Monobenzone
Synonym(s):4-(Benzyloxy)phenol;4-(Phenylmethoxy)phenol;4-Benzyloxyphenol;Hydroquinone monobenzyl ether
- CAS NO.:103-16-2
- Empirical Formula: C13H12O2
- Molecular Weight: 200.23
- MDL number: MFCD00002333
- EINECS: 203-083-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 16:15:04
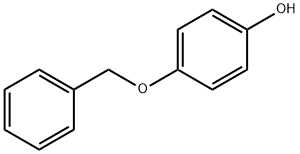
What is Monobenzone?
Description
4-(Benzyloxy)phenol, also called monobenzone and monobenzyl ether of hydroquinone (MBEH) is an organic chemical in the phenol family with chemical formula C6H5CH2OC6H4OH. It is used as a topical drug for medical depigmentation. Monobenzone occurs as a white, almost tasteless crystalline powder, soluble in alcohol and practically insoluble in water.
The topical application of monobenzone in animals, increases the excretion of melanin from the melanocytes. The same action is thought to be responsible for the depigmenting effect of the drug in humans.
Chemical properties
4-Benzyloxyphenol is a cream to beige-light brownish crystals classified as a hydroquinone monobenzyl ether. It is soluble in alcohol, benzene and ether, and almost insoluble in water. 4-Benzyloxyphenol is a depigmenting agent that has the effect of enhancing the rate of elimination of melanin secreted by skin cells, and studies have shown that the molecular mechanism of its action may be related to tyrosinase.
The Uses of Monobenzone
PBP is used as antiinflammatory, antisecretory, antiulcer.
The Uses of Monobenzone
Hydroquinone monobenzyl ether is an antidegradant added to rubber products; inhibitor in acrylic resins.
The Uses of Monobenzone
4-Benzyloxyphenol is used in the synthesis of bis(4-benzyloxyphenoxy)phenyl phosphine oxide. It plays an essential role in the preparation of hetaryl-azophenol dyes via heterocyclic amines in nitrosyl sulphuric acid. It is also used for polyester fiber dyeing and in rubber industry. It acts as a depigmenting agent.
Background
Monobenzone is the monobenzyl ether of hydroquinone used medically for depigmentation. Monobenzone occurs as a white, almost tasteless crystalline powder, soluble in alcohol and practically insoluble in water. It exerts a depigmenting effect on skin of mammals by increasing the excretion of melanin from the melanocytes. It may also cause destruction of melanocytes and permanent depigmentation.
Definition
ChEBI: Monobenzone is the monobenzyl ether of hydroquinone. It is used as a topical drug for medical depigmentation. It has a role as a melanin synthesis inhibitor, a dermatologic drug and an allergen. It derives from a hydroquinone.
Indications
Monobenzone (Benoquin) potently inhibits melanin production and destroys melanocytes. Like hydroquinone, monobenzone was originally introduced for the topical treatment of disorders of excess melanin pigmentation, including melasma. It is now used only to permanently depigment the remaining normally pigmented skin in patients with extensive vitiligo. Irritant and allergic contact dermatitis are common side effects.
Preparation
4-Benzyloxyphenol Synthesis: Add 2.63g (0.028mol) of hydroquinone to a 100mL conical flask, weigh 1.12g (0.028mol) of sodium hydroxide, add 8mL of water, wait for the sodium hydroxide to dissolve and add dropwise to the conical flask with hydroquinone, shake well, then add 15mL of DMF and 2.52g (0.02mol) of benzyl chloride, under microwave radiation power of 320W The reaction was cooled to room temperature at the end of the reaction. The reaction was first adjusted to alkalinity with 10% sodium hydroxide, filtered, and the filtrate was washed with 10% sodium hydroxide until the filtrate was colorless (the filtrate was hydroquinone bis(benzyl ether), which could be recycled). The filtrate was acidified with hydrochloric acid to make Monobenzone completely precipitated, and then washed by filtration and ice water, recrystallized with alcohol and water, and decolorized by activated carbon to obtain 2.55g of white solid, the yield was 63.79%.
brand name
Benoquin (Valeant).
