P-XYLENE
Synonym(s):p-Xylene;1;1,4-Dimethylbenzene;Dimethylbenzol;p-Xylene
- CAS NO.:106-42-3
- Empirical Formula: C8H10
- Molecular Weight: 106.17
- MDL number: MFCD00008556
- EINECS: 203-396-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-27 17:16:38
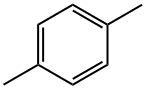
What is P-XYLENE?
Description
p-Xylene was first isolated from a wood distillate in 1850; today it is a widely produced petrochemical. Mixed xylenes are common industrial solvents, but the para isomer is the starting material for terephthalic acid, one of the monomers used in polyester production.?p-Xylene developments in the past 10 years include a method for producing it from toluene and methanol?and its use as an overcharge protectant for lithium ion batteries.
Chemical properties
colourless liquid
Physical properties
Clear, colorless, watery liquid with a sweet odor. Odor threshold concentrations reported in air were 47 ppbv by Leonardos et al. (1969) and 58 ppbv by Nagata and Takeuchi (1990).
The Uses of P-XYLENE
p-Xylene is used as a precursor in the production of benzoic, isophthalic, tetraphillic acids and dimethyle esters, which are used in the manufacture of polyester. It acts as an intermediate in plastic and rubber products.
The Uses of P-XYLENE
As solvent; raw material for production of benzoic acid, phthalic anhydride, isophthalic and terephthalic acids as well as their dimethyl esters used in the manufacture of polyester fibers; manufacture of dyes and other organics; sterilizing catgut; with Canada balsam as oil-immersion in microscopy; clearing agent in microscope technique.
The Uses of P-XYLENE
Xylene occurs in petroleum solvents andgasoline. The widest applications of xyleneare as solvents in paints, coatings, and rubber.Xylene isomers are used in the manufacture ofdyes, drugs, pesticides, and in many organicintermediates, such as terephthalic acid andphthalic anhydride.
What are the applications of Application
p-Xylene is A colorless organic solvent
Definition
ChEBI: A xylene with methyl groups at positions 1 and 4.
Production Methods
Pure p-xylene can be obtained from a mixture of o- and p-xylene by sulfonation and subsequent removal of water-soluble o-xylenesulfonic acid.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 53, p. 3247, 1988 DOI: 10.1021/jo00249a020
Tetrahedron Letters, 26, p. 1935, 1985 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)98345-X
General Description
A colorless watery liquid with a sweet odor. Less dense than water. Insoluble in water. Irritating vapor. Freezing point is 56°F.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
P-XYLENE may react with oxidizing materials. . Acetic acid forms explosive mixtures with P-XYLENE and air (Shraer, B.I. 1970. Khim. Prom. 46(10):747-750.).
Health Hazard
Vapors cause headache and dizziness. Liquid irritates eyes and skin. If taken into lungs, causes severe coughing, distress, and rapidly developing pulmonary edema. If ingested, causes nausea, vomiting, cramps, headache, and coma. Can be fatal. Kidney and liver damage can occur.
Health Hazard
The toxic properties of xylene isomers aresimilar to toluene or ethylbenzene. The targetorgans are the central nervous system, eyes,gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, liver, blood,and skin, which, however, are affected onlyat high levels of exposure. In humans itsexposure may cause irritation of the eyes,nose, and throat, headache, dizziness, excitement,drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, abdominalpain, and dermatitis. The irritation effectsin humans may be felt at a concentration of200 ppm in air, while exposure to 10,000 ppmfor 6–8 hours may be fatal.
The oral toxicity of xylene is low. Ingestionof a high dose, however, can causedepression of the central nervous system,dizziness, nausea, and vomiting and abdominalpain. The oral LD50 values in ratsfor xylene isomers are within the range of5000 mg/kg.
The major route of absorption of xyleneis inhalation. Another significant route isskin absorption of the liquid. About 5% ofabsorbed xylene is excreted unchanged inexpired air within a few hours, while less than2% is hydroxylated to xylenols. Over 90% ofabsorbed xylenes are metabolized to o-, m-,and p-isomers of methyl benzoic acid andexcreted in urine as methyl hippuric acids(ACGIH 1986). Small amounts of xylenesmay remain stored in adipose tissue. Repeatedexposures may cause accumulation in theblood.
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: Vapor is heavier than air and may travel considerable distance to a source of ignition and flash back.
