Nitroethane
- CAS NO.:79-24-3
- Empirical Formula: C2H5NO2
- Molecular Weight: 75.07
- MDL number: MFCD00007404
- EINECS: 201-188-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
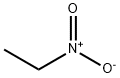
What is Nitroethane?
Chemical properties
colourless oily liquid with an unpleasant odour
Chemical properties
Nitroethane is a colorless, oily liquid with a mild, fruity odor. The Odor Threshold is 163 ppm.
Physical properties
Colorless, very flammable liquid with a fruity odor. Odor threshold concentration is 2.1 ppm (quoted, Amoore and Hautala, 1983). Concentrated mixtures usually contain 98 wt % nitroethane and 2 wt % moisture.
The Uses of Nitroethane
Common industrial solvent; more recently a commercial artificial nail remover
The Uses of Nitroethane
Solvent, artificial fingernail glue remover; in organic syntheses. Experimentally as liquid propellant.
Definition
ChEBI: A nitroalkane that is ethane substituted by a nitro group.
Production Methods
Industrial production of nitroethane is by vapor-phase nitration of propane with nitric acid, followed by fractional distillation (Baker and Bollmeier 1978). U.S. production was greater than 454 kg in 1975 (HSDB 1988).
General Description
A colorless oily liquid with a pleasant odor. Flash point of 82°F. Decomposes above 350°F. Density 1.052 g / cm3. Vapors much heavier than air. and insoluble in water. Vapors may irritate skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion. Used as a propellant and as a solvent.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
The nitroparaffins, nitromethane, nitropropane, etc. form salts with inorganic bases such as calcium hydroxide. The dry salts are explosive [Chem. Eng. News 30:2344. 1952]. Nitroethane and other nitro compounds are mild oxidizers and should not be heated with easily oxidizable hydrocarbons under confinement [Chem. Eng. News 30:2344. 1940].
Hazard
Moderate fire risk.Upper respiratory tract irritant, central nervous system impairment, and liver damage.
Health Hazard
Inhalation causes moderate irritation of respiratory tract. Ingestion causes irritation of mouth and stomach. Contact with liquid causes irritation of eyes and mild irritation of skin.
Health Hazard
Nitroethane is irritating to the eyes and mucous membranes (HSDB 1988), however, there have been no reports of serious toxic effects of the chemical in humans.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic oxides of nitrogen may form in fire.
Industrial uses
Nitroethane is used as a solvent for cellulose esters, vinyl and other resins and waxes and as a solvent in batteries (Baker and Bollmeier 1978).
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Mildly toxic by inhalation. Causes injury to liver and hdneys. An eye and mucous membrane irritant. Flammable liquid when exposed to heat, sparks, flame, or oxidizers. To fight fire, use alcohol foam, CO2, dry chemical; water can blanket fire. Incompatible with Ca(OH)2, hydrocarbons, hydroxides, inorganic bases, KOH, NaOH, metal oxides, Explodes when heated. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also NITRO COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Nitroethane is used as solvent for polymers, cellulose esters; vinyl, waxes, fats, dyestuffs, and alkyd resins; as a stabilizer. It has been used as a rocket propellant. It is used as an intermediate in pharmaceutical manufacture and in pesticide manufacture.
Environmental Fate
Chemical/Physical. 2-Nitroethane will not hydrolyze because it does not contain a hydrolyzable functional group.
Metabolism
Nitroethane was partially excreted by the lungs when given to rabbits intravenously
(1 g) or orally (1 or 2 g/kg). It was eliminated from the blood within 30 h after
the intravenous dose (Machle et al 1942). A peak blood nitroethane concentration
of 1.10 mg/ml was recorded after oral administration of 1.26 g/kg to rabbit. Following
inhalation exposure of rabbits to about 13,500 p.p.m. or 2,700 p.p.m., peak
nitroethane blood concentrations were 2.70 mg/ml after 360 min, and 0.36 mg/ml
after 500 min, respectively. Blood nitrite and nitrate concentrations increased
during the exposures, indicating that nitrite was formed as a result of the metabo-lism of nitroethane, and was oxidized to nitrate (Scott 1943). Absorption of
nitroethane during inhalation exposure occurs in both the upper (URT) and lower
(LRT) respiratory tract of rats (Stott and McKenna 1984). The isolated URT, LRT
and intact respiratory tract absorbed 65, 71 and 58%, respectively, of the nitroethane
presented at a rate comparable to a normal respiratory minute volume for
rats. The absorption of nitroethane by the URT was linear over a 10-fold exposure
range. During exposures only 2.8 and 2.0% of nitroethane was excreted from the
URT and LRT, respectively.
Porter and Bright (1977) showed that nitroethane is readily converted by
glucose oxidase in vitro to acetaldehyde, nitrite, nitrate, hydrogen peroxide and
dinitroethane. However, the role of this enzyme in vivo is unknown. Bray and
James (1958) recovered a small amount of a mercapturic acid metabolite from the
urine of rabbits dosed with nitroethane.
Shipping
UN2842 Nitroethane, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
Purification Methods
Purify it as described for nitromethane below. A spectroscopic impurity can be removed by shaking it with activated alumina, decanting and distilling it rapidly. [Beilstein 1 IV 170.]
Incompatibilities
A nitroparaffin, nitroethane forms explosive mixture with air. Explodes when heated or when shocked; in confined area, with elevated temperatures. A strong reducing agent. Violent reaction with oxidizers, hydrocarbons, other combustibles; amines, metal oxides. Forms shock-sensitive compounds with strong acids; strong alkalis. Attacks some plastics and coatings.
Waste Disposal
Incineration: large quantities of material may require nitrogen oxide removal by catalytic or scrubbing processes.
Properties of Nitroethane
| Melting point: | -90 °C |
| Boiling point: | 114-115 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.045 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.58 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 15.6 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 87 °F |
| storage temp. | Flammables area |
| solubility | acetone: soluble(lit.) |
| form | Colorless, oily liquid |
| pka | 8.5(at 25℃) |
| PH | 6 (1g/l, H2O, 25℃) |
| explosive limit | 3.4%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 4.6 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,6596 |
| BRN | 1209324 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 3.50 at 20.00 °C, 5.86 at 30.00 °C, 9.38 at 40.00 °C, 15.7 at 50.00 °C (inert gas stripping, Bene?
and Dohnal, 1999) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 100 ppm (310 mg/m3), IDLH 1,000 ppm; OSHA PEL:
TWA 100 ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 100 ppm (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 19.7(20℃) |
| Stability: | Stability Contact with a variety of materials may cause fire or explosion, especially if heated. Incompatible with amines, strong acids, strong oxidizing agents, combustible materials, metal oxides, strong bases, alkalies. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 79-24-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ethane, nitro-(79-24-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Nitroethane (79-24-3) |
Safety information for Nitroethane
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H302:Acute toxicity,oral H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P370+P378:In case of fire: Use … for extinction. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. |
Computed Descriptors for Nitroethane
Nitroethane manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Nitro ethane, 99.5% CAS 79-24-3View Details
Nitro ethane, 99.5% CAS 79-24-3View Details
79-24-3 -
 Nitroethane CAS 79-24-3View Details
Nitroethane CAS 79-24-3View Details
79-24-3 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8