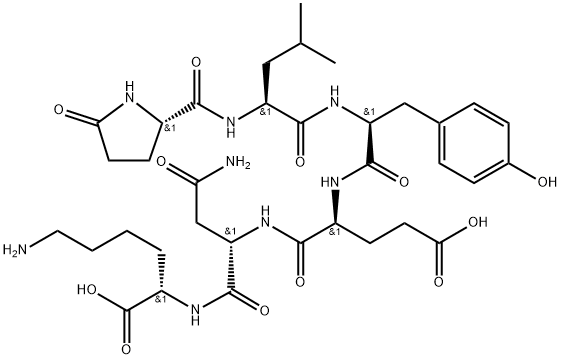
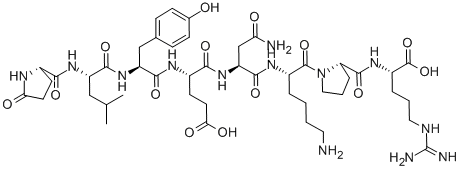
NEUROTENSIN
- CAS NO.:39379-15-2
- Empirical Formula: C78H121N21O20
- Molecular Weight: 1672.92
- MDL number: MFCD00076678
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
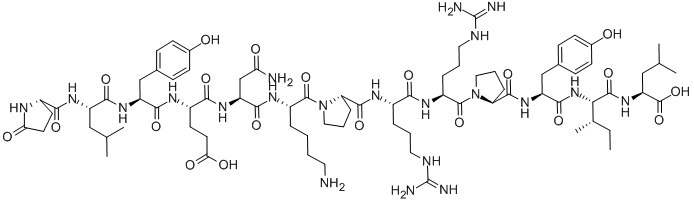
What is NEUROTENSIN?
Description
Neurotensin, a hypotensive peptide first isolated from the bovine hypothalamus, neurotensin acts as a neurotransmitter and neurotransmodulator in the central nervous system, and also as a local hormone in the small intestine. Neurotensin (NT) is a tridecapeptide that was originally isolated from extracts of the bovine hypothalamus in 1973, based on its ability to cause a visible vasodilation in the exposed cutaneous regions of anesthetized rats.
The Uses of NEUROTENSIN
Neurotensin is a selective, non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist.
What are the applications of Application
Neurotensin is a biologically active neuropeptide for proteomics research
Definition
ChEBI: Neurotensin is a 13 amino acid peptide hormone which is found in the central nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract. It behaves as a neurotransmitter in the brain, as a hormone in the gut, and also as a neuromodulator. It is implicated in the pathophysiology of several CNS disorders (including schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease, drug abuse, pain, cancer, inflammation, eating disorders and central control of blood pressure) due to its association with a wide variety of neurotransmitter systems such as dopaminergic, sertonergic, glutamatergic, GABAergic, and cholinergic systems. It has a role as a human metabolite, a mitogen, a neurotransmitter and a vulnerary. It is a conjugate base of a neurotensin(1+).
in vitro
due to nt/ntr1 signaling potentiates expression of mir-133α, the mechanism of nt-regulated mir-133α expression and examining the role of mir-133α in intracellular ntr1 trafficking in human ncm460 colonocytes are very important. the negative transcription regulator (zinc finger e-box binding homeobox 1) is involved in nt-induced mir-133α upregulation. a binding target of mir-133α (silencing of mir-133α or overexpression of aftiphilin (aftph)) lowered ntr1 trafficking to plasma membrane in human colonocytes without affecting ntr1 internalization. aftph to early endosomes and the trans-golgi network (tgn) were localized in unstimulated human colonic epithelial cells. ntr1 localization was reduced by aftph overexpression in early endosomes. at the same time, it also increased expression of proteins related to endosomes and the tgn trafficking pathway. ntr1 expression was increased by aftph overexpression and de-acidification of intracellular vesicles. these results suggest a novel mechanism of gpcr trafficking in human colonic epithelial cells accounts for why a microrna, mir-133α regulates ntr1 trafficking through its downstream target aftph.
storage
Store at -20°C
References
[1]. law ik, jensen d, bunnett nw, pothoulakis c. neurotensin-induced mir-133α expression regulates neurotensin receptor 1 recycling through its downstream target aftiphilin. sci rep. 2016 feb 23;6:22195.
