Neotame
Synonym(s):N-[N-(3,3-Dimethylbutyl)-L -α-aspartyl]-L -phenylalanine 1-methyl ester;N-[N-(3,3-Dimethylbutyl)-L -α-aspartyl]-L -phenylalanine 1-methyl ester monohydrate;Neotame monohydrate
- CAS NO.:165450-17-9
- Empirical Formula: C20H30N2O5
- Molecular Weight: 378.46
- MDL number: MFCD09039056
- EINECS: 605-408-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
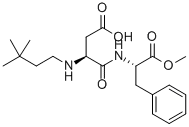
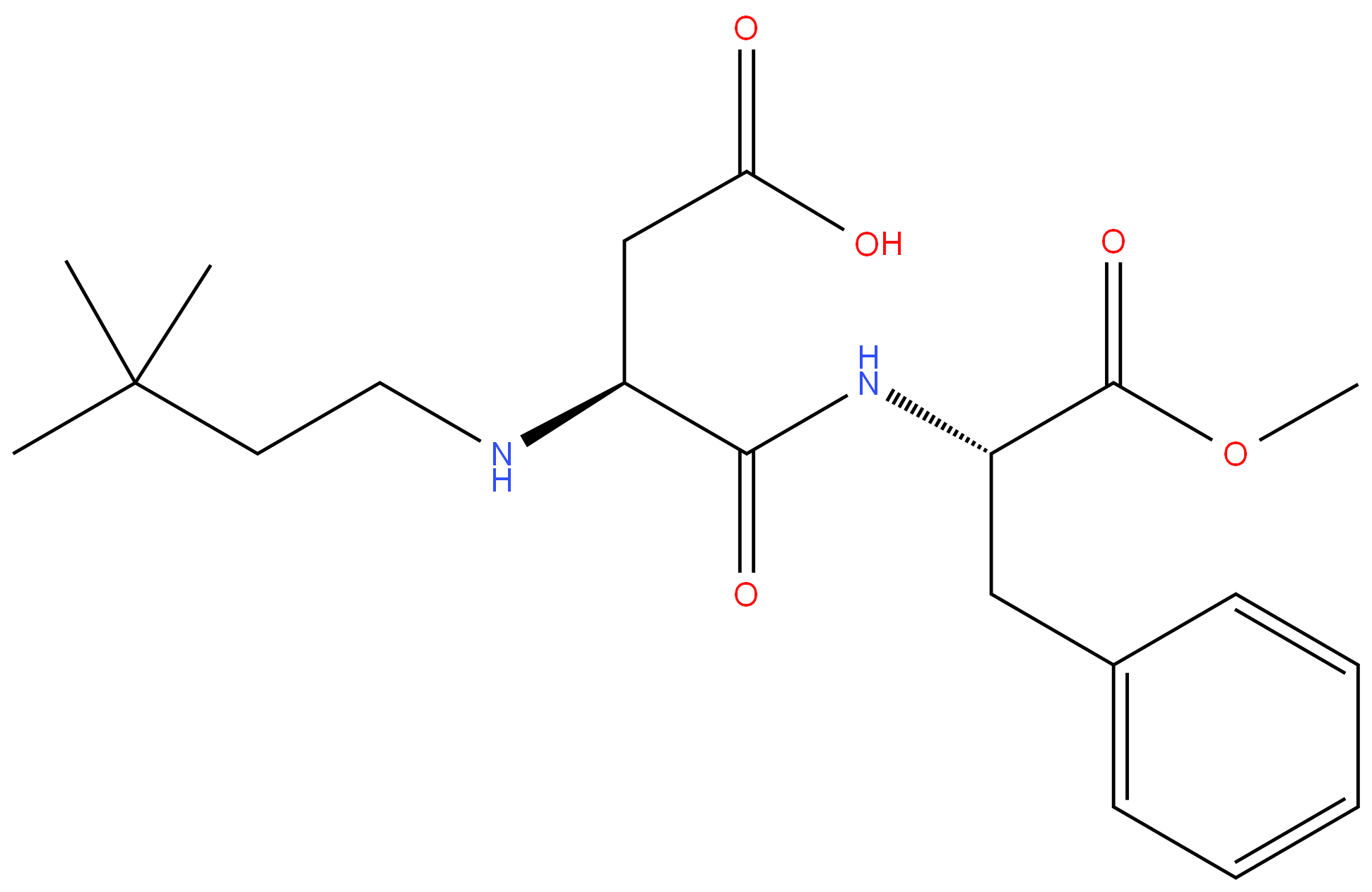
What is Neotame?
Chemical properties
Neotame occurs as an odorless, white to off-white powder. It has an intense sweet taste 7000–13 000 times sweeter than sucrose depending on the matrix.
Chemical properties
Neotame is odorless and has an intense, sweet taste. It is 7,000 to 13,000 times sweeter than sucrose, depending on the food matrix. Normal metabolic processes convert neotame to de-esterified neotame and methanol. Based on its metabolism and extremely low use levels, neotame provides no calories. The stability of neotame is affected by moisture, pH and temperature
The Uses of Neotame
Neotame is a high intensity sweetener and flavor enhancer for use in foods, except in meat and poultry. it is 7,000–13,000 times sweeter than sugar and has a clean, sweet taste. it is a derivative of the dipep- tide composed of amino acids, aspartic acid, and phenylalanine. it can be blended with nutritive sweeteners such as sucrose and high fructose corn syrup as well as with high intensity sweeteners such as aspartame and sucralose. uses include beverages, baked goods, desserts, cereals. it functions as a flavor enhancer in certain applica- tions and flavor systems, such as mint-flavored chewing gum.
