oxyphenisatine di(acetate)
- CAS NO.:115-33-3
- Empirical Formula: C24H19NO5
- Molecular Weight: 401.41
- EINECS: 204-083-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
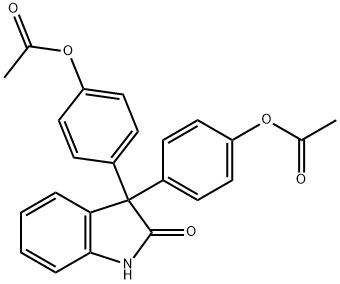
What is oxyphenisatine di(acetate)?
Originator
Lavema,Winthrop,US,1959
The Uses of oxyphenisatine di(acetate)
Laxative.
The Uses of oxyphenisatine di(acetate)
Oxyphenisatin Diacetate is the pro-drug of Oxyphenisatin (O876965). Results confirm that Oxyphenisatin Diacetate inhibits the growth of breast cancer cell lines MCF7, T47D, HS578T, and MDA-MB-468.
Background
Oxyphenisatin acetate is the pro-drug of oxyphenisatin (3,3-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1H-indol-2-one). The FDA withdrew its approval for the use of oxyphenisatin acetate due to safety reasons.
Definition
ChEBI: Oxyphenisatine acetate is a member of phenols and a benzoate ester.
Manufacturing Process
235 gravimetrical parts of acetic acid anhydride (90%) are poured over 106 gravimetrical parts of diphenolisatin (Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesselschsft, 18, 1885, p. 2641) and the mixture is heated on the water-bath while stirring. The solid starting material temporarily dissolves almost entirely and shortly afterwards the reaction product turns into a crystalline paste. In order to complete the reaction the heating on the water-bath is continued for a short time and then the whole is left to get cold. The reaction product may, for instance, be separated in the following manner: To the cold reaction mixture is gradually added about the same volumetrical quantity of alcohol; in this manner the excess of acetic acid anhydride is destroyed and the paste becomes thinner. Then the fluid is drawn off and the product washed with alcohol. For complete cleansing another extraction is made with warm alcohol and the product crystallized, for instance, from 10 parts of acetic acid. The product represents a light, fine crystalline powder, which is difficultly soluble or even insoluble in the usual organic solvents. Its melting point lies at 242°C.
brand name
Isocrin (Parke-Davis); Lavema (Sterling Winthrop);Acelax;Acetalax;Alophen pills;Ameiax;Api-slender;Artzone;Belloform;Biivectan;Bisflatan;Boxogetten;Brocatine;Buta pirone;Buteril;Butofen;Butolfen;Bydolax;Chlofel;Chur-lax;Ciracen;Cirotex;Cirotyl;Contax;Critex;Curolax;Darmoletten;Deililax;Dialose plus;Diasatin;Ditinil;Ditmedol;Eulaxin;Evac-u-lax;Ex-lax pills;Febutolo;Fibutrox;Fim-a-mint;Fin-a-mint gum;Fisiolax;Flib 518;Inlax;Ipebutona;Isaaxan;Isaphenyn;Izaman;Laveman;Laxan-vomoxin;Laxaseptol;Laxem;Laxnormal;Laxocoleva;Laxon;Laxos;Laxyl;Med-laxan;Menabil complex;Muxol;Naleran;Neocervulax;Neo-favmadol;Neo-soldana;Nourilax;Nurilaksi;Obstilax;Otone;Oxybutazone;Phlogase;Phlogistol;Phlogont;Potsilo;Promassoletten;Prusol;Rheumapax;Rivolax;Schokilax;Syndian;Tanderil-alka;Tete-lax;Validil.
Therapeutic Function
Laxative
World Health Organization (WHO)
Oxyphenisatine acetate was widely used as a laxative after its cathartic activity was first described in 1925. In 1969 its use was first associated with cases of acute and chronic liver disease. This association is considered by some, but not all, national drug regulatory authorities to warrant the withdrawal from the market of preparations containing oxyphenisatine and its derivatives.
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of oxyphenisatine di(acetate)
| Melting point: | 244℃ |
| Boiling point: | 566.5±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.282±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), Methanol (Slig |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 13.55±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
Safety information for oxyphenisatine di(acetate)
Computed Descriptors for oxyphenisatine di(acetate)
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1