, which is used to produce detergents and cosmetics.
Recently, a long-acting antipsychotic medication, paliperidone palmitate (marketed as INVEGA Sustenna), used in the treatment of schizophrenia, has been synthesized using the oily palmitate ester as a long-acting release carrier medium when injected intramuscularly. The underlying method of drug delivery is similar to that used with decanoic acid to deliver long-acting depot medication, in particular, neuroleptics such as haloperidol decanoate.
Preparation
Palmitic acid is prepared from Palm kernel oil, Olive oil, Japan wax or Chinese vegetable tallow by saponification of the natural glycerylesters.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 27, p. 2950, 1962 DOI: 10.1021/jo01055a527
Tetrahedron Letters, 17, p. 4697, 1976 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)92999-X
Pharmaceutical Applications
Palmitic acid is used in oral and topical pharmaceutical formulations. Palmitic acid has been used in implants for sustained release of insulin in rats.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Palmitic acid (PA) is a component of membrane phospholipids (PL) and adipose triacylglycerols (TAG). Elevated levels of palmitic acid contributes to the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis, type 2 diabetes mellitus, neurodegenerative diseases, obesity and cancer. PA promotes apoptosis in the endothelial cell by modulating the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and favors expression of TNF-α and reactive oxygen species accumulation. PA promotes interleukin 8 (IL-8) synthesis in hepatocytes contributing to hepatic inflammation. PA by interacting with toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) induces inflammatory injury in cardiomyoctes.
Biotechnological Applications
Excess carbohydrates in the body are converted to palmitic acid. Palmitic acid is the first fatty acid produced during fatty acid synthesis and the precursor to longer fatty acids. Palmitate negatively feeds back on acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), which is responsible for converting acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA, which in turn is used to add to the growing acyl chain, thus preventing further palmitate generation. In biology, some proteins are modified by the addition of a palmitoyl group in a process known as palmitoylation. Palmitoylation is important for membrane localisation of many proteins.
Pharmacokinetics
Palmitic acid is the first fatty acid produced during lipogenesis (fatty acid synthesis) and from which longer fatty acids can be produced. Palmitate negatively feeds back on acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) which is responsible for converting acetyl-ACP to malonyl-ACP on the growing acyl chain, thus preventing further palmitate generation
Safety Profile
A poison by intravenous route. A human skin irritant. Questionable carcinogen with experimental neoplastigenic data. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes
Safety
Palmitic acid is used in oral and topical pharmaceutical formulations
and is generally regarded as nontoxic and nonirritant at the
levels employed as an excipient. However, palmitic acid is reported
to be an eye and skin irritant at high levels and is poisonous by
intravenous administration.
LD50 (mouse, IV): 57 mg/kg
Metabolism
Not Available
Storage
The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry, place.
Purification Methods
Purify palmitic acid by slow (overnight) recrystallisation from hexane. Some samples are also crystallised from acetone, EtOH or EtOAc. The crystals are kept in air to lose solvent, or are pumped dry of solvent on a vacuum line. [Iwahashi et al. J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 1 81 973 1985, pK: White J Am Chem Soc 72 1858 1950, Beilstein 2 IV 1157.]
Incompatibilities
Palmitic acid is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and bases.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral tablets). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK.
Properties of Palmitic acid
| Melting point: | 61-62.5 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 351.5 °C |
| Density | 0.852 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 10 mm Hg ( 210 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4273 |
| FEMA | 2832 | PALMITIC ACID |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | chloroform: 0.5 M, clear, colorless |
| form | Flakes |
| pka | 4.78±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White or almost white |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. slightly waxy fatty |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Merck | 14,6996 |
| JECFA Number | 115 |
| BRN | 607489 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.3(71℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with bases, oxidizing agents, reducing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 57-10-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Hexadecanoic acid(57-10-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Palmitic acid (57-10-3) |
Safety information for Palmitic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Palmitic acid
| InChIKey | IPCSVZSSVZVIGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Palmitic acid manufacturer
Paxal Chemical Industry Private Limited
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 57-10-3 98%View Details
57-10-3 98%View Details
57-10-3 -
 PALMITIC ACID 99%View Details
PALMITIC ACID 99%View Details -
 Palmitic Acid CAS 57-10-3View Details
Palmitic Acid CAS 57-10-3View Details
57-10-3 -
 Palmitic acid CAS 57-10-3View Details
Palmitic acid CAS 57-10-3View Details
57-10-3 -
 Palmitic acid 95% CAS 57-10-3View Details
Palmitic acid 95% CAS 57-10-3View Details
57-10-3 -
 Palmitic acid, for biochemistry CAS 57-10-3View Details
Palmitic acid, for biochemistry CAS 57-10-3View Details
57-10-3 -
 Palmitic Acid CASView Details
Palmitic Acid CASView Details -
 Godrej Palmitic Acid 90 (Fractionated Fatty Acid), Purity: 90% Min., 50 Kg / Bulk ContainerView Details
Godrej Palmitic Acid 90 (Fractionated Fatty Acid), Purity: 90% Min., 50 Kg / Bulk ContainerView Details
57-10-3
