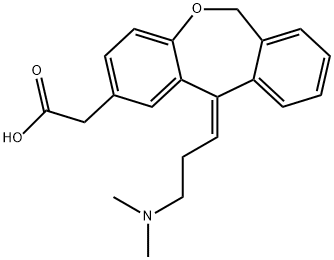
Olopatadine
- CAS NO.:113806-05-6
- Empirical Formula: C21H23NO3
- Molecular Weight: 337.41
- MDL number: MFCD00865645
- EINECS: 810-050-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-07-04 14:25:36
What is Olopatadine?
Absorption
Ocular administration of olopatadine in healthy subjects resulted in the Cmax of 1.6 ± 0.9 ng/mL, which was reached after about 2.0 hours. The AUC was 9.7 ± 4.4 ngxh/mL.
The average absolute bioavaiability of intranasal olopatadine is about 57%. Following intranasal administration in healthy subjects, the Cmax of 6.0 ± 8.99 ng/mL at steady-state was reached between 30 minutes to 1 hour after twice daily intranasal administration. The average AUC was 66.0 ± 26.8 ng·h/mL. In patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis, the Cmax of 23.3 ± 6.2 ng/mL at steady-state was reached between 15 minutes and 2 hours post-dosing and the average AUC was 78.0 ± 13.9 ng·h/mL.
Toxicity
Based on the findings of an acute toxicity study in animals, the oral LD50 of olopatadine was >1150 mg/kg in mice and >3870 mg/kg in rats. The Lowest published toxic dose via the oral route was 20 mg/kg in rat and 0.1 mg/kg in mouse.
There are no known reports on overdosage following oral, ophthalmic, or intranasal administration of olopatadine. Likely symptoms of antihistamine overdose may include drowsiness in adults and, initially, agitation and restlessness, followed by drowsiness in children. In case of suspected overdose, supportive and symptomatic treatment is recommended.
Description
Olopatadine belongs to a kind of antihistamine reagent. It is a relatively selective H1-receptor antagonist and can inhibit the histamine release process from the mast cell, subsequently leading to temporary relief on the negative symptoms associated with histamine. It is devoid of effects on alpha-adrenergic, dopamine and muscarinic type I and II receptors. Its 0.1% solution can be used for topical administration to the eyes. It is indicated for the treatment of itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis.
Originator
Patanol,Alcon,UK
The Uses of Olopatadine
Olopatadine is a dual acting histamine H1-receptor antagonist and mast cell stabilizer. Antiallergic; antihistaminic.
The Uses of Olopatadine
Anti-allergic.
Background
Olopatadine is a selective histamine H1 antagonist and mast cell stabilizer that works by attenuating inflammatory and allergic reactions. It is a structural analog of doxepin, which has a minimal anti-allergic activity. Olopatadine works by blocking the effects of histamine, which is a primary inflammatory mediator that causes inflammatory and allergic reactions. An ophthalmic solution of olopatadine was approved by the FDA and European Union for the treatment of seasonal and perennial allergic conjunctivitis in 1996 and 2002, respectively. In comparison to other anti-allergenic ophthalmic medications, olopatadine displays a good comfort and tolerability profile since it does not cause perturbation of cell membranes. Olopatadine is used for the symptomatic treatment of ocular itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis in ophthalmic formulations and seasonal allergic rhinitis in intranasal formulations. It is currently marketed under several brand names, including Pazeo, Patanase, and Opatanol.
Indications
Olopatadine is indicated for the symptomatic treatment of ocular itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis as ophthalmic solution.
As a nasal spray, as a monotherapy or in combination with mometasone furoate, olopatadine is indicated for the symptomatic relief of seasonal allergic rhinitis in patients 12 years of age and older.
Definition
ChEBI: 2-[11-[3-(dimethylamino)propylidene]-6H-benzo[c][1]benzoxepin-2-yl]acetic acid is a heterotricyclic compound.
Manufacturing Process
402.4 g of phthalide and 200 g of sodium chloride and equal molecular
quantity of p-hydroxyphenyl acetic acid are mixed with one another and
stirred at 150°C for 6 hours. After completion of the reaction, the mixture is
cooled until the temperature is brought back to room temperature, 4 L of
aqueous 10% acetic acid solution is added thereto and the mixture is allowed
to stand at room temperature overnight. After stirring the mixture at room
temperature for 3 hours, deposited crystals are separated by filtration, and 6
L of water is added thereto. After stirring the mixture at room temperature for
30 minutes, the deposited crystals are separated by filtration. After the
addition of 3 L of toluene to the crystals, the mixture is stirred at room
temperature for one hour. The crystals are separated by filtration and dried
over heating under reduced pressure to yield of 2-(4-acetoxyphenoxy)benzoic
acid.
266.0 g of trifluoroacetic anhydride is added to the equal molecular quantity
of 2-(4-acetoxyphenoxy)benzoic acid suspended in 5.0 L of methylene chloride
and thereto. After stirring the mixture at room temperature for one hour, 19.4
g of boron trifluoride-ethylether complex is added thereto and the mixture is
stirred at room temperature for two hours. The reaction solution is poured
into ice water. After an organic solvent layer is separated from the mixture,
the organic layer is washed with diluted aqueous sodium hydroxide solution
and water, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and concentrated under
reduced pressure to obtain 335.3 g of methyl 11-oxodibenz[b,e]oxepin-2-
carboxylate as a white crystal melting point 130°-132°C
Methyl 11-methylene-6,11-dihydrodibenz-[b,e]oxepin-2-acetate.
