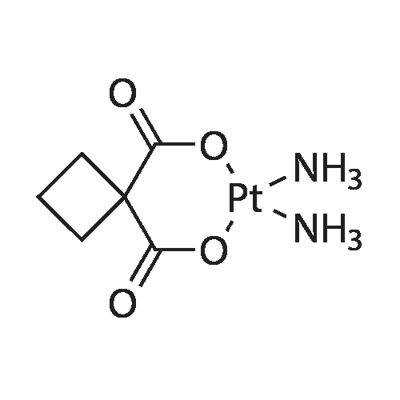
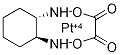
Oxaliplatin
Synonym(s):[SP-4-2-(1R-trans)]-(1,2-Cyclohexanediamine-N,N′)[ethanedioata(2--)-O,O’]platinum;Oxaliplatin
- CAS NO.:61825-94-3
- Empirical Formula: C8H12N2O4Pt
- Molecular Weight: 395.28
- MDL number: MFCD00866327
- EINECS: 621-248-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 08:49:36

What is Oxaliplatin?
Absorption
The reactive oxaliplatin derivatives are present as a fraction of the unbound platinum in plasma ultrafiltrate. After a single 2-hour intravenous infusion of oxaliplatin at a dose of 85 mg/m2, pharmacokinetic parameters expressed as ultrafiltrable platinum was Cmax of 0.814 mcg/mL. Interpatient and intrapatient variability in ultrafiltrable platinum exposure (AUC0-48hr) assessed over 3 cycles was 23% and 6%, respectively.
Toxicity
The maximum dose of oxaliplatin that has been administered in a single infusion is 825 mg. Several cases of overdoses have been reported with oxaliplatin. Adverse reactions observed following an overdosage were grade 4 thrombocytopenia (less than 25,000/mm3) without bleeding, anemia, sensory neuropathy (including paresthesia, dysesthesia, laryngospasm, and facial muscle spasms), gastrointestinal disorders (including nausea, vomiting, stomatitis, flatulence, abdomen enlarged and grade 4 intestinal obstruction), grade 4 dehydration, dyspnea, wheezing, chest pain, respiratory failure, severe bradycardia, and death. Closely monitor patients suspected of receiving an overdose, including for the adverse reactions described above, and administer appropriate supportive treatment.
Based on its direct interaction with DNA, ELOXATIN can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. The available human data do not establish the presence or absence of major birth defects or miscarriages related to the use of oxaliplatin. Reproductive toxicity studies demonstrated adverse effects on embryo-fetal development in rats at maternal doses that were below the recommended human dose based on body surface area. Advise a pregnant woman of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the adjuvant treatment trial, 400 patients who received oxaliplatin with fluorouracil/leucovorin were greater than or equal to 65 years. The effect of oxaliplatin in patients greater than or equal to 65 years was not conclusive. Patients greater than or equal to 65 years receiving ELOXATIN experienced more diarrhea and grade 3-4 neutropenia (45% vs 39%) compared to patients less than 65 years.
The AUC of unbound platinum in plasma ultrafiltrate was increased in patients with renal impairment. No dose reduction is recommended for patients with mild (creatinine clearance 50 to 79 mL/min) or moderate (creatinine clearance 30 to 49 mL/min) renal impairment, calculated by Cockcroft-Gault equation. Reduce the dose of oxaliplatin in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min).
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of oxaliplatin. Oxaliplatin was not mutagenic to bacteria (Ames test) but was mutagenic to mammalian cells in vitro (L5178Y mouse lymphoma assay). Oxaliplatin was clastogenic both in vitro (chromosome aberration in human lymphocytes) and in vivo (mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay).
In a fertility study, male rats were given oxaliplatin at 0, 0.5, 1, or 2 mg/kg/day for five days every 21 days for a total of three cycles prior to mating with females that received two cycles of oxaliplatin on the same schedule. A dose of 2 mg/kg/day (less than one-seventh the recommended human dose on a body surface area basis) did not affect the pregnancy rate but resulted in 97% postimplantation loss (increased early resorptions, decreased live fetuses, decreased live births), and delayed growth (decreased fetal weight).
Testicular damage, characterized by degeneration, hypoplasia, and atrophy, was observed in dogs administered oxaliplatin at 0.75 mg/kg/day (approximately one-sixth of the recommended human dose on a body surface area basis) × 5 days every 28 days for three cycles. A no-effect level was not identified.
