n-Butyllithium
Synonym(s):n-BuLi;Butyl lithium;Butyllithium solution;Lithium-1-butanide
- CAS NO.:109-72-8
- Empirical Formula: C4H9Li
- Molecular Weight: 64.06
- MDL number: MFCD00009414
- EINECS: 203-698-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
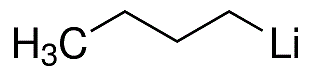
What is n-Butyllithium?
Description
n-BuLi is a strong base (pKa ~ 50) and is typically sold as a solution in hexanes (1.6M or 2.5M). It reacts violently with water and needs to be stored under an inert atmosphere to prevent its reacting with moisture in the air.
Chemical properties
n-Butyllithium is a colorless crystalline solid or clear yellow solution. Due to its high reactivity and extreme solubility, even in its impurities, it is commonly thought to be a viscous liquid.
The Uses of n-Butyllithium
n-Butyllithium is used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers like polybutadiene and styrene- butadiene- styrene. As a strong base, it is utilized in the synthesis of organic compounds. It undergoes thermal decomposition to prepare 1-butene.
The Uses of n-Butyllithium

To a solution of the SM (5.56 g, 19.6 mmol) in THF (20 mL) was added LDA (2M in THF/heptane/ethylbenzene, 19.6 mL, 39.2 mmol) dropwise at -78 C. The reaction was stirred at -78 C for 1 h, after which time was added dropwise a solution of Iodine (9.94 g, 39.2 mmol) in THF (10 mL). After 30 min, the dry ice bath was removed and the reaction was warmed to RT. The mixture was quenched by the addition of sat aq Na2S2O3, then extracted with EtOAc. The combined organics were washed with H2O, brine, dried (MgSO4), and concentrated. The resulting material was purified by silica gel chromatography (0-20% EtOAc/hexane) to provide the product as a white solid. [2.65 g, 33%]
The Uses of n-Butyllithium
n-Butyllithium is a strong nucleophile in the synthetic organic chemistry. It is also used as an initiator in the polymerization process.
Preparation
Industrially, n-butyllithium is produced by the
reaction of n-butyl chloride with lithium metal dispersion in various hydrocarbon solvents.
Hexane is the most commonly used solvent. Up to one-half of the lithium is replaced with
sodium in order to lower the cost of the butyllithium and increase the reactivity of the dispersion.
The reaction is carried out below the boiling point of the solvent.
The laboratory procedure is essentially the same except that pentane and diethyl ether
are two of the more popular solvents. The preparation runs smoothly in ether at lower
temperatures but the product must either be used immediately or kept refrigerated due to
the rapid cleavage of ether by n-butyllithium.
Definition
ChEBI: Butyllithium is an alkyllithium compound.
Flammability and Explosibility
The risk of fire or explosion on exposure of butyllithium solutions to the atmosphere depends on the identity of the organolithium compound, the nature of the solvent, the concentration of the solution, and the humidity. t-Butyllithium solutions are the most pyrophoric and may ignite spontaneously on exposure to air. Dilute solutions (1.6 M, 15% or less) of n-butyllithium in hydrocarbon solvents, although highly flammable, have a low degree of pyrophoricity and do not spontaneously ignite. Under normal laboratory conditions (25 °C, relative humidity of 70% or less), solutions of -20% concentration will usually not ignite spontaneously on exposure to air. More concentrated solutions of n-butyllithium (50 to 80%) are most dangerous and will immediately ignite on exposure to air. Contact with water or moist materials can lead to fires and explosions, and the butyllithiums also react violently with oxygen.
Storage
In particular, butyllithium should be stored and handled in areas free of ignition sources, and containers of butyllithium should be stored under an inert atmosphere. Work with butyllithium should be conducted in a fume hood under an inert gas such as nitrogen or argon. Safety glasses, impermeable gloves, and a fire-retardant laboratory coat are required.
Incompatibilities
The butyllithiums are extremely reactive organometallic compounds. Violent explosions occur on contact with water with ignition of the solvent and of the butane produced. t-Butyllithium will ignite spontaneously in air. The butyllithiums ignite on contact with water, carbon dioxide, and halogenated hydrocarbons. The butyllithiums are incompatible with acids, halogenated hydrocarbons, alcohols, and many other classes of organic compounds.
Waste Disposal
Excess butyllithium solution can be destroyed by dilution with hydrocarbon solvent to a concentration of
approximately 5 wt %, followed by gradual addition to water with vigorous stirring under an inert
atmosphere. Alternatively, the butyllithium solution can be slowly poured (transfer by cannula for s- or tbutyllithium)
into a plastic tub or other container of powdered dry ice.
The residues from the above procedures and excess butyllithium should be placed in an appropriate
container, clearly labeled, and handled according to your institution's waste disposal guidelines.
Properties of n-Butyllithium
| Melting point: | -95 °C |
| Boiling point: | 80 °C |
| Density | 0.68 g/mL at 20 °C |
| Flash point: | 10 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Miscible with diethyl ether and cyclohexane. |
| form | liquid |
| appearance | Colorless solution |
| Specific Gravity | 0.695 |
| color | yellow |
| Odor | Odor of the solvent |
| Water Solubility | vigorous reaction |
| Sensitive | Air & Moisture Sensitive |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 8: reacts rapidly with moisture, water, protic solvents |
| BRN | 1209227 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 50 ppm (Skin) OSHA: TWA 500 ppm(1800 mg/m3) NIOSH: IDLH 1100 ppm; TWA 50 ppm(180 mg/m3) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 109-72-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Butyl lithium(109-72-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lithium, butyl- (109-72-8) |
Safety information for n-Butyllithium
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H250:Pyrophoric liquids; Pyrorophoric solids H252:Self-heating substances and mixtures H260:Substances And Mixtures Which, In Contact With Water,Emit Flammable Gases H261:Substances And Mixtures Which, In Contact With Water,Emit Flammable Gases H304:Aspiration hazard H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects H361:Reproductive toxicity H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H401:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P222:Do not allow contact with air. P223:Keep away from any possible contact with water, because of violent reaction and possible flash fire. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P231+P232:Handle under inert gas. Protect from moisture. P331:Do NOT induce vomiting. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P302+P334:IF ON SKIN: Immerse in cool water/wrap in wet bandages. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P370+P378:In case of fire: Use … for extinction. P405:Store locked up. P422:Store contents under … |
Computed Descriptors for n-Butyllithium
n-Butyllithium manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Sainor Laboratories Pvt Ltd Unit III
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Butyl Lithium 98%View Details
Butyl Lithium 98%View Details -
 Butyl Lithium 98%View Details
Butyl Lithium 98%View Details -
 n-Butyllithium, 2.5M in hexane 99%View Details
n-Butyllithium, 2.5M in hexane 99%View Details -
 n-Butyllithium, 1.6M in hexane 99%View Details
n-Butyllithium, 1.6M in hexane 99%View Details -
 Butyllithium 2M in cyclohexane CAS 109-72-8View Details
Butyllithium 2M in cyclohexane CAS 109-72-8View Details
109-72-8 -
 N-BUTYLLITHIUM 2.5M in Hexanes CAS 109-72-8View Details
N-BUTYLLITHIUM 2.5M in Hexanes CAS 109-72-8View Details
109-72-8 -
 N-butyllithium 1.6M in Hexanes CAS 109-72-8View Details
N-butyllithium 1.6M in Hexanes CAS 109-72-8View Details
109-72-8 -
 N-ButyllithiumView Details
N-ButyllithiumView Details
109-72-8