In 100 ml of tetrahydrofuran is suspended 25 g of
methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide and 40 ml of 1.6 N n-butyl lithium
hexane solution is dropwise added thereto under a nitrogen atmosphere and
ice-cooling. After stirring the mixture under ice-cooling for 30 minutes, a
solution obtained by dissolving equal molar quantity of 11-oxo-6,11-
dihydrodibenz[b,e]oxepin-2-acetic acid in 250 ml of tetrahydrofuran is
dropwise added thereto and the mixture is stirred at room temperature for
two hours. The solvent is distilled away under reduced pressure and the
residue is purified by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent:
hexane:ethyl acetate = 3:1) to obtain the desired product as a colorless oily matter.
brand name
Patanol (Alcon).
Therapeutic Function
Antiallergic
Pharmacokinetics
Inflammatory reactions in response to various stimuli are mediated by endogenous mediators and other pro-inflammatory factors. Histamine receptor activation and mast cell degranulation are primary mechanisms that cause inflammatory reactions such as ocular itching, hyperemia, chemosis, eyelid swelling, and tearing of seasonal allergic conjunctivitis. Olopatadine is an anti-allergenic molecule and mast cell stabilizer that inhibits the in vivo type 1 immediate hypersensitivity reaction. By blocking the effects of histamine, olopatadine works to reduce the symptoms of allergies and inflammation at various sites of administration, including the eyes and nose. It has shown to exert antihistaminic effects in isolated tissues, animal models, and humans. Olopatadine also demonstrated dose-dependent inhibition of immunologically-stimulated release of histamine from rat basophilic leukemia cells and human conjunctival mast cells in vitro. Olopatadine has a relatively rapid onset of action and prolonged duration, where it was shown to mediate anti-histaminic effects at 5 minutes to 24 hours post-administration.
While olopatadine is a non-sedating antihistamine agent, there have been reports of somnolence in some patients taking nasal olopatadine during clinical trials. Temporary blurred vision or other visual disturbances were observed following ophthalmic administration. Olopatadine has negligible effects on alpha-adrenergic, dopamine, muscarinic type 1 and 2, and serotonin receptors. In clinical trials, there was no evidence of any effect of olopatadine on QT prolongation was observed following intranasal administration.
Metabolism
Olopatadine undergoes hepatic metabolism in a non-extensive manner. Based on oral pharmacokinetic studies, there are at least 6 circulating metabolites in human plasma. Following topical ocular application of olopatadine, olopatadine N-oxide is formed by metabolism catalyzed by flavin-containing monooxygenase (FMO) 1 and 3 and was detected in the plasma after 4 hours post-dosing in less than 10% of the total plasma in half of the patients. Mono-desmethyl olopatadine, or N-desmethyl olopatadine, is formed by CYP3A4 and may be detected in minimal levels.
References
https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00768
http://www.rxlist.com/patanol-drug/clinical-pharmacology.htm
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Olopatadine
Properties of Olopatadine
| Melting point: | 188-189.5° |
| Boiling point: | 523.0±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1?+-.0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Amber Vial, Refrigerator |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly, Heated), DMSO (Slightly) |
| pka | 4.29±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Pale Yellow to Pale Beige |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 113806-05-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Olopatadine
Computed Descriptors for Olopatadine
Olopatadine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
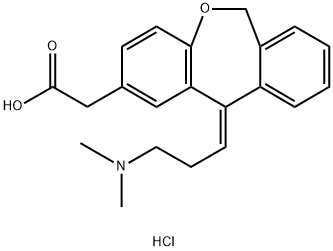
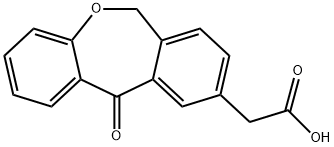
![6,11-dihydro-11-oxo-dibenz[b,e]oxepin-2-acetic acid (Olopatadine),6,11-DIHYDRO-11-OXO-DIBENZ[B,E]OXEPIN-2-ACETIC ACID(FOR OLOPATADINE)](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/55453-87-7.gif)

![6,11-dihydro-11-oxo-dibenz[b,e]oxepin-2-acetate,methyl ester(Olopatadine)](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/55689-64-0.gif)

![[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]triphenylphosphonium bromide hydrobromide](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/27710-82-3.gif)
You may like
-
 OLOPATADINE 99%View Details
OLOPATADINE 99%View Details -
 113806-05-6 98%View Details
113806-05-6 98%View Details
113806-05-6 -
 Olopatadine 98%View Details
Olopatadine 98%View Details
113806-05-6 -
 Olopatadine 113806-05-6 98%View Details
Olopatadine 113806-05-6 98%View Details
113806-05-6 -
 Olopatadine Hcl ApiView Details
Olopatadine Hcl ApiView Details
113806-05-6 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
