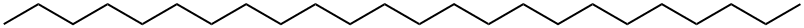N-EICOSANE
Synonym(s):n-Eicosane
- CAS NO.:112-95-8
- Empirical Formula: C20H42
- Molecular Weight: 282.55
- MDL number: MFCD00009344
- EINECS: 204-018-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-21 15:02:05
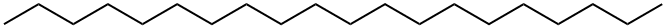
What is N-EICOSANE?
Chemical properties
colourless crystals or wax-like solid
The Uses of N-EICOSANE
n-Eicosane is a saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon, which is used to form candles and paraffin waxes with solar energy storage capacity. It is also used in cosmetics, lubricants, plasticizers and in the petrochemical industry. Further, it is useful for special surfactants and in the preparation of certain organic chemicals. In addition to this, it is used as a chromatographic analysis reference material.
The Uses of N-EICOSANE
Eicosane is a long chain saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon. Eicosane has a high flashpoint which makes it an inefficient fuel for use in the petrochemical industry. Eicosane is used to form candles and paraffin waxes with solar energy storage capacity.
Definition
ChEBI: Icosane is a straight chain alkane composed of 20 carbon atoms. It has been isolated from the leaves of Agave attenuata. It has a role as a plant metabolite.
General Description
Colorless crystals or white crystalline solid.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons, such as N-EICOSANE, may be incompatible with strong oxidizing agents like nitric acid. Charring of the hydrocarbon may occur followed by ignition of unreacted hydrocarbon and other nearby combustibles. In other settings, aliphatic saturated hydrocarbons are mostly unreactive. They are not affected by aqueous solutions of acids, alkalis, most oxidizing agents, and most reducing agents. When heated sufficiently or when ignited in the presence of air, oxygen or strong oxidizing agents, they burn exothermically to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Fire Hazard
N-EICOSANE is combustible.
Purification Methods
Crystallise eicosane from EtOH. [Beilstein 1 IV 563.]
Properties of N-EICOSANE
| Melting point: | 35-37 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 220 °C30 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 0.7886 |
| vapor density | 9.8 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | <0.001 hPa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4425 |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | hexane: soluble100mg/mL, clear |
| form | Crystalline Solid |
| color | White |
| Odor | at 100.00?%. waxy |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in ether, petroleum ether and benzene. Slightly soluble in acetone and chloroform. Insoluble in water. |
| BRN | 1700722 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 112-95-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Eicosane (112-95-8) |
Safety information for N-EICOSANE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H304:Aspiration hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P331:Do NOT induce vomiting. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for N-EICOSANE
| InChIKey | CBFCDTFDPHXCNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Abamectin manufacturer
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid 5-Aminoimidazole-4-Carbonitrile 4-chloro-3,5-dinitropyridine 2'-Methoxy-biphenyl-2-carboxaldehyde 2-(2-Aminoethyl)isothiourea dihydrobromide, 1-(4-chlorophenyl)propan-1-one 2-Ethyl-4-methyl-1-pentanol DIISOPROPYL MALONATE PENTAFLUOROPHENOL 2-Aminonicotinic acid 6-(4-AMINOPHENYL)-5-METHYL-4,5-DIHYDRO-3(2 H)-PYRDAZINONE β-BUTYROLACTONE 3-OXO-CYCLOBUTANECARBOXYLIC ACID 3-methyl xanthine 1H-Pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid [1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-carboxylic acid (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-hexahydro-2-oxo-4-[(1E)-3-oxo-4-[3- (trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-1-buten-1-yl]-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-5-yl ester 2H-Cyclopenta[b]furan-2,5-diol, hexahydro-4-[(1E,3R)-3-hydroxy-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-1- buten-1-yl]-, (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)- 2,5-Dibromopyridine Dimethyl (2-oxo-4-phenylbutyl)phosphonate S-(2-Chloro-3-nitrophenyl) O-ethyl carbonodithioate 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid 2,4-Dichloro-1-[2-nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]benzeneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Eicosane CAS 112-95-8View Details
Eicosane CAS 112-95-8View Details
112-95-8 -
 Eicosane,98% CAS 112-95-8View Details
Eicosane,98% CAS 112-95-8View Details
112-95-8 -
 Eicosane,98% CAS 112-95-8View Details
Eicosane,98% CAS 112-95-8View Details
112-95-8 -
 n-Eicosane CAS 112-95-8View Details
n-Eicosane CAS 112-95-8View Details
112-95-8 -
![Eicosane [Standard Material for GC] CAS 112-95-8](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) Eicosane [Standard Material for GC] CAS 112-95-8View Details
Eicosane [Standard Material for GC] CAS 112-95-8View Details
112-95-8 -
 Eicosane CAS 112-95-8View Details
Eicosane CAS 112-95-8View Details
112-95-8 -
 n-Eicosane CAS 112-95-8View Details
n-Eicosane CAS 112-95-8View Details
112-95-8 -
 Eicosane CAS 112-95-8View Details
Eicosane CAS 112-95-8View Details
112-95-8