Properties of NEUROTENSIN
| RTECS | QQ4482000 |
| storage temp. | Desiccate at -20°C |
| solubility | insoluble in EtOH; ≥15.33 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥22.55 mg/mL in H2O |
| form | Lyophilized powder. |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble to 0.70 mg/ml in water |
Safety information for NEUROTENSIN
Computed Descriptors for NEUROTENSIN
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
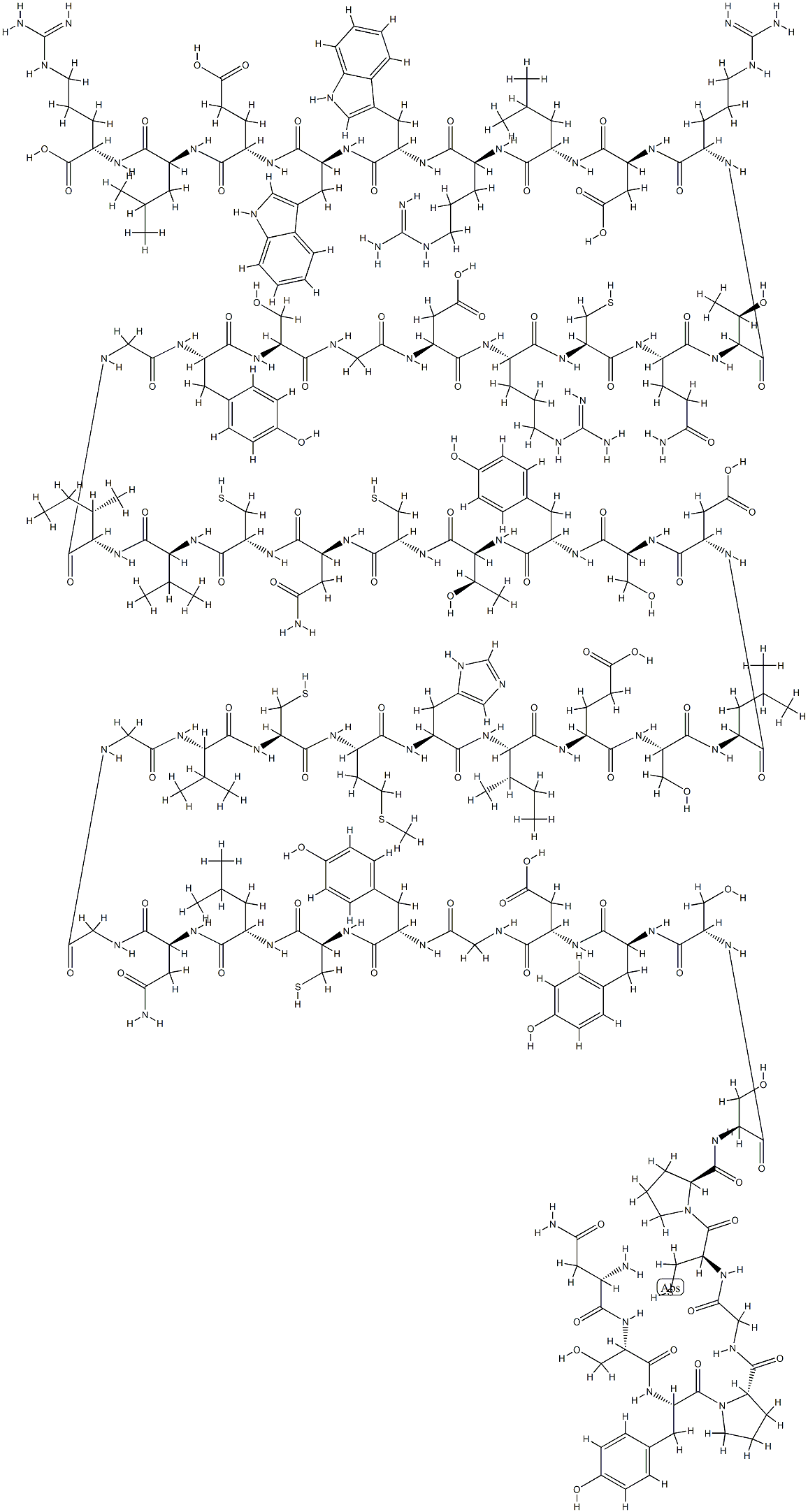
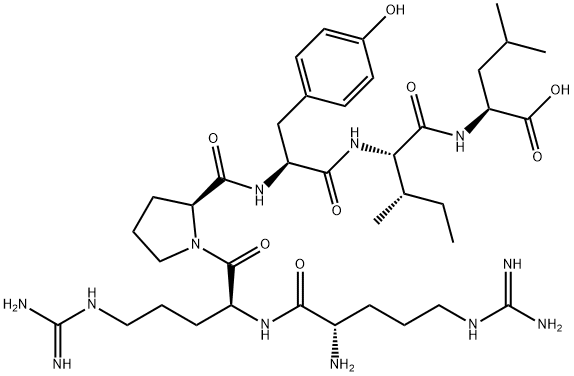

You may like
-
 Neurotensin CAS 39379-15-2View Details
Neurotensin CAS 39379-15-2View Details
39379-15-2 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8