Description
Oxaliplatin is a second generation platinum drug prepared in three steps from either k2tCl4 or K2Ptl4. It has an antitumor spectrum similar to cisplatin, however, it is more effective against L1210 leukemia and cisplatin resistant L1210. It is also effective against B16 melanoma but has a dose limiting toxicity of peripheral sensory neuropathy that is reversible upon cessation of the drug. The (R,R)- enantiomer has greater activity than the (S,S)-isomer but this is tumor line dependent, e.g., there was no difference found for P-388 or Sarcoma 180. Clinical drug administration based on circadium timing showed it was better tolerated when given 16 h after the onset of light. Oxaliplatin binds to guanineN7 and can lead to bidentate chelation that results in the bending of DNA. This feature is recognized by high mobility group proteins (HMG) which impedes repair reactions and stops replication and transcription.
Chemical properties
White Crystalline Solid
Originator
Bebiopharm (Switzerland)
The Uses of Oxaliplatin
Third generation platinum complex. An antitumor agent with activity against colorectal cancer. Cytotoxicity follows the formation of adducts with DNA. Antineoplastic.
The Uses of Oxaliplatin
A potent anti-neoplastic agent that binds to DNA and shows efficacy in Cisplatin resistant cell lines
The Uses of Oxaliplatin
Oxaliplatin is a platinum-based antineoplastic agent that functions by forming DNA adducts specifically in cancer cells, preventing DNA replication and transcription which leads to cell death. Oxaliplatin has cytotoxic effects in a broad range of cell lines, including colon, ovarian, and lung cancer, with IC50 values ranging from 0.5-240, 0.12-19.8, and 2.6-6.1 μM, respectively. Through its general cytotoxic effects, oxaliplatin has anti-tumor activity against advanced colorectal cancer and is typically administered with fluorouracil and leucovorin in a combination known as FOLFOX.
Background
Oxaliplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapy drug in the same family as cisplatin and carboplatin. Compared to cisplatin the two amine groups are replaced by diamino cyclohexane (DACH) group to provide a greater antitumor effect. However, this leads to poorer water solubility, which was compensated by the addition of the chloride moieties. Due to this chemical moiety, oxaliplatin readily undergoes non-enzymatic biotransformation, thus complicating oxaliplatin's pharmacokinetics. Like most platinum-based compounds, oxaliplatin's mechanism of action is primarily through DNA damage through DNA crosslinking, particularly intrastrand and interstrand crosslinking. However, due to the structure of oxaliplatin, its adducts make the binding of mismatch repair protein to DNA harder compared to cisplatin or carboplatin's adducts, resulting in greater cytotoxic effects. The DACH moiety also prevents cross-resistance with cisplatin and carboplatin.
Although oxaliplatin has been investigated as a monotherapy, it is typically administered in combination with fluorouracil and leucovorin, known as the FOLFOX regimen, for the treatment of colorectal cancer. This is an effective combination treatment both as a first-line treatment and in patients refractory to an initial fluorouracil and leucovorin combination. Ongoing trials have also shown promising results for oxaliplatin use in nonHodgkin’s lymphoma, breast cancer, mesothelioma, and non-small cell lung cancer.
Oxaliplatin was approved by the FDA on January 9, 2004 and is currently marketed by Sanofi-Aventis under the trademark Eloxatin?.
Indications
Oxaliplatin, in combination with infusional fluorouracil and leucovorin, is indicated for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer and adjuvant treatment of stage III colon cancer in patients who have undergone complete resection of the primary tumor.
What are the applications of Application
Oxaliplatin is a potent anti-neoplastic agent that binds to DNA and shows efficacy in Cisplatin resistant cell lines
Indications
Oxaliplatin, also called Eloxatin or Eloxatine, is a platinum derivative. Used clinically to treat patients with metastatic colorectal cancer after failure of fluorouracil treatment, can be used alone or in combination with 5-fluorouracil. It is the third-generation platinum antitumor compound after cisplatin and carboplatin, and so far the only platinum-based drug with significant effectiveness against colorectal cancer. It also inhibits proliferation of ovarian cancer and melanoma cell lines.
brand name
Eloxatin (Sanofi Aventis).