Flammability and Explosibility
Flammable
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reaction; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Mildly toxic by ingestion and inhalation. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. May be narcotic in hgh concentrations. Chronic toxicity not established, but is less toxic than benzene. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxidzing materials. Explosive in the form of vapor when exposed to heat or flame. To fight fire, use foam, CO2, dry chemical. Potentially explosive reaction with acetic acid + air, 1,3-dichloro-5,5-dimethyl-2,4- imidazolidinhone, nitric acid + pressure. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also other xylene entries.
Source
Detected in distilled water-soluble fractions No. 2 fuel oil (1.11 mg/L), jet fuel A (1.23
mg/L), diesel fuel (0.56 mg/L), and military jet fuel JP-4 (5.48 mg/L) (Potter, 1996); in new and
used motor oil at concentrations of 0.26 to 0.29 and 302 to 339 μg/L, respectively (Chen et al.,
1994). The average volume percent and estimated mole fraction in American Petroleum Institute
PS-6 gasoline are 1.809 and 0.02263, respectively (Poulsen et al., 1992). Diesel fuel obtained from
a service station in Schlieren, Switzerland contained m/p-xylene at a concentration of 336 mg/L
(Schluep et al., 2001).
Thomas and Delfino (1991) equilibrated contaminant-free groundwater collected from
Gainesville, FL with individual fractions of three individual petroleum products at 24–25 °C for
24 h. The aqueous phase was analyzed for organic compounds via U.S. EPA approved test method
602. Average m+p-xylene concentrations reported in water-soluble fractions of unleaded gasoline,
kerosene, and diesel fuel were 8.611, 0.658, and 0.228 mg/L, respectively. When the authors
analyzed the aqueous-phase via U.S. EPA approved test method 610, average m+p-xylene
concentrations in water-soluble fractions of unleaded gasoline, kerosene, and diesel fuel were
lower, i.e., 6.068, 0.360, and 0.222 mg/L, respectively.
Based on laboratory analysis of 7 coal tar samples, m+p-xylene concentrations ranged from ND
to 6,000 ppm (EPRI, 1990). Detected in 1-yr aged coal tar film and bulk coal tar at concentrations
of 260 and 830 mg/kg, respectively (Nelson et al., 1996). A high-temperature coal tar contained pxylene
at an average concentration of 0.03 wt % (McNeil, 1983).
Schauer et al. (2001) measured organic compound emission rates for volatile organic
compounds, gas-phase semi-volatile organic compounds, and particle-phase organic compounds
from the residential (fireplace) combustion of pine, oak, and eucalyptus. The gas-phase emission
rate of m-xylene + p-xylene was 60.0 mg/kg of pine burned. Emission rates of both isomers were
not measured during the combustion of oak and eucalyptus.
Drinking water standard (final): For all xylenes, the MCLG and MCL are both 10 mg/L. In
addition, a DWEL of 70 mg/L was recommended (U.S. EPA, 2000).
Environmental Fate
Biological. Microbial degradation of p-xylene produced 4-methylbenzyl alcohol, pmethylbenzaldehyde,
p-toluic acid, and 4-methylcatechol (quoted, Verschueren, 1983). Dimethylcis,
cis-muconic acid, and 2,3-dihydroxy-p-toluic acid were reported to be biooxidation products of
p-xylene by Nocardia corallina V-49 using n-hexadecane as the substrate (Keck et al., 1989).
Reported biodegradation products of the commercial product containing xylene include
α-hydroxy-p-toluic acid, p-methylbenzyl alcohol, benzyl alcohol, 4-methylcatechol, m- and ptoluic
acids (Fishbein, 1985). It was reported that p-xylene was cometabolized resulting in the
formation of p-toluic and 2,3-dihydroxy-o-toluic acids (Pitter and Chudoba, 1990). In anoxic
groundwater near Bemidji, MI, p-xylene anaerobically biodegraded to the intermediate p-toluic
acid (Cozzarelli et al., 1990). In gasoline-contaminated groundwater, methylbenzylsuccinic acid
was identified as the first intermediate during the anaerobic degradation of xylenes (Reusser and
Field, 2002).
Photolytic. A n-hexane solution containing m-xylene and spread as a thin film (4 mm) on cold
water (10 °C) was irradiated by a mercury medium pressure lamp. In 3 h, 18.5% of the p-xylene
photooxidized into p-methylbenzaldehyde, p-benzyl alcohol, p-benzoic acid, and pmethylacetophenone
(Moza and Feicht, 1989). Glyoxal and methylglyoxal were produced from
the photooxidation of p-xylene by OH radicals in air at 25 °C (Tuazon et al., 1986a). The rate
constant for the reaction of p-xylene and OH radicals at room temperature was 1.22 x 10-11
cm3/molecule?sec (Hansen et al., 1975). A rate constant of 7.45 x 10-9 L/molecule?sec was reported
for the reaction of p-xylene with OH radicals in the gas phase (Darnall et al., 1976). Similarly, a
room temperature rate constant of 1.41 x 10-11 cm3/molecule?sec was reported for the vapor-phase
reaction of p-xylene with OH radicals (Atkinson, 1985). At 25 °C, a rate constant of 1.29 x 10-11
cm3/molecule?sec was reported for the same reaction (Ohta and Ohyama, 1985).
