Molybdenum disulfide
Synonym(s):Molybdenum sulfide;Molybdenum (IV) sulfide;Molybdenum disulphide;2H-MoS2;2D Dispersion
- CAS NO.:1317-33-5
- Empirical Formula: MoS2
- Molecular Weight: 160.07
- MDL number: MFCD00003470
- EINECS: 215-263-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 21:30:20
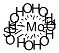
What is Molybdenum disulfide?
Description
Few-layer molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) is considered to be one of the most attractive?materials?for next-generation nanoelectronics. This is due to its silicon-level charge mobility and high current on/off ratio in thin-film transistors. Compared to monolayer? MoS2 (which needs?a deposition of an additional high-k?dielectric layer such as HfO2), few-layer?MoS2 can be operated on its own. This makes it more appealing for fabricating transistors and other optoelectronic devices.
What are the applications of Application
As a result of its direct band-gap, single-layer MoS2?has received much interest for applications in electronic and optoelectronic devices (such as transistors, photodetectors, photovoltaics and light-emitting diodes). It is also being explored for applications in photonics, and can be combined with other TMDCs to create advanced heterostructured devices.
Synthesis
High quality molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) few-layer?films were grown directly on the substrates (SiO2/Si and Sapphire) by chemical vapour deposition (CVD) method. The films were later transferred to the desired substrates?using wet chemical transfer process.
Preparation
Synthetic?- Chemical Vapour Transport (CVT)
Description
Molybdenum disulfide [molybdenum(IV) sulfide, MoS2] is an inorganic compound that exists in nature in the mineral molybdenite. Its crystals have a hexagonal layered structure (shown) that is similar to graphite.
In 1957, Ronald E. Bell and Robert E. Herfert at the now-defunct Climax Molybdenum Company of Michigan (Ann Arbor) prepared what was then a new rhombohedral crystalline form of MoS2. Rhombohedral crystals were subsequently discovered in nature.
Like most mineral salts, MoS2 has a high melting point, but it begins to sublime at a relatively low 450 oC. This property is useful for purifying the compound.
Because of its layered structure, hexagonal MoS2, like graphite, is an excellent “dry” lubricant. It and its cousin tungsten disulfide can be used as surface coatings on machine parts (e.g., in the aerospace industry), in two-stroke engines (the type used for motorcycles), and in gun barrels (to reduce friction between the bullet and the barrel).
Unlike graphite, MoS2 does not depend on adsorbed water or other vapors for its lubricant properties. It can be used at temperatures as high as 350 oC in oxidizing environments and up to 1100 oC in nonoxidizing environments. Its stability makes it useful in high-temperature applications in which oils and greases are not practical.
In addition to its lubricating properties, MoS2 is a semiconductor. It is also known that it and other semiconducting transition-metal chalcogenides become superconductors at their surfaces when doped with an electrostatic field.
The mechanism of superconductivity was uncertain until 2018, when Andrea C. Ferrari at the University of Cambridge (UK) and colleagues there and at the Polytechnic Institute of Turin (Italy) reported that a multivalley Fermi surface is associated with the superconductivity state in MoS2. The authors believe that “this [Fermi surface] topology will serve as a guideline in the quest for new superconductors.”
Chemical properties
dark grey or black powder,Molybdenum disulfide, MoS2, the most common natural form of molybdenum, is extracted from the ore and then purified for direct use in lubrication. Since molybdenum disulfide is of geothermal origin, it has the durability to withstand heat and pressure. This is particularly so if small amounts of sulfur are available to react with iron and provide a sulfide layer which is compatible with MoS2 in maintaining the lubricating film.
The Uses of Molybdenum disulfide
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) is one of the most widely used lubricants in space systems.it is a common additive that improves the antiseize properties of wheel bearing grease.Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) has been used for many years as a solid lubricant because of its interesting friction-reducing properties related to its crystalline structure. MoS2 is a lamellar compound made of a stacking of S-Mo-S layers . In each of them, the molybdenum atom is surrounded by six sulfur atoms located at the top of a trigonal prism. The distance between a molybdenum atom and a sulfur atom is equal to 0.241 nm, whereas the distance between two sulfur atoms from two adjacent layers is equal to 0.349 nm. This characteristic was often used to explain easy cleavage between the layers and therefore the lubricating properties of MoS2.
The Uses of Molybdenum disulfide
Dry lubricant and lubricant additive. Hydrogenation catalyst.
The Uses of Molybdenum disulfide
In addition to serving as the primary natural source of molybdenum, purified molybdenum disulfide MoS2 is an excellent lubricant when in the form of a dry film, or as an additive to oil or grease. The compound also is used as a filler in nylons, and as an effective catalyst for hydrogenation-dehydrogenation reactions.
Definition
Natural molybdenum sul-fide found in igneous rocks and metallic veins.
General Description
Molybdenum disulfide is a two dimensional layered material. Monolayers of transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs)exhibit photoconductivity. The layers of the TMD can be mechanically or chemicaly exfoliated to form nanosheets.
Hazard
Toxic material.
Properties of Molybdenum disulfide
| Melting point: | 2375 °C |
| Density | 5.06 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| solubility | insoluble |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O; soluble in concentrated acid solutions |
| form | powder |
| appearance | black or lead-gray crystals or powder |
| Specific Gravity | 4.8 |
| color | Gray to dark gray or black |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in hot sulfuric acid, and aquaregia. Insoluble in water, concentrated sulfuric acid and dilute acid. |
| Merck | 14,6236 |
| Boiling point: | 100°C (water) |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 10 mg/m3; TWA 3 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 5000 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1317-33-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Molybdenum sulfide (MoS2) (1317-33-5) |
| Bandgap | 1.23 eV |
| Electronic properties | 2D Semiconductor |
Safety information for Molybdenum disulfide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Molybdenum disulfide
| InChIKey | CWQXQMHSOZUFJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Molybdenum disulfide manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
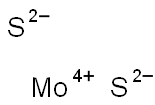



You may like
-
 Molybdenum Disulphide 98%View Details
Molybdenum Disulphide 98%View Details -
 Molybdenum(IV) sulfide CAS 1317-33-5View Details
Molybdenum(IV) sulfide CAS 1317-33-5View Details
1317-33-5 -
 Molybdenum(IV) sulfide CAS 1317-33-5View Details
Molybdenum(IV) sulfide CAS 1317-33-5View Details
1317-33-5 -
 Molybdenum(IV) sulfide CAS 1317-33-5View Details
Molybdenum(IV) sulfide CAS 1317-33-5View Details
1317-33-5 -
 Molybdenum(IV) sulfide CAS 1317-33-5View Details
Molybdenum(IV) sulfide CAS 1317-33-5View Details
1317-33-5 -
 Molybdenum(IV) sulfide CAS 1317-33-5View Details
Molybdenum(IV) sulfide CAS 1317-33-5View Details
1317-33-5 -
 Molybdenum Disulfide Nanopowder Lubricant Grade CAS 1317-33-5View Details
Molybdenum Disulfide Nanopowder Lubricant Grade CAS 1317-33-5View Details
1317-33-5 -
 Molybdenum Disulfide pure CAS 1317-33-5View Details
Molybdenum Disulfide pure CAS 1317-33-5View Details
1317-33-5