General Description
Oxaliplatin is available in 50- and 100-mg vials for IV administrationin the treatment of ovarian cancer, metastaticcolorectal cancer, and early stage colon cancer in combinationwith 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin. The activation of theagent occurs in low-chloride environments to give theaquated species, which subsequently reacts with DNA in amanner similar to cisplatin. The mechanisms of resistance aresimilar for the two agents; however, oxaliplatin is not recognizedby MMR enzymes and does not show cross-resistancewith cisplatin. The agent is widely distributed, highly proteinbound (85%–88%), and irreversibly binds to erythrocytes.Numerous metabolites have been identified many of whichare produced as a result of nonenzymatic processes and includechloro-, dichloro-, monoaquo-, and diaquo-species.The parent and metabolites are eliminated primarily in theurine with a long terminal elimination half-life of 240 hours.Neurotoxicity is dose limiting and normally presents as peripheralneuropathy, which may be exacerbated by exposureto low temperatures. The neurotoxicity is normally reversiblein contrast to that seen with cisplatin, which may be irreversible.Other adverse effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,myelosuppression, and hypersensitivity reactions.Ototoxicity and renal toxicity occur only rarely in contrast tocisplatin.
Biological Activity
Oxaliplatin is a platinum-containing DNA-crosslinking agent. It induces the formation of DNA inter- and intrastrand crosslinks and DNA-protein crosslinks, inhibits DNA and RNA synthesis, and induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Oxaliplatin is cytotoxic to cisplatin-sensitive A2780(1A9) and KB-3-1 cells and cisplatin-resistant A2780-E(80) and KB-CP20 cells (IC50s = 0.12, 0.39, 4.7, and 2.7 μM, respectively). It reduces tumor growth in an HCCLM3 mouse xenograft model when administered at doses of 5 or 10 mg/kg once per week. Formulations containing oxaliplatin have been used in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer and as an adjuvant in stage III colon cancer.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Oxaliplatin a platinum analogue, causes DNA damage and cell death by binding to DNA and forming inter and intrastrand crosslinks preventing replication and transcription. Oxaliplatin is an anti-tumor agent with activity against colorectal cancer; cytotoxicity follows the formation of adducts with DNA. Oxaliplatin is an approved drug for treating colorectal cancer. It is an active ingredient in FOLFOX (Folinic acid:5-FU:oxaliplatin in the ratio 1:10:1 of micromolar concentrations respectively). Oxaliplatin causes both acute and chronic neurotoxicity in patients in a dose dependent manner and is reversible either by reducing or stopping the drug.
Pharmacokinetics
In vivo studies have shown antitumor activities of oxaliplatin against colon carcinoma. In combination with fluorouracil, oxaliplatin exhibits in vitro and in vivo antiproliferative activity greater than either compound alone in several tumor models (HT29 [colon], GR [mammary], and L1210 [leukemia]).
Side Effects
Hematopoietec system: Oxaliplatin has a certain blood toxicity. When used alone, it can cause the following adverse effects: anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, sometimes reaching grade 3 or 4. Increases hematologic toxicities such as neutropenia and thrombocytopenia when combined with 5-fluorouracil.
Digestive system: can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea when used alone. These symptoms can sometimes be very serious. These side effects are significantly exacerbated when used in combination with 5-fluorouacil. Use of prophylactic and/or therapeutic antiemetic drugs is recommended.
Nervous system: Peripheral sensory neuropathy characterized by peripheral neuritis. Sometimes associated with convulsions and sensory disturbances in the mouth, upper respiratory tract, and upper GI tract.
Safety Profile
A poison by intraperitoneal route. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of NOx and Pt.
Synthesis
An aqueous solution of 5 g of (1R,2R)-(-)-1,2-DiaMinocyclohexane and 18 g of K2(PtCl4) was reacted for 12 h at room temperature to give 12 g of compound (I). 6: 8 g of silver nitrate was added to an aqueous solution of 3 g of compound (I) and stirred for 2-3 h away from light, then 4.8 g of dipotassium oxalate was added and the reaction was carried out for 8 h at room temperature to give oxaliplatin.
in vitro
oxaliplatin is active against human melanoma cell lines c32 and g361 with the ic50 values of 0.98 mm and 0.14 mm, respectively. oxaliplatin effectively inhibited bladder carcinoma cell lines rt4 and tccsup, ovarian carcinoma cell line a2780, colon carcinoma cell line ht-29, glioblastoma cell lines u-87mg and u-373mg, and melanoma cell lines sk-mel-2 and ht-144 with the ic50 values of 11 μm, 15 μm, 0.17 μm, 0.97 μm, 17.6 μm, 2.95 μm, 30.9 μm and 7.85 μm, respectively.
in vivo
a weekly injection of oxaliplatin (10 mg/kg, i.p.) to nude mice bearing hepatocellular hcclm3 tumors significantly reduces tumor volume and apoptotic index. oxaliplatin (5 mg/kg, i.v. on days 1, 5 and 9) was active on t-leukemia-lymphoma l40 akr with t/c of 1.77. oxaliplatin was also efficient on intracerebrally grafted l1210 leukemia, b16 melanoma xenografts, ma 16-c xenografts, lewis lung xenografts and c26 colon carcinoma xenografts. oxaliplatin induced impairment of retrograde neuronal transport in mice.