Chemical/Physical. Under atmospheric conditions, the gas-phase reaction with OH radicals and
nitrogen oxides resulted in the formation of p-tolualdehyde (Atkinson, 1990). Kanno et al. (1982)
studied the aqueous reaction of p-xylene and other aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene, toluene, oand
m-xylene, and naphthalene) with hypochlorous acid in the presence of ammonium ion. They
reported that the aromatic ring was not chlorinated as expected but was cleaved by chloramine
forming cyanogen chloride. The amount of cyanogen chloride formed increased at lower pHs
(Kanno et al., 1982). Products identified from the OH radical-initiated reaction of p-xylene in the
presence of nitrogen dioxide were 3-hexene-2,5-dione, p-tolualdehyde, and 2,5-dimethylphenol
(Bethel et al., 2000).
Purification Methods
The general purification methods listed for xylene above are applicable. p-Xylene can readily be separated from its isomers by crystallisation from such solvents as MeOH, EtOH, isopropanol, acetone, butanone, toluene, pentane or pentene. It can be further purified by fractional crystallisation by partial freezing, and stored over sodium wire or molecular sieves Linde type 4A. [Stokes & French J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 1 76 537 1980, Beilstein 5 H 382, 5 I 185, 5 II 296, 5 III 845, 5 IV 951.]
Properties of P-XYLENE
| Melting point: | 12-13 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 138 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.861 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.7 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 9 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 77 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | water: soluble0.2g/L |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | >15 (Christensen et al., 1975) |
| color | Colorless |
| Odor | Like benzene; characteristic aromatic. |
| Relative polarity | 0.074 |
| explosive limit | 1.1-7%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 0.058ppm |
| Water Solubility | Miscible with alcohol, ether, acetone, benzene and chloroform. Immiscible with water. |
| λmax | λ: 294 nm Amax: 1.00 λ: 320 nm Amax: 0.10 λ: 350 nm Amax: 0.05 λ: 380-400 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| Merck | 14,10081 |
| BRN | 1901563 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 16.1 at 45.00 °C, 18.6 at 50.00 °C, 20.3 at 55.00 °C, 23.4 at 60.00 °C, 30.5 at 70.00 °C (static
headspace-GC, Park et al., 2004) |
| Dielectric constant | 2.6(20℃) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA100 ppm (~434 mg/m3) (ACGIH,
MSHA, and OSHA); STEL 150 ppm
(~651 mg/m3) (ACGIH); ceiling 200 ppm/
10 min (NIOSH); IDLH 1000 ppm (NIOSH). |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents. Hygroscopic. Flammable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 106-42-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | p-Xylene (106-42-3) |
Safety information for P-XYLENE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H304:Aspiration hazard H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P331:Do NOT induce vomiting. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. |
Computed Descriptors for P-XYLENE
| InChIKey | URLKBWYHVLBVBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
P-XYLENE manufacturer
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 P-XYLENE 106-42-3 99%View Details
P-XYLENE 106-42-3 99%View Details
106-42-3 -
 p-Xylene CAS 106-42-3View Details
p-Xylene CAS 106-42-3View Details
106-42-3 -
 p-Xylene CAS 106-42-3View Details
p-Xylene CAS 106-42-3View Details
106-42-3 -
![p-Xylene [Tag Closed Flash Point Check Fluid] CAS 106-42-3](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) p-Xylene [Tag Closed Flash Point Check Fluid] CAS 106-42-3View Details
p-Xylene [Tag Closed Flash Point Check Fluid] CAS 106-42-3View Details
106-42-3 -
 p-Xylene CAS 106-42-3View Details
p-Xylene CAS 106-42-3View Details
106-42-3 -
 p-Xylene CAS 106-42-3View Details
p-Xylene CAS 106-42-3View Details
106-42-3 -
 p-XYLENE For Synthesis CAS 106-42-3View Details
p-XYLENE For Synthesis CAS 106-42-3View Details
106-42-3 -
 p-Xylene CAS 106-42-3View Details
p-Xylene CAS 106-42-3View Details
106-42-3