Origin
Monobenzone (monobenzyl ether of hydroquinone, MB) is a depigmenting agent that was discovered by Oliver et al. in 1939. It has been approved by the FDA as a cream formulation for skin depigmentation of patients with vitiligo. The mechanism of action for depigmentation by MB is correlated with the inhibition of tyrosinase[1]. The compound also is cytotoxic to melanocytes and melanoma cells and increases melanocyte and melanoma cell immunogenicity.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 33, p. 5129, 1992 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)61209-1
Biological Activity
The skin-depigmenting effect of MB is correlated with the inhibition of tyrosinase, the rate-limiting enzyme in melanin synthesis, in both melanocytes and melanoma cells. The metabolites of MB have been proven to exert toxic effects on melanocytes and increase melanocyte and melanoma cell immunogenicity. MB potently inhibited RNR enzyme activity by targeting RRM2 and thereby suppressed AML cell growth in vitro and in a mouse xenograft experiment[1-2].
Pharmacokinetics
Monobenzone is the monobenzyl ether of hydroquinone. Monobenzone, applied topically to the skin, is used as a depigmenting agent inhibitting melanin?produced by polymerization of oxidation products of tyrosine and dihydroxyphenyl compounds. Monobenzone works by permanently removing color from normal skin located around skin with vitiligo.
Side Effects
Side effects:
Allergic reaction: Itching or hives, swelling in your face or hands, swelling or tingling in your mouth or throat, chest tightness, trouble breathing
Intense itching, blistering, burning, or swelling of the skin.
Mild skin rash, tenderness, or redness.
Indications
Used topically to treat the loss of skin color (vitiligo).
Monobenzone is a depigmenting agent. It works by increasing elimination of melanin (pigment molecules) from skin cells.
Monobenzone topical (for the skin) is used to permanently lighten
skin in people with vitiligo. Depigmenting darker skin around the areas
of vitiligo helps even out coloring and appearance of the skin.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from EtOH or H2O, and dry (P2O5) under vacuum. [Walter et al. J Am Chem Soc 108 5210 1986, Beilstein 6 IV 5778.]
References
[1] Jingwen Dong. “Identification of Monobenzone as a Novel Potential Anti-Acute Myeloid Leukaemia Agent That Inhibits RNR and Suppresses Tumour Growth in Mouse Xenograft Model.” Cancers (2022).
[2] Jasper G. van den Boorn . “Skin-Depigmenting Agent Monobenzone Induces Potent T-Cell Autoimmunity toward Pigmented Cells by Tyrosinase Haptenation and Melanosome Autophagy.” Journal of Investigative Dermatology 131 6 (2011): Pages 1240-1251.
Properties of Monobenzone
| Melting point: | 119-120 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 297.96°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1,26 g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 1.5906 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 10.29±0.15(Predicted) |
| form | Powder, Crystals, and/or Chunks |
| color | Off-white to beige to brown |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble |
| Merck | 14,6248 |
| BRN | 1958305 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 103-16-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Monobenzone(103-16-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Monobenzone (103-16-2) |
Safety information for Monobenzone
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Monobenzone
| InChIKey | VYQNWZOUAUKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Monobenzone manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 4-(Benzyloxy)phenol CAS 103-16-2View Details
4-(Benzyloxy)phenol CAS 103-16-2View Details
103-16-2 -
 Hydroquinone monobenzyl ether 98% CAS 103-16-2View Details
Hydroquinone monobenzyl ether 98% CAS 103-16-2View Details
103-16-2 -
 4-(Benzyloxy)phenol, 98% CAS 103-16-2View Details
4-(Benzyloxy)phenol, 98% CAS 103-16-2View Details
103-16-2 -
 4-(Benzyloxy)phenol CAS 103-16-2View Details
4-(Benzyloxy)phenol CAS 103-16-2View Details
103-16-2 -
 Monobenzone CAS 103-16-2View Details
Monobenzone CAS 103-16-2View Details
103-16-2 -
 Monobenzone CAS 103-16-2View Details
Monobenzone CAS 103-16-2View Details
103-16-2 -
 Anti-MED1 antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details
Anti-MED1 antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details -
 Monobenzone Powder ApiView Details
Monobenzone Powder ApiView Details
103-16-2