Metabolism
Oxaliplatin undergoes rapid and extensive nonenzymatic biotransformation. There is no evidence of cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism in vitro. Up to 17 platinum-containing derivatives have been observed in plasma ultrafiltrate samples from patients, including several cytotoxic species (monochloro DACH platinum, dichloro DACH platinum, and monoaquo and diaquo DACH platinum) and a number of noncytotoxic, conjugated species.
Storage
Store at +4°C
Mode of action
Oxaliplatin, a platinum derivative, is an alkylating agent. Acts on DNA through production of alkylating conjugates, inhibiting its synthesis and reproduction by forming interchain and intrachain cross-links. Following intracellular hydrolysis, the platinum compound binds to DNA forming cross-links which inhibit DNA replication and transcription, resulting in cell death.
References
[1]. culy cr, clemett d, wiseman lr. oxaliplatin.a review of its pharmacological properties and clinical efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer and its potential in other malignancies.drugs. 2000 oct;60(4):895-924.
[2]. raymond e, faivre s, chaney s et al. cellular and molecular pharmacology of oxaliplatin. mol cancer ther. 2002 jan;1(3):227-35.
[3]. stein a, arnold d. oxaliplatin: a review of approved uses. expert opin pharmacother. 2012 jan;13(1):125-37.
[4]. hoff pm, saad ed, costa f et al. literature review and practical aspects on the management of oxaliplatin-associated toxicity. clin colorectal cancer. 2012 jun;11(2):93-100.
[5]. hall md, et al. say no to dmso: dimethylsulfoxide inactivates cisplatin, carboplatin, and other platinum complexes. cancer res. 2014 jul 15;74(14):3913-22.
Properties of Oxaliplatin
| alpha | +74.5-78.0 (D/20)(c=0.5,H2O) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Slightly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in methanol, practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol. |
| form | solid |
| color | White to Almost white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water with heating and/or sonication |
| Merck | 14,6912 |
| Stability: | Stable. Store cool. Incompatible with oxidizing agents. |
| InChI | InChI=1/C6H12N2.C2H2O4.Pt/c7-5-3-1-2-4-6(5)8;3-1(4)2(5)6;/h5-8H,1-4H2;(H,3,4)(H,5,6);/q-2;;+4/p-2/t5-,6-;;/s3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 61825-94-3 |
Safety information for Oxaliplatin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H340:Germ cell mutagenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Oxaliplatin
| InChIKey | ZROHGHOFXNOHSO-BNTLRKBRSA-L |
| SMILES | O=C1C([O-][Pt+2]2(N[C@]3([H])CCCC[C@@]3([H])N2)[O-]1)=O |&1:6,12,r| |
Oxaliplatin manufacturer
Kromozome
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 61825-94-3 98%View Details
61825-94-3 98%View Details
61825-94-3 -
 Oxaliplatin CAS 61825-94-3View Details
Oxaliplatin CAS 61825-94-3View Details
61825-94-3 -
 Oxaliplatin CAS 61825-94-3View Details
Oxaliplatin CAS 61825-94-3View Details
61825-94-3 -
 Oxaliplatin 98% CAS 61825-94-3View Details
Oxaliplatin 98% CAS 61825-94-3View Details
61825-94-3 -
 Oxaliplatin CAS 61825-94-3View Details
Oxaliplatin CAS 61825-94-3View Details
61825-94-3 -
 Oxaliplatin CAS 61825-94-3View Details
Oxaliplatin CAS 61825-94-3View Details
61825-94-3 -
 Oxaliplatin Chemical, Grade Standard: MedicineView Details
Oxaliplatin Chemical, Grade Standard: MedicineView Details
61825-94-3 -
 Oxaliplatin API PowderView Details
Oxaliplatin API PowderView Details
132539-06-1