The Uses of Neotame
A labelled alkylated dipeptide reported to be 6000 to 10000 times sweeter than sucrose; structurally related to Aspartame. A non-nutritive sweetener.
What are the applications of Application
Neotame is a non-nutritive sweetener and an alkylated dipeptide
Definition
ChEBI: A dipeptide composed of N-(3,3-dimethylbutyl)-L-aspartic acid and methyl L-phenylalanate units joined by a peptide linkage.
Production Methods
Neotame is manufactured by the reaction of aspartame and 3,3- dimethylbutyraldehyde, followed by purification, drying, and milling.
Preparation
Neotame is manufactured by the reaction of aspartame and 3,3-dimethylbutyraldehyde, followed by purification, drying and milling
Benefits
Neotame is sweet. 7,000 to 13,000 times sweeter than sugar. It has no unwanted off-taste or aftertaste that many other sweeteners is burden with. Neotame does not contribute energy (0 kcal), does not affect blood sugar levels (glycaemic index GI is 0) and does not cause caries. Compared to aspartame, it is cheaper and has several food technology advantages.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Neotame is a water-soluble, nonnutritive, intense sweetening agent
used in beverages and foods. It is structurally related to aspartame
and is about 7000–13 000 times sweeter than sucrose, and about
30–60 times sweeter than aspartame, making it the sweetest
artificial sweetener available. Neotame is said to have a ‘clean’
sweet taste in contrast to the bitter, metallic aftertaste associated
with saccharin. Although neotame has approximately the same
caloric value as sucrose (1.2 kJ/g) the small quantities used to
achieve a desired level of sweetness in a formulation mean that it is
essentially nonnutritive.
Neotame may be used in sub-sweetening quantities as a flavor
enhancer, e.g. with mint or strawberry flavor.
Safety
Neotame is a nonnutritive intense sweetening agent used in
beverages and foods. Studies in animals and humans have shown
that neotame is a relatively nontoxic, nonteratogenic, and
noncarcinogenic substance. It is reported as safe for use during
pregnancy and lactation, and by children and persons with diabetes.
At least 30% of ingested neotame is rapidly absorbed. Neotame
is metabolized to de-esterified neotame and methanol, with
practically all neotame being eliminated from the body in the urine
and feces. Peak plasma concentrations of neotame are observed at approximately 30–60 minutes after ingestion. Human studies in
healthy and diabetic patients suggest that neotame is well-tolerated
at doses up to 1.5 mg/kg body-weight daily (the highest dose
studied). Following reviews of over 100 animal and human toxicity
studies the European Food Safety Authority and WHO have
established an acceptable daily intake for neotame at up to 2 mg/kg
body-weight.
Metabolism
In the body, neotame is broken down rapidly and completely. The residual products are de-esterified neotame (92 per cent) and methanol (8 per cent). 80 per cent have left the body the natural way within two days. The rest will follow. 64 per cent via faeces. The rest via urine. Nothing accumulates in the body.
storage
Neotame is stable in bakery products and pasteurized dairy
products.
The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed container, in
a cool, dry place; it is stable for up to 5 years at room temperature.
Regulatory Status
Accepted for use as a food additive in several countries including the USA, Mexico, Australia, and New Zealand. Approved for use in India in pharmaceutical preparations.
Properties of Neotame
| Melting point: | 83-85°C |
| Boiling point: | 565.3±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D -54.84° (c = 1 in methanol); D20 -39.8° (c = 0.5 in water) |
| Density | 1.133±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), Ethanol (Sparingly), Ethyl Acetate (Sparingly), Methanol |
| form | neat |
| pka | pKa1 3.01; pKa2 8.02(at 25℃) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| optical activity | [α]/D -41.0±3.0°, c = 0.5 in H2O |
| BRN | 8352678 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| InChI | InChI=1/C20H30N2O5/c1-20(2,3)10-11-21-15(13-17(23)24)18(25)22-16(19(26)27-4)12-14-8-6-5-7-9-14/h5-9,15-16,21H,10-13H2,1-4H3,(H,22,25)(H,23,24)/t15-,16-/s3 |
Safety information for Neotame
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Neotame
| InChIKey | HLIAVLHNDJUHFG-HOTGVXAUSA-N |
| SMILES | C(=O)([C@@H](NCCC(C)(C)C)CC(O)=O)N[C@@H](CC1=CC=CC=C1)C(OC)=O |&1:2,15,r| |
Neotame manufacturer
HRV Global Life Sciences
Gangwal Healthcare Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 165450-17-9 Neotame 99%View Details
165450-17-9 Neotame 99%View Details
165450-17-9 -
 165450-17-9 Neotame 98%View Details
165450-17-9 Neotame 98%View Details
165450-17-9 -
 Neotame 97% CAS 165450-17-9View Details
Neotame 97% CAS 165450-17-9View Details
165450-17-9 -
 Neotame CAS 165450-17-9View Details
Neotame CAS 165450-17-9View Details
165450-17-9 -
 Neotame CASView Details
Neotame CASView Details -
 Neotame CAS 165450-17-9View Details
Neotame CAS 165450-17-9View Details
165450-17-9 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1