OCHRATOXIN A
Synonym(s):N-[(3R)-(5-Chloro-8-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-oxo-7-isochromanyl)carbonyl]-L -phenylalanine;N-[(3R)-(5-Chloro-8-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-oxo-7-isochromanyl)carbonyl]-L-phenylalanine;Ochratoxin A - CAS 303-47-9 - Calbiochem;OTA
- CAS NO.:303-47-9
- Empirical Formula: C20H18ClNO6
- Molecular Weight: 403.81
- MDL number: MFCD00078079
- EINECS: 206-143-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-06-13 14:48:16
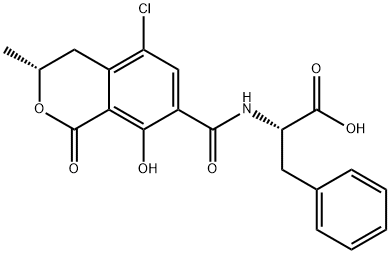
What is OCHRATOXIN A?
Chemical properties
white to off-white crystalline powder
Chemical properties
White crystalline solid or powder.
The Uses of OCHRATOXIN A
Ochratoxin A is a chlorinated benzopyran coupled to phenylalanine, produced by several Aspergillus and Penicillium sp. associated with food spoilage. Ochratoxins are widely distributed in the environment and are known to be nephrotoxic, teratogenic and possibly carcinogenic. Ochratoxin A may act by inducing DNA strand breaks, sister chromatid exchanges, DNA adduct formation, or reactive oxygen but the mechanism of action as a toxin is not yet resolved. At the molecular level, ochratoxin A specifically inhibits NK cell activity, increases growth of transplantable tumour cells in mice, increases apoptosis, activates c-Jun N terminal kinase in human kidney epithelial cells, and blocks metaphase/anaphase transition. It also inhibits plasminogen activator inhibitor-2 production by human blood mononuclear cells.
The Uses of OCHRATOXIN A
Ochratoxins are toxic metabolites from Aspergillus orchraceus.
The Uses of OCHRATOXIN A
A nephrotoxic mycotoxin inhibitor of phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetases.
What are the applications of Application
Ochratoxin A is a nephrotoxic mycotoxin inhibitor of phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetases
Definition
ChEBI: A phenylalanine derivative resulting from the formal condensation of the amino group of L-phenylalanine with the carboxy group of (3R)-5-chloro-8-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-oxo-3,4-dihydro-1H-2-benzopyran-7-carb xylic acid. It is among the most widely occurring food-contaminating mycotoxins, produced by Aspergillus ochraceus, Aspergillus carbonarius and Penicillium verrucosum.
General Description
White crystalline powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
OCHRATOXIN A is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids and strong bases. . OCHRATOXIN A is a carboxylic acid derivative. Carboxylic acids donate hydrogen ions if a base is present to accept them. They react in this way with all bases, both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic. Their reactions with bases, called "neutralizations", are accompanied by the evolution of substantial amounts of heat. Neutralization between an acid and a base produces water plus a salt.
Hazard
Hepatotoxic, nephrotoxic, extremely toxic; possible carcinogen.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for OCHRATOXIN A are not available; however, OCHRATOXIN A is probably combustible.
Biological Activity
Mycotoxin that increases activity of the endoplasmic reticulum ATP-dependent calcium pump. Induces JNK activation and apoptosis in MDCK-C7 cells at nanomolar concentrations. Stimulates lipid peroxidation.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with carcinogenic and neoplastigenic data. Poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, intravenous, and subcutaneous routes. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cland NOx.
Potential Exposure
Ochratoxin A, a carboxylic acid derivative and a naturally occurring toxic mold (strain of Aspergillus ochraceus), occasionally in storage grains such as wheat and on field crops such as corn and oilseed (i.e., cottonseed), in ancient tombs, and decayed vegetation. Used as a laboratory chemical for research. Not currently produced in the United States.
Carcinogenicity
Ochratoxin A is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN3462 Toxins, extracted from living sources, solid, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Ochratoxin A is Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fire. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, and epoxides. Compounds of the carboxyl group R.COOH Compounds of the carboxyl group react with all bases, both inorganic and organic (i.e.,amines) releasing substantial heat, water, and a salt that may be harmful. Incompatible with arsenic compounds (releases hydrogen cyanide gas), diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides (releasing heat, toxic, and possibly flammable gases), thiosulfates and dithionites (releasing hydrogen sulfate and oxides of sulfur).
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Under 40 CFR 261.5 small quantity generators of this waste may qualify for partial exclusion from hazardous waste regulations.
Properties of OCHRATOXIN A
| Melting point: | 169°C |
| Boiling point: | 632.4±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D -118° (c = 1.1 in CHCl3) |
| Density | 1.2459 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 2 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | ethanol: soluble |
| form | powder |
| pka | 3.29±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Merck | 13,6772 |
| BRN | 8169012 |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. Sup 7, 56) 1993 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ochratoxin A (303-47-9) |
Safety information for OCHRATOXIN A
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H350:Carcinogenicity H360:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for OCHRATOXIN A
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Ochratoxin A−BSA conjugate from Aspergillus ochraceus CAS 303-47-9View Details
Ochratoxin A−BSA conjugate from Aspergillus ochraceus CAS 303-47-9View Details
303-47-9 -
 Ochratoxin A CAS 303-47-9View Details
Ochratoxin A CAS 303-47-9View Details
303-47-9 -
 Ochratoxin A solution CAS 303-47-9View Details
Ochratoxin A solution CAS 303-47-9View Details
303-47-9 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
