monazomycin
- CAS NO.:11006-31-8
- Empirical Formula: C72H133NO22
- Molecular Weight: 1364.82
- MDL number: MFCD01714647
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-21 10:59:17
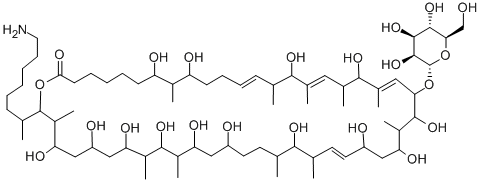
What is monazomycin?
The Uses of monazomycin
Monazomycin is a macrocylic polyol lactone isolated from several species of Streptoverticillium, first reported in 1963. Monazomycin is active against Gram positive bacteria with weak Gram negative activity. In solution, monazomycin exists as hydrophilic clusters which, when adsorbed onto a lipid bilayer, can induce channel formation. Monazomycin is an important bioprobe for understanding membrane channels.
The Uses of monazomycin
Monazomycin is a macrocyclic polyol lactone antibiotic isolated from Streptoverticilium.
What are the applications of Application
Monazomycin is a macrocyclic polyol lactone antibiotic isolated from Streptoverticilium
Biological Activity
monazomycin is a positively charged and polyenelike antibiotic produced by streptomyces [1].monazomycin is able to induce a voltage-dependent conductance in lipid bilayer membranes. monazomycin is selective for monovalent cations and can alter the membrane conductance when applied to one or both sides of the membrane [1]. application of micromolar amounts of monazomycin on one side of phospholipid bilayer membranes induced dramatic voltage-dependent conductance effects. the steady-state conductance was proportional to the 5th power of the monazomycin concentration and increased exponentially with positive voltage (monazomycin side positive); there was an e-fold change in conductance per 4–6 mv. the major current-carrying ions were univalent cations. monazomycin monomers cooperated to form a multimolecular conductance channel. the voltage control of conductance arose from the electric field driving monazomycin molecules at the membrane surface into the membrane and thus affecting the number of channels that were formed [2].
References
[1] bamberg e, janko k. single channel conductance at lipid bilayer membranes in presence of monazomycin[j]. biochimica et biophysica acta (bba)-biomembranes, 1976, 426(3): 447-450.
[2] muller r u, finkelstein a. voltage-dependent conductance induced in thin lipid membranes by monazomycin[j]. the journal of general physiology, 1972, 60(3): 263-284.
Properties of monazomycin
| Melting point: | 127°C |
| Boiling point: | 866.56°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 0.9708 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5280 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| form | solid |
| pka | 12.89±0.70(Predicted) |
Safety information for monazomycin
Computed Descriptors for monazomycin
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1